Abstract
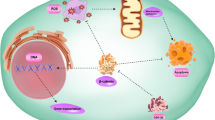
The circadian rhythm disorder and abnormal expression of rhythm genes are related to many diseases, especially cancer. Rhythm gene NFIL3 is involved in energy metabolism and immune cell differentiation, and its aberrant expression is associated with metabolic diseases and inflammation. Previously, numerous studies have shown that aberrant NFIL3 expression is associated with tumorigenesis, progression, and chemotherapy resistance. For instance, NFIL3 performs as a nuclear transcription factor, impacts cell proliferation, represses apoptosis, and promotes cancer cell invasion and metastasis by regulating the transcription of target genes. In addition, NFIL3 expressed in cancer cells influences the type and proportion of infiltrated immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Increased expression of NFIL3 induces the chemotherapy and immunotherapy resistance in cancer. In this review, we summarized the pathological functions of NFIL3 in tumorigenesis, cancer development, and treatment. The rhythm gene NFIL3 can be used as a promising target in cancer therapy in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used during the current review are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- bZIP:
-
Basic leucine zipper
- DBP:
-
Albumin D-site-binding protein
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FGF21:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21
- FOXO:
-
Forkhead box
- Foxp3:
-
Forkhead box protein p3
- HDAC2:
-
Histone deacetylase-2
- HKDC1:
-
Hexokinase domain containing 1
- IGF-2:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2
- M1:
-
Type I macrophages
- M2:
-
Type II macrophages
- NAFLD:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NFIL3:
-
Nuclear factor, interleukin-3 regulated
- NFKBIA:
-
NF-κB inhibitor alpha
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- NK:
-
Natural Killer
- PEPCK:
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
- PER:
-
Period
- PHEX:
-
Phosphate regulating endopeptidase homolog X-linked
- PRNP:
-
Prion protein
- PrPc:
-
Cellular prion protein
- RASSF8:
-
Ras-association domain family member 8
- RORγt:
-
Orphan nuclear receptor
- SOSTDC1:
-
Sclerostin domain containing 1
- SREBP-1c:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- SUV39H1:
-
Suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 1
- Th1:
-
T-helper1
- Th17:
-
T-helper17
- Th2:
-
T-helper2
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- TRAIL:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory cells
- TTFL:
-
Transcriptional and translational feedback loop
References
Jagannath A, Taylor L, Wakaf Z, Vasudevan SR, Foster RG. The genetics of circadian rhythms, sleep and health. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(R2):R128–38.
Matsui MS, Pelle E, Dong K, Pernodet N. Biological rhythms in the skin. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6):801.
Bollinger T, Schibler U. Circadian rhythms—from genes to physiology and disease. Swiss Med Wkly. 2014;144: w13984.
Reszka E, Zienolddiny S. Epigenetic basis of circadian rhythm disruption in cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1856:173–201.
Ye Y, Xiang Y, Ozguc FM, Kim Y, Liu CJ, Park PK, et al. The genomic landscape and pharmacogenomic interactions of clock genes in cancer chronotherapy. Cell Syst. 2018;6(3):314-328e312.
Kashiwada M, Levy DM, McKeag L, Murray K, Schroder AJ, Canfield SM, et al. IL-4-induced transcription factor NFIL3/E4BP4 controls IgE class switching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(2):821–6.
Qi J, Yu Y, Akilli Ozturk O, Holland JD, Besser D, Fritzmann J, et al. New Wnt/beta-catenin target genes promote experimental metastasis and migration of colorectal cancer cells through different signals. Gut. 2016;65(10):1690–701.
Wang Y, Kuang Z, Yu X, Ruhn KA, Kubo M, Hooper LV. The intestinal microbiota regulates body composition through NFIL3 and the circadian clock. Science. 2017;357(6354):912–6.
Zhao Z, Yin L, Wu F, Tong X. Hepatic metabolic regulation by nuclear factor E4BP4. J Mol Endocrinol. 2021;66(1):R15–21.
Mitsui S, Yamaguchi S, Matsuo T, Ishida Y, Okamura H. Antagonistic role of E4BP4 and PAR proteins in the circadian oscillatory mechanism. Genes Dev. 2001;15(8):995–1006.
Yamajuku D, Shibata Y, Kitazawa M, Katakura T, Urata H, Kojima T, et al. Cellular DBP and E4BP4 proteins are critical for determining the period length of the circadian oscillator. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(14):2217–22.
Chen ST, Choo KB, Hou MF, Yeh KT, Kuo SJ, Chang JG. Deregulated expression of the PER1, PER2 and PER3 genes in breast cancers. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26(7):1241–6.
Kubo M. Diurnal rhythmicity Programs of Microbiota and transcriptional oscillation of circadian regulator, NFIL3. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 552188.
