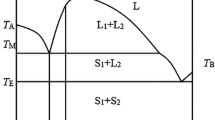
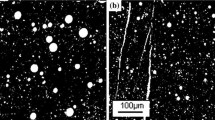
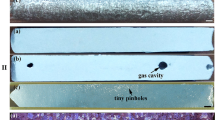
Abstract
Immiscible alloys have aroused considerable interest in last few decades due to their excellent physical and mechanical characteristics as well as potential industrial applications. Up to date, plenty of researches have been carried out to investigate the solidification of immiscible alloys on the ground or in space and great progress has been made. It is demonstrated that the continuous solidification technique have great future in the manufacturing of immiscible alloys, it also indicates that the addition of surface active micro-alloying or inoculants for the nucleation of the minority phase droplets and proper application of external fields, e.g., static magnetic field, electric current, microgravity field, etc. may promote the formation of immiscible alloys with an expected microstructure. The objective of this article is to review the research work in this field.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborn, H., Lohberg, K.: Aluminium-Indium experiment solouf-a sounding rocket experiment on immiscible alloys. In: 17th Aerospace Sciences Meeting. New Orleans 79-0172 (1979)
Ahmed, S., Mckannan, E.C.: Control of \(\gamma ^{\prime }\) morphologyin nickel base superalloys through alloy design and densification processing under electric field. Mater. Sci. Technol. 10, 941–946 (1994)
Carlberg, T., Fredriksson, H.: The influence of microgravity on the solidification of Zn-Bi immiscible alloys. Metall. Trans. A 11, 1665–1676 (1980)
Ding, W.W., Xia, T.D., Zhao, W.J., Xu, Y.T.: Effect of Al-5Ti-C master alloy on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-20%Si alloy. Materials 7, 1188–1200 (2014)
Fei, L.H., Ikebukuro, K., Katsuta, T., Kaneko, T., Ueno, I., Pettit, D.R.: Effect of static deformation on basic flow patterns in thermocapillary-driven free liquid film. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 29–36 (2017)
Fujii, H., Kimura, T., Kitaguchi, H., Kumakura, H., Togano, K.: Fabrication of uniform Al-Pb-Bi monotectic alloys under microgravity utilizing the space shuttle: microstructure and superconducting properties. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 3429–3434 (1995)
Gelles, S.H., Markworth, A.J.: Microgravity studies in the liquid phase immiscible system, aluminum-indium. In: 15th Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Los Angeles 77-112 (1977)
Gezer, B.T., Toptan, F., Daglilar, S., Kerti, I.: Production of Al-Ti-C grain refiners with the addition of elemental carbon. Mater. Des. 31, S30–S35 (2010)
Gu, G.D., Xu, Y.Y., An, G.Y., Li, Q.C.: Cellular growth of Sn-5%Bi alloy in electric field. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 27, 37–41 (1991)
He, J., Zhao, J.Z., Wang, X.F., Zhang, Q.X., Li, H.L., Chen, G.Y.: Investigation of rapid directional solidification of Al-based immiscible alloy I. Effect of solid/liquid interface. Acta Metall. Sin. 43(6), 561–566 (2007a)
He, J., Zhao, J.Z., Wang, X.F., Zhang, Q.X., Li, H.L., Chen, G.Y.: Investigation of rapid directional solidification of Al-based immiscible alloy II. Effect of static magnetic field. Acta Metall. Sin. 43(6), 567–572 (2007b)
He, J., Zhao, J.Z., Wang, X.F., Zhang, Q.X., Li, H.L., Chen, G.Y.: Investigation of rapid directional solidification of Al-based immiscible alloy III. Effect of the third element. Acta Metall. Sin. 43(6), 573–577 (2007c)
He, J., Zhao, J.Z., Li, H.L., Zhang, X.F., Zhang, Q.X.: Directional solidification and microstructural refinement of immiscible alloys. Mater. Trans. A 39, 1174–1182 (2008)
