Abstract
Palmitic acid (PA) is the most common saturated long-chain fatty acid in food that causes cell apoptosis. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of PA toxicity. In this study, we explore the effects of PA on proliferation and apoptosis in human osteoblast-like Saos-2 cells and uncover the signaling pathways involved in the process. Our study showed that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy are involved in PA-induced Saos-2 cell apoptosis. We found that PA inhibited the viability of Saos-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. At the same time, PA induced the expression of ER stress marker genes (glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)), altered autophagy-related gene expression (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), ATG5, p62, and Beclin), promoted apoptosis-related gene expression (Caspase 3 and BAX), and affected autophagic flux. Inhibiting ER stress with 4-PBA diminished the PA-induced cell apoptosis, activated autophagy, and increased the expression of Caspase 3 and BAX. Inhibiting autophagy with 3-MA attenuated the PA and ER stress-induced cell apoptosis and the apoptosis-related gene expression (Caspase 3 and BAX), but seemed to have no obvious effects on ER stress, although the CHOP expression was downregulated. Taken together, our results suggest that PA-induced Saos-2 cell apoptosis is activated via ER stress and autophagy, and the activation of autophagy depends on the ER stress during this process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben SI, Prola A, Boussabbeh M, Guilbert A, Bacha H, Abid-Essefi S, Lemaire C (2015) Crocin and quercetin protect HCT116 and HEK293 cells from Zearalenone-induced apoptosis by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 20:927–938
Cawley K, Deegan S, Samali A, Gupta S (2011) Assays for detecting the unfolded protein response. Methods Enzymol 490:31–51
Chamolstad H, Yu JE, Lee SH, Kim JG, Sung KS, Hwang J, Yoo YD, Lee YJ, Kim ST, Lee DH (2016) Modulation of SQSTM1/p62 activity by N-terminal arginylation of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone HSPA5/GRP78/BiP. Autophagy 12:426–428
Chen YJ, Liu WH, Kao PH, Wang JJ, Chang LS (2010) Involvement of p38 MAPK- and JNK-modulated expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in Naja nigricollis CMS-9-induced apoptosis of human leukemia K562 cells. Toxicon 55:1306–1316
Chen F, Li Q, Zhang Z, Lin P, Lei L, Wang A, Jin Y (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress cooperates in zearalenone-induced cell death of RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 16:19780–19795
Chen F, Lin P, Wang N, Yang D, Wen X, Zhou D, Wang A, Jin Y (2016) Herp depletion inhibits zearalenone-induced cell death in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Toxicol in Vitro 32:115–122
Cunha DAD, Hekerman P, Ladriere L, Bazarracastro A, Ortis F, Wakeham MC, Moore F, Rasschaert J, Cardozo AK, Bellomo EA (2008) Initiation and execution of lipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic beta-cells. J Cell Sci 121:2308–2318
Dikic I, Elazar Z (2018) Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:349–364
Feng D, Wang B, Wang L, Abraham N, Tao K, Huang L, Shi W, Dong Y, Qu Y (2017) Pre-ischemia melatonin treatment alleviated acute neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by inhibiting ER stress-dependent autophagy via PERK and IRE1 signalings. J Pineal Res 62:e12395
Gunn P (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129:1337–1349
Gwak H, Kim S, Dhanasekaran DN, Song YS (2016) Resveratrol triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis by disrupting N-linked glycosylation of proteins in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett 371:347–353
Han J, Wang Y (2017) mTORC1 signaling in hepatic lipid metabolism. Protein Cell 1–7
He Y, Zhou L, Fan Z, Liu S, Fang W (2018) Palmitic acid, but not high-glucose, induced myocardial apoptosis is alleviated by N-acetylcysteine due to attenuated mitochondrial-derived ROS accumulation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis 9:568
Hino S, Kondo S, Yoshinaga K, Saito A, Murakami T, Kanemoto S, Sekiya H, Chihara K, Aikawa Y, Hara H (2010) Regulation of ER molecular chaperone prevents bone loss in a murine model for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 28:131–138
Hsiao YH, Lin CI, Liao H, Chen YH, Lin SH (2014) Palmitic acid-induced neuron cell cycle G2/M arrest and endoplasmic reticular stress through protein palmitoylation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Int J Mol Sci 15:20876–20899
Hsu HC, Li SJ, Chen CY, Chen MF (2017) Eicosapentaenoic acid protects cardiomyoblasts from lipotoxicity in an autophagy-dependent manner. Cell Biol Toxicol 1–13
Huang Z, Wu S, Kong F, Cai X, Ye B, Shan P, Huang W (2017) MicroRNA-21 protects against cardiac hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in H9c2 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med 21:467–474
Jaishy B, Abel ED (2016) Lipids, lysosomes and autophagy. J Lipid Res 57:1619–1635
Jiang H, Liang C, Liu X, Jiang Q, He Z, Wu J, Pan X, Ren Y, Fan M, Li M (2010) Palmitic acid promotes endothelial progenitor cell apoptosis via p38 and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Atherosclerosis 210:71–77
