Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether improvement of regional inflammatory findings in knee joints of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) could be detected by positron-emission tomography (PET) using 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) after acupuncture treatments, as well as improvement of systemic inflammatory markers.
Methods
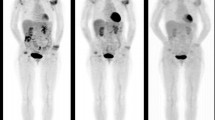
Six RA patients (all female, 61 ± 12 years old) received 10 acupuncture treatments in 2 months, to 11 traditional acupuncture points around a knee joint considered effective on RA. A visual analogue scale (VAS) for intensity of pain, knee joint range of motion (ROM), face scale for patient mood, and modified health assessment questionnaire (MHAQ) for disability of daily activities were assessed just before and after acupuncture. Maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) and the volume with SUV more than 1.0 [Volume(SUV > 1)] on FDG–PET images as well as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were also measured before and after the treatments.
Results
VAS, ROM, face scale and MHAQ improved in all patients and significantly after acupuncture, but no significant change was detected in ESR, CRP, SUVmax, or Volume(SUV > 1).
Conclusions
Acupuncture relieves symptom, remedies physical function, and improves quality of life in RA patients, but may have no or very limited anti-inflammatory effect systemically. The regional effects of acupuncture are unlikely to be induced through reduction of regional inflammation. We believe this clinical study is the first step for elucidating therapeutic mechanisms of acupuncture, which must be important for the rational use and further development of acupuncture.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guidelines for Clinical Research on Acupuncture. Manila: World Health Organization regional office for the western pacific; 1995.
WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy 2002–2005. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
Lewith GT, White PJ, Pariente J. Investigating acupuncture using brain imaging techniques: the current state of play. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2005;2:315–9.
Wang C, de Pablo P, Chen X, Schmid C, McAlindon T. Acupuncture for pain relief in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1249–56.
Zhuang H, Alavi A. 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomographic imaging in the detection and monitoring of infection and inflammation. Semin Nucl Med. 2002;32:47–59.
Bleeker-Rovers CP, Vos FJ, Corstens FH, Oyen WJ. Imaging of infectious diseases using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose PET. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;52:17–29.
Beckers C, Ribbens C, André B, Marcelis S, Kaye O, Mathy L, et al. Assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with (18)F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:956–64.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24.
Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature, 2nd ed. Manila: World Health Organization regional office for the Western Pacific; 1993.
Scott J, Huskisson EC. Graphic representation of pain. Pain. 1976;2:175–84.
Lorish CD, Maisiak R. The Face Scale: a brief, nonverbal method for assessing patient mood. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29:906–9.
Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford health assessment questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum. 1983;26:1346–53.
Hudson HM, Larkin RS. Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1994;13:601–9.
Strauss LG, Conti PS. The applications of PET in clinical oncology. J Nucl Med. 1991;32:623–4.
Zijlstra FJ, van den Berg-de Lange I, Huygen FJ, Klein J. Anti-inflammatory actions of acupuncture. Mediators Inflamm. 2003;12:59–69.
Oke SL, Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex and the role of complementary and alternative medical therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; in press. [Epub ahead of print].
Otsuka N, Fukunaga M, Morita K, Ono S, Nagai K, Katagiri M, et al. Iodine-131 uptake in a patient with thyroid cancer and rheumatoid arthritis during acupuncture treatment. Clin Nucl Med. 1990;15:29–31.
Elzinga EH, van der Laken CJ, Comans EF, Lammertsma AA, Dijkmans BA, Voskuyl AE. 2-Deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-d-glucose joint uptake on positron emission tomography images: rheumatoid arthritis versus osteoarthritis. Mol Imaging Biol. 2007;9:357–60.
Goerres GW, Forster A, Uebelhart D, Seifert B, Treyer V, Michel B, et al. F-18 FDG whole-body PET for the assessment of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Nucl Med. 2006;31:386–90.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Chietsugu Kato of Department of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, and Dr. Koichi Morita of Sousei Higashi Hospital, Sapporo for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, M., Inubushi, M., Shiga, T. et al. Therapeutic effects of acupuncture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study using 18F-FDG–PET. Ann Nucl Med 23, 311–316 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0238-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0238-4