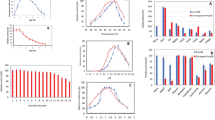
Abstract
An extracellular amylase secreted by Aspergillus niveus was purified using DEAE fractogel ion exchange chromatography and Sephacryl S-200 gel filtration. The purified protein migrated as a single band in 5 % polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and 10 % sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS-PAGE). The enzyme exhibited 4.5 % carbohydrate content, 6.6 isoelectric point, and 60 and 52 kDa molar mass estimated by SDS-PAGE and Bio-Sil-Sec-400 gel filtration column, respectively. The amylase efficiently hydrolyzed glycogen, amylose, and amylopectin. The end-products formed after 24 h of starch hydrolysis, analyzed by thin layer chromatography, were maltose, maltotriose, maltotetraose, and maltopentaose, which classified the studied amylase as an α-amylase. Thermal stability of the α-amylase was improved by covalent immobilization on glyoxyl agarose (half-life of 169 min, at 70 °C). On the other hand, the free α-amylase showed a half-life of 20 min at the same temperature. The optima of pH and temperature were 6.0 and 65 °C for both free and immobilized forms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali FS, Abdel-Moneim AA (1989) Physico-chemical properties of Aspergillus flavus var. columnaris alpha-amylase. Zentralbl Mikrobiol 144:615–21. doi:10.1016/S0232-4393(89)80122-2
Aquino ACMM, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2003) Studies on a thermostable α-amylase from the thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:323–328. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1290-y
Baks T, Janssen AEM, Boom RM (2006) A kinetic model to explain the maximum in α-amylase activity measurements in the presence of small carbohydrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:431–440. doi:10.1002/bit.20779
Balkan B, Ertan F (2010) The production of a new fungal alpha-amylase degraded the raw starch by means of solid-state fermentation. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 40:213–228. doi:10.1080/10826068.2010.488549
Betini JHA, Michelin M, Peixoto-Nogueira SC, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2009) Xylanases from Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus niveus and Aspergillus ochraceus produced under solid-state fermentation and their application in cellulose pulp bleaching. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32:819–824. doi:10.1007/s00449-009-0308-y
Chang CT, Tang MS, Lin CF (1995) Purification and properties of alpha-amylase from Aspergillus oryzae ATCC 76080. Biochem Mol Biol Int 36:185–93
Chaplin MF, Bucke C (1990) The preparation and kinetics of immobilized enzymes. In: Enzyme technology. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. pp 141–146
Crabb WD, Mitchinson C (1997) Enzymes involved in the processing of starch to sugars. Trends Biotechnol 15:349–352
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis II. Methods and application to human serum proteins. Ann New York Acad Sci 121:404–427
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356. doi:10.1021/ac60111a017
Fontana JD, Gebara M, Blumel M, Schneider H, Mackenzie CR, Johnson KG (1988) α-4-O-Methyl-d-glucuronidase component of xylanolytic complexes. Methods Enzymol 160:560–571. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(88)60169-8
Guisán JM, Alvaro G, Fernández-Lafuente R, Rosell CM, Garcia JL, Tagliani A (1993) Stabilization of heterodimeric enzyme by multipoint covalent immobilization: penicillin G acylase from Kluyvera citrophila. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:455–464. doi:10.1002/bit.260420408
Gupta R, Gigras P, Mohapatra H, Goswami VK, Chauhan B (2003) Microbial α-amylases: a biotechnological perspective. Process Biochem 38:1599–1616. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00053-0
Hanes CS (1932) The effect of starch concentration upon the velocity of hydrolysis by the amylase of germinated barley. Biochem J 26:1406–1421
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Horvathova V, Janecek S, Sturdik E (2000) Amylolytic enzymes: their specifities, origins and properties. Biologia Bratislava 55:605–615
Janecek S (1997) Alpha-amylase family: molecular biology and evolution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 67:67–97. doi:10.1016/S0079-6107(97)00015-1
Jensen B, Olsen J (1992) Extracellular α-glucosidase with dextran-hydrolyzing activity from the thermophilic fungus, Thermomyces lanuginosus. Enzyme Microbial Technol 14:112–116. doi:10.1007/s002849900092
Khanna P, Sundari SS, Kumar NJ (1995) Production, isolation and partial purification of xylanase from Aspergillus sp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:242–243. doi:10.1007/BF00704661