Jiang X, Chen X, Wan J, Gui H, Ruan X, Du X (2017) Autophagy protects against palmitic acid-induced apoptosis in podocytes in vitro. Sci Rep 7:42764
Katsoulieris E, Mabley JG, Samai M, Green IC, Chatterjee PK (2009) Alpha-linolenic acid protects renal cells against palmitic acid lipotoxicity via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur J Pharmacol 623:107–112
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Jr PG, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I, Flavell RA (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Las G, Shirihai OS (2010) The role of autophagy in β-cell lipotoxicity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 12:15–19
Leroy C, Tricot S, Lacour B, Grynberg A (2008) Protective effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on palmitate-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes. BBA-Biomembranes 1781:685–693
Levine B, Yuan J (2005) Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest 115:2679–2688
Li S, Li J, Shen C, Zhang X, Sun S, Cho M, Sun C, Song Z (2014) Tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) protects hepatocytes against lipotoxicity via inducing autophagy independently of Nrf2 activation. BBA-Biomembranes 1841:22–33
Li J, Yang S, Li X, Liu D, Wang Z, Guo J, Tan N, Gao Z, Zhao X, Zhang J (2017) Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disuse osteoporosis. Bone 97:2–14
Liang Q, Kobayashi S (2016) Mitochondrial quality control in the diabetic heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 95:57–69
Lin P, Yang Y, Li X, Chen F, Cui C, Hu L, Li Q, Liu W, Jin Y (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in granulosa cell apoptosis during follicular atresia in goat ovaries. Mol Reprod Dev 79:423–432
Lin P, Chen F, Sun J, Zhou J, Wang X, Wang N, Li X, Zhang Z, Wang A, Jin Y (2015) Mycotoxin zearalenone induces apoptosis in mouse Leydig cells via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent signalling pathway. Reprod Toxicol 52:71–77
Lisse TS, Thiele F, Fuchs H, Hans W, Przemeck GKH, Abe K, Rathkolb B, Quintanillamartinez L, Hoelzlwimmer G, Helfrich M (2008) ER stress-mediated apoptosis in a new mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta. PLoS Genet 4:e7
Liu Y, Levine B (2015) Autosis and autophagic cell death: the dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ 22:367–376
Lu J, Wang Q, Huang L, Dong H, Lin L, Lin N, Zheng F, Tan J (2012) Palmitate causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human mesenchymal stem cells: prevention by AMPK activator. Endocrinology 153:5275–5284
Ma Y, Shimizu Y, Mann MJ, Jin Y, Hendershot LM (2010) Plasma cell differentiation initiates a limited ER stress response by specifically suppressing the PERK-dependent branch of the unfolded protein response. Cell Stress Chaperones 15:281–293
Ma XH, Piao SF, Dey S, Mcafee Q, Karakousis G, Villanueva J, Hart LS, Levi S, Hu J, Zhang G (2014) Targeting ER stress-induced autophagy overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. J Clin Invest 124:1406–1417
Maeyashiki C, Oshima S, Otsubo K, Kobayashi M, Nibe Y, Matsuzawa Y, Onizawa M, Nemoto Y, Nagaishi T, Okamoto R (2017) HADHA, the alpha subunit of the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, is involved in long-chain fatty acid-induced autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem Bioph Res Commun 484:636–641
Martinez SC, Tanabe K, Cras-Méneur C, Abumrad NA, Bernal-Mizrachi E, Permutt MA (2008) Inhibition of Foxo1 protects pancreatic islet beta-cells against fatty acid and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Diabetes 57:846–859
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M, Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B, Sadoshima J (2007) Distinct roles of autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: roles of AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy. Circ Res 100:914–922
Mei S, Ni H, Manley S, Bockus A, Kassel KM, Luyendyk JP, Copple BL, Ding W (2011) Differential roles of unsaturated and saturated fatty acids on autophagy and apoptosis in hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339:487–498
Momoi T (2006) ER stress (PERK/eIF2alpha phosphorylation) mediates the polyglutamine-induced LC3 conversion, an essential step for autophagy formation. Cell Death Differ 14:230–239
Mu YM, Yanase T, Nishi Y, Tanaka A, Saito M, Jin CH, Mukasa C, Okabe T, Nomura M, Goto K (2001) Saturated FFAs, palmitic acid and stearic acid, induce apoptosis in human granulosa cells. Endocrinology 142:3590–3597
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Qaisiya M, Brischetto C, Jašprová J, Vitek L, Tiribelli C, Bellarosa C (2016) Bilirubin-induced ER stress contributes to the inflammatory response and apoptosis in neuronal cells. Arch Toxicol 91:1–12
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7:880–885
Szpigel A, Hainault I, Carlier A, Venteclef N, Batto AF, Hajduch E, Bernard C, Ktorza A, Gautier JF, Ferré P (2018) Lipid environment induces ER stress, TXNIP expression and inflammation in immune cells of individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 61:399–412
