Abstract
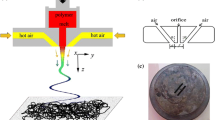
Melt blowing is a major process for producing nanofibrous nonwovens. Compared to another technology for producing nanofibrous nonwovens, electrospinning, melt blowing applies high-speed air flow field to attenuate the extruded polymer jet. It is known that the essential electrospinning mechanism is a rapidly whipping jet in an electric field. While there are few studies on the fiber whipping in the melt-blowing process. In this study, a high-speed camera was used to capture the fiber path below a single-orifice melt-blowing swirl die. The spiral path of the fiber was revealed. The characteristics of the whipping amplitude, whipping frequency, and the fiber velocity were obtained. Fiber diameter reduction ratio contributed by the spiral path was calculated by establishing a mathematical model. The study indicates that spiral path of the whipping plays an important role in fiber attenuation near the die.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. M. Hohman, M. Shin, G. Rutledge, and M. P. Brenner, Phys. Fluids., 13, 2221 (2001).
Y. M. Shin, M. M. Hohman, M. P. Brenner, and G. C. Rutledge, Appl. Phys. Lett., 78, 1149 (2011).
D. H. Reneker, A. L. Yarin, H. Fong, and S. Koombhongse, J. Appl. Phys., 87, 4531 (2000).
S. A. Theron, A. L. Yarin, E. Zussman, and E. Kroll, Polymer, 46, 2889 (2005).
Y. M. Shin, M. M. Hohman, M. P. Brenner, and G. C. Rutledge, Polymer, 42, 9955 (2001).
D. H. Reneker and A. L. Yarin, Polymer, 49, 2387 (2008).
R. S. Rao and R. L. Shambaugh, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 32, 3100 (1993).
R. Chhabra and R. L. Shambaugh, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 35, 4366 (1996).
J. H. Beard, R. L. Shambaugh, B. R. Shambaugh, and D. W. Schmidtke, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 46, 7340 (2007).
S. Xie and Y. C. Zeng, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 5346 (2012).
D. H. Tan, P. K. Herman, A. Janakiraman, F. S. Bates, S. Kumar, and C. W. Macosko, Chem. Eng. Sci., 80, 342 (2012).
V. M. Entov and A. L. Yarin, J. Fluid Mech., 140, 9 (1984).
C. Chung and S. Kumar, Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech., 192, 37 (2013).
H. Yin, Z. Y. Yan, and R. R. Bresee, Int. Nonwovens J., 8, 60 (1999).
R. R. Bresee and W. C. Ko, Int. Nonwovens J., 12, 21 (2003).
V. Bansal and R. L. Shambaugh, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 37, 1799 (1998).
V. T. Marla, R. L. Shambaugh, and D. V. Papavassiliou, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 48, 8376 (2009).
Y. C. Zeng, Y. F. Sun, and X. H. Wang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 119, 2112 (2011).
C. F. Zhou, D. H. Tan, A. P. Janakiraman, and S. Kumar, Chem. Eng. Sci., 66, 4172 (2011).
D. H. Tan, C. F. Zhou, C. J. Ellison, S. Kumar, C. W. Macosko, and F. S. Bates, J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech., 165, 892 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Zeng, Y. Fiber spiral motion in a swirl die melt-blowing process. Fibers Polym 15, 553–559 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0553-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0553-9