Khoo SL, Amirul AA, Kamaruzaman M, Nazalan N, Azizan MA (1994) Purification and characterization of alpha-amylase from Aspergillus flavus. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 39:392–398. doi:10.1007/BF02814445
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. doi:10.1038/227680a0
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:267–275
MacGregor EA, Janecek S, Svensson B (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the alpha-amylase family of enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1546:1–20. doi:10.1016/S0167-4838(00)00302-2
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–489. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030
Moreira FG, Lenartovicz V, Peralta RM (2003) A thermostable maltose-tolerant α-amylase from Aspergillus tamarii. J Basic Microbiol 44:29–35. doi:10.1002/jobm.200310302
Nigam P, Singh D (1995) Enzyme and microbial systems involved in starch processing. Enzyme Microbial Technol 17:770–778. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(94)00003-A
O’Farrel PZ, Goodman HM, O’Farrel PH (1977) High resolution two dimensional electrophoresis of basic as acidic proteins. Cell 12:1133–1142. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3
Peixoto-Nogueira SC, Michelin M, Betini JHA, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2008) Production of xylanase by Aspergilli using alternative carbon sources: application of the crude extract on cellulose pulp biobleaching. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:149–155. doi:10.1007/s10295-008-0482-y
Regulapati R, Malav PN, Gummadi SN (2007) Production of thermostable α-amylases by solid state fermentation—a review. Am J Food Technol 2:1–11. doi:10.3923/ajft.2007.1.11
Sharma A, Kawarabayasi Y, Satyanarayana T (2012) Acidophilic bacteria and archaea: acid stable biocatalysts and their potential applications. Extremophiles 16(1):1–19. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0402-3
Silva TM, Michelin M, Damásio ARL, Maller A, Dos Reis Almeida FB, Ruller R, Ward RJ, Rosa JC, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2009) Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel α-glucosidase from Aspergillus niveus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 96:569–578. doi:10.1007/s10482-009-9372-1
Tanyildizi MS, Ozer D, Elibol M (2005) Optimization of α-amylase production by Bacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 40:2291–2296. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.06.018
van der Kaaij RM, Janecek S, van der Maarel LMJE, Dijkhuizen C (2007) Phylogenetic and biochemical characterization of a novel cluster of intracellular fungal α-amylase enzymes. Microbiology 153:4003–4015. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2007/008607-0
Van der Maarel MJ, van der Veen B, Uitdehaag JC, Leemhuis H, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the alpha-amylase family. J Biotechnol 94:137–55. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00407-2
Vandamme EJ (1983) Peptide antibiotic production through immobilized biocatalyst technology. Enzyme Microb Technol 5:403–415. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(83)90021-2
Varavinit S, Chaokasem N, Shobsngob S (2002) Immobilization of a thermostable alpha-amylase. Science Asia 28:247–251
Wanderley JK, Torres GAF, Moraes PML, Ulhoa JC (2004) Biochemical characterization of α-amylase from the yeast Cryptococcus flavus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 231:165–169. doi:10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00955-8
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) and Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). João Atílio Jorge; Maria de Lourdes Teixeira de Moraes Polizeli are Research Fellows of CNPq. Tony Márcio da Silva was a recipient of a FAPESP Fellowship and this work was part of his Doctoral Thesis. This project is part of National Institute of Science and Technology of the Bioethanol and National System for Research on Biodiversity (Sisbiota-Brazil, CNPq 563260/2010-6/FAPESP no 2010/52322-3). We thank Ricardo Alarcon, Mauricio de Oliveira for technical assistance and Mariana Cereia for technical assistance and English review. We also appreciate the availability of using of the Mass Spectrometer from National Laboratory Biosciences by coordination of Dr. Adriana Franco Paes Leme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, T.M., Damásio, A.R.d.L., Maller, A. et al. Purification, partial characterization, and covalent immobilization–stabilization of an extracellular α-amylase from Aspergillus niveus . Folia Microbiol 58, 495–502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0230-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0230-1