Zhou J, Li X, Zhang M, Gong J, Li Q, Shan B, et al. The aberrant expression of rhythm genes affects the genome instability and regulates the cancer immunity in pan-cancer. Cancer Med. 2020;9(5):1818–29.
Benito A, Gutierrez O, Pipaon C, Real PJ, Gachon F, Ritchie AE, et al. A novel role for proline- and acid-rich basic region leucine zipper (PAR bZIP) proteins in the transcriptional regulation of a BH3-only proapoptotic gene. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(50):38351–7.
Wu S, Li J, Cao M, Yang J, Li YX, Li YY. A novel integrated gene coexpression analysis approach reveals a prognostic three-transcription-factor signature for glioma molecular subtypes. BMC Syst Biol. 2016;10(Suppl 3):71.
Yang W, Li J, Zhang M, Yu H, Zhuang Y, Zhao L, et al. Elevated expression of the rhythm gene NFIL3 promotes the progression of TNBC by activating NF-kappaB signaling through suppression of NFKBIA transcription. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):67.
Blau J, Young MW. Cycling vrille expression is required for a functional Drosophila clock. Cell. 1999;99(6):661–71.
Astiz M, Heyde I, Oster H. Mechanisms of communication in the mammalian circadian timing system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(2):343.
Doi M, Nakajima Y, Okano T, Fukada Y. Light-induced phase-delay of the chicken pineal circadian clock is associated with the induction of cE4bp4, a potential transcriptional repressor of cPer2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(14):8089–94.
Farshadi E, van der Horst GTJ, Chaves I. Molecular links between the circadian clock and the cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(12):3515–24.
Altura RA, Inukai T, Ashmun RA, Zambetti GP, Roussel MF, Look AT. The chimeric E2A-HLF transcription factor abrogates p53-induced apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 1998;92(4):1397–405.
McTiernan CF, Lemster BH, Bedi KC, Margulies KB, Moravec CS, Hsieh PN, et al. Circadian pattern of ion channel gene expression in failing human hearts. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2021;14(1): e009254.
Savvidis C, Koutsilieris M. Circadian rhythm disruption in cancer biology. Mol Med. 2012;18:1249–60.
Keniry M, Dearth RK, Persans M, Parsons R. New frontiers for the NFIL3 bZIP transcription factor in cancer, metabolism and beyond. Discoveries (Craiova). 2014;2(2): e15.
Pellicelli M, Taheri M, St-Louis M, Beriault V, Desgroseillers L, Boileau G, et al. PTHrP(1–34)-mediated repression of the PHEX gene in osteoblastic cells involves the transcriptional repressor E4BP4. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(6):2378–87.
Chen B-C, Shibu MA, Kuo C-H, Shen C-Y, Chang-Lee SN, Lai C-H, et al. E4BP4 inhibits AngII-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts by activating the PI3K-Akt pathway and promoting calcium uptake. Exp Cell Res. 2018;363(2):227–34.
Tamai S, Imaizumi K, Kurabayashi N, Nguyen MD, Abe T, Inoue M, et al. Neuroprotective role of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor NFIL3 in models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(3):1629–38.
Dang F, Sun X, Ma X, Wu R, Zhang D, Chen Y, et al. Insulin post-transcriptionally modulates Bmal1 protein to affect the hepatic circadian clock. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12696.
Tong X, Zhang D, Buelow K, Guha A, Arthurs B, Brady HJ, et al. Recruitment of histone methyltransferase G9a mediates transcriptional repression of Fgf21 gene by E4BP4 protein. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(8):5417–25.
Tong X, Li P, Zhang D, VanDommelen K, Gupta N, Rui L, et al. E4BP4 is an insulin-induced stabilizer of nuclear SREBP-1c and promotes SREBP-1c-mediated lipogenesis. J Lipid Res. 2016;57(7):1219–30.
Yang M, Zhang D, Zhao Z, Sit J, Saint-Sume M, Shabandri O, et al. Hepatic E4BP4 induction promotes lipid accumulation by suppressing AMPK signaling in response to chemical or diet-induced ER stress. FASEB J. 2020;34(10):13533–47.
Day EA, Ford RJ, Steinberg GR. AMPK as a therapeutic target for treating metabolic diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017;28(8):545–60.
Kang G, Han HS, Koo SH. NFIL3 is a negative regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Metabolism. 2017;77:13–22.
Ohta Y, Taguchi A, Matsumura T, Nakabayashi H, Akiyama M, Yamamoto K, et al. Clock gene dysregulation induced by chronic ER stress disrupts beta-cell function. EBioMedicine. 2017;18:146–56.
Rijo-Ferreira F, Takahashi JS. Genomics of circadian rhythms in health and disease. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):82.
Masri S, Sassone-Corsi P. The emerging link between cancer, metabolism, and circadian rhythms. Nat Med. 2018;24(12):1795–803.