Huang, Z.: Microstructural feature in metallic alloy solidified under microgravity. Scr. Metall. Mater. 25(1), 149–152 (1991)
Huang, Q., Luo, X.H., Li, Y.Y.: An alloy solidification experiment conducted on Shenzhou spacecraft. Adv. Space Res. 36, 86–91 (2005)
Jiang, H.X.: Study of the Continuous Solidification of Monotectic Alloys under the Effect of Electric Current. PhD thesis, Shenyang (2014)
Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z.: Effect mechanism of a direct current on the solidification of immiscible alloys. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29, 088104 (2012)
Jiang, Y., Xu, Z.L.: Numerical investigation of nanofluid thermocapillary convection based on two-phase mixture model. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 365–370 (2017)
Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z., Wang, C.P., Liu, X.J.: Effect of electric current pulses on solidification of immiscible alloys. Mater. Lett. 132, 66–69 (2014a)
Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z., He, J.: Solidification behavior of immiscible alloys under the effect of a direct current. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 1027–1035 (2014b)
Jiang, H.X., He, J., Zhao, J.Z.: Influence of electric current pulses on the solidification of Cu-Bi-Sn immiscible alloys. Sci. Rep. 5, 12680 (2015)
Kaban, I., Köhler, M., Ratke, L., Hoyer, W., Mattern, N., Eckert, J., Greer, A.L.: Interfacial tension, wetting and nucleation in Al-Bi and Al-Pb monotectic alloys. Acta Mater. 59, 6880–6889 (2011)
Lacy, L.L., Otto, G.H.: The behavior of immiscible liquids in space. In: Thermophysics and Heat Transfer Conference. Boston 74-668 (1974)
Li, H.L.: Study of the Mechanism of the Microstructure Evolution in Directionally Solidified Monotectic Alloys. PhD thesis, Shenyang (2009)
Li, H.L., Zhao, J.Z.: Convective effect on the microstructure evolution during a liquid-liquid decomposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 241902 (2008)
Li, H.L., Zhao, J.Z.: Directional solidification of an Al-Pb alloy in a static magnetic field. Comp. Mater. Sci. 46, 1069–1075 (2009)
Li, X., Fautrelle, Y., Ren, Z.M.: High-magnetic-field-induced solidification of diamagnetic Bi. Scr. Mater. 59, 407–410 (2008a)
Li, X., Ren, Z.M., Fautrelle, Y.: Phase distribution and phase structure control through a high gradient magnetic field during the solidification process. Mater. Design 29, 1796–1801 (2008b)
Li, H.L., Zhao, J.Z., Zhang, Q.X., He, J.: Microstructure formation in a directionally solidified immiscible alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39, 3308–3316 (2008c)
Li, X., Fautrelle, Y., Ren, Z.M., Gagnoud, A., Moreau, R., Zhang, Y.D., Esling, C.: Effect of a high magnetic field on the morphological instability and irregularity of the interface of a binary alloy during directional solidification. Acta Mater. 57, 1689–1701 (2009a)
Li, X., Zhang, Y.D., Fautrelle, Y., Ren, Z.M., Esling, C.: Experimental evidence for liquid/solid interface instability caused by the stress in the solid during directional solidification under a strong magnetic field. Scr. Mater. 60, 489–492 (2009b)
Li, M.J., Tamura, T., Omura, N., Miwa, K.: Effects of magnetic field and electric current on the solidification of AZ91D magnesium alloys using an electromagnetic vibration technique. J. Alloys Compd. 487, 187–193 (2009c)
Li, J.Q., Ma, B.Q., Min, S., Lee, J., Yuan, Z.F., Zang, L.K.: Effect of Ce addition on macroscopic core-shell structure of Cu-Sn-Bi immiscible alloy. Mater. Lett. 64, 814–816 (2010)
Li, X., Gagnoud, A., Fautrelle, Y., Ren, Z.M., Moreau, R.: Influence of thermoelectric effects on the morphology of Al-Si eutectic during directional solidification under an axial strong magnetic field. J. Cryst. Growth 367, 94–103 (2013)