Tan SH, Shui G, Zhou J, Li JJ, Bay BH, Wenk MR, Shen HM (2012) Induction of autophagy by palmitic acid via protein kinase C-mediated signaling pathway independent of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). J Biol Chem 287:14364–14376
Tu QQ, Zheng RY, Li J, Hu L, Chang YX, Li L, Li MH, Wang RY, Huang DD, Wu MC (2014) Palmitic acid induces autophagy in hepatocytes via JNK2 activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35:504–512
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334:1081–1086
Wang X, Lin P, Yin Y, Zhou J, Lei L, Zhou X, Jin Y, Wang A (2015) Brucella suis vaccine strain S2-infected immortalized caprine endometrial epithelial cell lines induce non-apoptotic ER-stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 20:399–409
Wang X, Lin P, Li Y, Xiang C, Yin Y, Chen Z, Du Y, Zhou D, Jin Y, Wang A (2016) Brucella suis vaccine strain 2 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress that affects intracellular replication in goat trophoblast cells in vitro. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:19
Wen H, Wu Z, Hu H, Wu Y, Yang G, Lu J, Yang G, Guo G, Dong Q (2017) The anti-tumor effect of pachymic acid on osteosarcoma cells by inducing PTEN and Caspase 3/7-dependent apoptosis. J Nat Med 72:1–7
Xia X, Kar R, Gluhakheinrich J, Yao W, Lane NE, Bonewald LF, Biswas SK, Lo W, Jiang JX (2010) Glucocorticoid-induced autophagy in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res 25:2479–2488
Yamada H, Nakajima T, Domon H, Honda T, Yamazaki K (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress response and bone loss in experimental periodontitis in mice. J Periodontal Res 50:500–508
Yang Y, Cheung HH, Tu J, Miu KK, Chan W (2016a) New insights into the unfolded protein response in stem cells. Oncotarget 7:54010–54027
Yang Y, Pei X, Jin Y, Wang Y, Zhang C (2016b) The roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress response in female mammalian reproduction. Cell Tissue Res 363:589–597
Yong Z, Xue R, Zhang Z, Xia Y, Shi H (2012) Palmitic and linoleic acids induce ER stress and apoptosis in hepatoma cells. Lipids Health Dis 11:1
Zeng M, Sang W, Chen S, Chen R, Zhang H, Xue F, Li Z, Liu Y, Gong Y, Zhang H (2017) 4-PBA inhibits LPS-induced inflammation through regulating ER stress and autophagy in acute lung injury models. Toxicol Lett 271:26–37
Zhang Y, Yang X, Shi H, Dong L, Bai J (2011) Effect of α-linolenic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis of palmitic acid lipotoxicity in primary rat hepatocytes. Lipids Health Dis 10:122
Zhang W, Meng H, Yang R, Yang M, Sun G, Liu J, Shi P, Liu F, Yang B (2016) Melatonin suppresses autophagy in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. Oncotarget 7:52179–52194
Zhao L, Jiang H, Papasian CJ, Maulik D, Drees BM, Hamilton JJ, Deng H (2007a) Correlation of obesity and osteoporosis: effect of fat mass on the determination of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 23:17–29
Zhao L, Liu Y, Liu P, Hamilton JJ, Recker RR, Deng H (2007b) Relationship of obesity with osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1640–1646
Zheng YZ, Cao ZG, Hu X, Shao ZM (2014) The endoplasmic reticulum stress markers GRP78 and CHOP predict disease-free survival and responsiveness to chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 145:349–358
Zhu Q, Yang J, Zhu R, Jiang X, Li W, He S, Jin J (2016) Dihydroceramide-desaturase-1-mediated caspase 9 activation through ceramide plays a pivotal role in palmitic acid-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Apoptosis 21:1033–1044
Funding
This research study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81660152) and Doctoral Research Start-Up Foundation of Jiujiang University (No. 8879522).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Fig. S1
The morphology of Saos-2 cells after treatment with different doses of PA (0–800 μM) for 24 h. (PNG 18533 kb)
Fig. S2
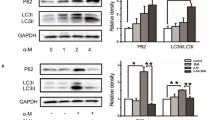
Effects of PA on ER Stress, autophagy, and apoptosis related protein expression. (A) The expression of GRP78 and CHOP in Saos-2 cells after treatment with different doses of PA (0–800 μM) for 24 h; (B) The expression of GRP78 and CHOP after treatment with 200 μM PA for different times (0–48 h); (C) The expression of Beclin1, LC3, ATG5 and p62 in Saos-2 cells after treatment with different doses of PA (0–800 μM) for 24 h; (D) The expression of Beclin1, LC3, ATG5 and p62 after treatment with 200 μM PA for different times (0–48 h); (E) The expression of BAX in Saos-2 cells after treatment with different dose of PA (0–800 μM) for 24 h; (F) The expression of BAX after treatment with 200 μM PA for different times (0–48 h). (PNG 395 kb)
Fig. S3
The related protein expression of ER Stress, autophagy, and apoptosis in different treatment groups. (A) Effect of 4-PBA in PA-treated Saos-2 cells; (B) Effect of 3-MA in PA-treated Saos-2 cells; (C) Effect of 3-MA in TG-treated Saos-2 cells. (PNG 1311 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Guan, G., Lei, L. et al. Palmitic acid induces human osteoblast-like Saos-2 cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Stress and Chaperones 23, 1283–1294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0936-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0936-8