Lin, L.Y.: Chinese Microgravity Science and Space Experiment. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing (1988)
Luo, S.B., Wang, W.L., Chang, J., Xia, Z.C., Wei, B.: A comparative study of dendritic growth within undercooled liquid pure Fe and Fe50Cu50 alloy. Acta Mater. 69, 355–364 (2014)
Man, T.N., Zhang, L., Xu, N.K., Wang, W.B., Xiang, Z.L., Wang, E.G.: Effect of rare-earth Ce on macrosegregation in Al-Bi immiscible alloys. Metals 6, 177 (2016)
Misra, A.K.: A novel solidification technique of metals and alloys: under the influence of applied potential. Metall. Trans. A 16, 1354–1355 (1985)
Misra, A.K.: Effect of electric potentials on solidification of near eutectic Pb-Sb-Sn alloy. Mater. Lett. 4, 176–177 (1986)
Potard, C.: Structures of immiscible Al-In alloys solidified under microgravity conditions. Acta Astronaut. 9(4), 245–254 (1982)
Prinz, B., Romero, A., Ratke, L.: Casting process for hypermonotectic alloys under terrestrial conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 4715–4719 (1995)
Prodhan, A., Sivaramakrishnan, C.S., Chakrabarti, A.K.: Solidification of aluminum in electric field. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 32, 372–378 (2001)
Ratke, L., Diefenbach, S.: Liquid immiscible alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 15, 263–347 (1995)
Schaffer, P.L., Mathiesen, R.H., Arnberg, L.: L2 droplet interaction with \(\alpha \)-Al during solidification of hypermonotectic Al-8 wt% Bi alloys. Acta Mater. 57, 2887–2895 (2009)
Shen, Z., Zhong, Y.B., Wang, H., Ren, W.L., Lei, Z.S., Ren, Z.M.: Effect of a transverse magnetic field on solidification morphology and microstructures of pure Sn and Sn-15wt%Pb alloys grown by a Czochralski method. J. Cryst. Growth 432, 116–122 (2015)
Shi, W.Y., Rong, S.M., Feng, L.: Marangoni convection instabilities induced by evaporation of liquid layer in an open rectangular pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29, 91–96 (2017)
Sun, Q.: Study of the Solidification of Monotectic Alloys under the Effect of Microalloying. PhD thesis, Shenyang (2017)
Sun, Q., Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z.: Effect of micro-alloying element Bi on solidification and microstructure of Al-Pb alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 52(4), 497–504 (2016a)
Sun, Q., Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z., He, J.: Effect of TiC particles on the liquid-liquid decomposition of Al-Pb alloys. Mater. Des. 91, 361–367 (2016b)
Sun, Q., Jiang, H.X., Zhao, J.Z., He, J.: Microstructure evolution during the liquid-liquid phase transformation of Al-Bi alloys under the effect of TiC particles. Acta Mater. 129, 321–330 (2017)
Wang, C.P., Liu, X.J., Ohnuma, I., Kainuma, R., Ishida, K.: Formation of immiscible alloy powders with egg-type microstructure. Science 297(5583), 990–993 (2002)
Wang, T., Gao, T., Nie, J.F., Li, P.T., Liu, X.F.: Influence of carbon source on the microstructure of Al-Ti-C master alloy and its grain refining efficiency. Mater. Charact. 83, 13–20 (2013)
Wang, T., Gao, T., Zhang, P., Nie, J.F., Liu, X.F.: Influence of a new kind of Al-Ti-C master alloy on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-5Cu alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 589, 19–24 (2014)
Wang, Z.M., Sun, Z.P., Wang, X.L., Zhang, H., Jiang, S.N.: Effects of element addition on liquid phase separation of Bi-Ga immiscible alloy: characterization by electrical resistivity and coordination tendency. Mater. Des. 114, 111–115 (2017)
Wu, M.H., Ludwig, A., Ratke, L.: Modeling of marangoni-induced droplet motion and melt convection during solidification of hypermonotectic alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 3009–3019 (2003)
Xie, H.Q., Zeng, Z., Zhang, L.Q., Yokota, Y., Kawazoe, Y., Yoshikawa, A.: Simulation on thermocapillary-driven drop coalescence by hybrid lattice boltzmann method. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 123–132 (2016)
Xuan, W.D., Lan, J., Liu, H., Li, C., Wang, J., Ren, W.L., Zhong, Y.B., Li, X., Ren, Z.M.: Effects of a high magnetic field on the microstructure of Ni-based single-crystal superalloys during directional solidification. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48, 3804–3813 (2017)
Yasuda, H., Ohnaka, I., Fujimoto, S., Takezawa, N., Tsuchiyama, A., Nakano, T., Uesugi, K.: Fabrication of aligned pores in aluminum by electrochemical dissolution of monotectic alloys solidified under a magnetic field. Scr. Mater. 54, 527–532 (2006)
Zhang, L., Wang, E.G., Zuo, X.W., He, J.C.: Effect of high magnetic field on the transition behavior of Cu-rich particles in Cu-80%Pb hypermonotectic alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. 46(4), 423–428 (2010)
Zhao, J.Z., Ratke, L.: Modeling of the microstructure evolution in continuously cast Al-Pb alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 18(4), 306–310 (2002)
Zhao, J.Z., Ratke, L.: A model describing the microstructure evolution during a cooling of immiscible alloys in the miscibility gap. Scr. Mater. 50, 543–546 (2004)
Zhao, L., Zhao, J.Z.: Microstructure formation in a gas-atomized drop of Al-Pb-Sn immiscible alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43, 5019–5028 (2012)
Zhao, J.Z., Jiang, H.X., Sun, Q., Li, W., He, J.: Progress of research on solidification process and microstructure control of immiscible alloys. Mater. China 36(4), 252–261 (2017)
Zheng, T.X., Zhong, Y.B., Lei, Z.S., Ren, W.L., Ren, Z.M., Debray, F., Beaugnon, E., Fautrelle, Y.: Effects of high static magnetic field on distribution of solid particles in BiZn immiscible alloys with metastable miscibility gap. J. Alloys Compd. 623, 36–41 (2015)
Zhou, X.M., Liu, Z.G., Huai, X.L.: Evolution of free surface in the formation of thermo-solutocapillary convection within an open cavity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 421–430 (2016)
Zhu, J., Wang, T.M., Cao, F., Fu, H.W., Fu, Y.N., Xie, H.L., Xiao, T.Q.: Real-time observation on evolution of droplets morphology affected by electric current pulse in Al-Bi immiscible alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22, 1319–1323 (2013)
Zou, J., Xie, S.F., Zhou, Z., Fu, Q.F., Chen, Y., Zhai, Q.J., Lu, D.P.: Solidification microstructure and properties of Cu-14Fe composites under alternating magnetic field. T. Mater. Heat Treat. 37, 6–11 (2016)
Zuo, X.W., Wang, E.G., Han, H., Zhang, L., He, J.C.: Microstructures and magnetic properties of Fe-49%Sn monotectic alloys solidified under a high magnetic field. Acta Metall. Sin. 44(10), 1219–1223 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 51501207 51471173, 51771210), the China’s Manned Space Station Project (mission number TGJZ800-2-RW024), and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (grant number 201501043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Approaching the Chinese Space Station - Microgravity Research in China
Guest Editors: Jian-Fu Zhao, Shuang-Feng Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Zhao, J. Continuous Solidification of Immiscible Alloys and Microstructure Control. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 747–760 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9617-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9617-6