Yuan P, Yang T, Mu J, Zhao J, Yang Y, Yan Z, et al. Circadian clock gene NPAS2 promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2020;469:498–509.
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123(3191):309–14.
Pascale RM, Calvisi DF, Simile MM, Feo CF, Feo F. The Warburg Effect 97 Years after Its Discovery. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(10):2819.
Fuhr L, El-Athman R, Scrima R, Cela O, Carbone A, Knoop H, et al. The Circadian clock regulates metabolic phenotype rewiring via HKDC1 and modulates tumor progression and drug response in colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine. 2018;33:105–21.
Kim HS, Sohn H, Jang SW, Lee GR. The transcription factor NFIL3 controls regulatory T-cell function and stability. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(7):1–15.
Male V, Nisoli I, Gascoyne DM, Brady HJ. E4BP4: an unexpected player in the immune response. Trends Immunol. 2012;33(2):98–102.
Kamizono S, Duncan GS, Seidel MG, Morimoto A, Hamada K, Grosveld G, et al. Nfil3/E4bp4 is required for the development and maturation of NK cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 2009;206(13):2977–86.
Firth MA, Madera S, Beaulieu AM, Gasteiger G, Castillo EF, Schluns KS, et al. Nfil3-independent lineage maintenance and antiviral response of natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 2013;210(13):2981–90.
Onyilagha C, Kuriakose S, Ikeogu N, Kung SKP, Uzonna JE. NK cells are critical for optimal immunity to experimental trypanosoma congolense infection. J Immunol. 2019;203(4):964–71.
Chen Z, Lund R, Aittokallio T, Kosonen M, Nevalainen O, Lahesmaa R. Identification of novel IL-4/Stat6-regulated genes in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2003;171(7):3627–35.
Motomura Y, Kitamura H, Hijikata A, Matsunaga Y, Matsumoto K, Inoue H, et al. The transcription factor E4BP4 regulates the production of IL-10 and IL-13 in CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(5):450–9.
Gallo E, Katzman S, Villarino AV. IL-13-producing Th1 and Th17 cells characterize adaptive responses to both self and foreign antigens. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(9):2322–8.
Yu X, Rollins D, Ruhn KA, Stubblefield JJ, Green CB, Kashiwada M, et al. TH17 cell differentiation is regulated by the circadian clock. Science. 2013;342(6159):727–30.
Zielinski MR, Systrom DM, Rose NR. Fatigue, sleep, and autoimmune and related disorders. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1827.
Gu WB, Liu ZP, Zhou YL, Li B, Wang LZ, Dong WR, et al. The nuclear factor interleukin 3-regulated (NFIL3) transcription factor involved in innate immunity by activating NF-kappaB pathway in mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019;101: 103452.
Liu C, Chen S, Zhang H, Chen Y, Gao Q, Chen Z, et al. Bioinformatic analysis for potential biological processes and key targets of heart failure-related stroke. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021;22(9):718–32.
Wang X, Wang Q, Wang K, Ni Q, Li H, Su Z, et al. Is immune suppression involved in the ischemic stroke? A study based on computational biology. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14: 830494.
Tang H, Tan C, Cao X, Liu Y, Zhao H, Liu Y, et al. NFIL3 facilitates neutrophil autophagy, neutrophil extracellular trap formation and inflammation during gout via REDD1-dependent mTOR inactivation. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8: 692781.
Zhao M, Liu Q, Liang G, Wang L, Luo S, Tang Q, et al. E4BP4 overexpression: a protective mechanism in CD4+ T cells from SLE patients. J Autoimmun. 2013;41:152–60.
Kobayashi T, Matsuoka K, Sheikh SZ, Elloumi HZ, Kamada N, Hisamatsu T, et al. NFIL3 is a regulator of IL-12 p40 in macrophages and mucosal immunity. J Immunol. 2011;186(8):4649–55.
Kobayashi T, Steinbach EC, Russo SM, Matsuoka K, Nochi T, Maharshak N, et al. NFIL3-deficient mice develop microbiota-dependent, IL-12/23-driven spontaneous colitis. J Immunol. 2014;192(4):1918–27.
Bene K, Halasz L, Nagy L. Transcriptional repression shapes the identity and function of tissue macrophages. FEBS Open Biol. 2021;11(12):3218–29.
Fu L, Lee CC. The circadian clock: pacemaker and tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(5):350–61.
Cadenas C, van de Sandt L, Edlund K, Lohr M, Hellwig B, Marchan R, et al. Loss of circadian clock gene expression is associated with tumor progression in breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(20):3282–91.
Ikushima S, Inukai T, Inaba T, Nimer SD, Cleveland JL, Look AT. Pivotal role for the NFIL3/E4BP4 transcription factor in interleukin 3-mediated survival of pro-B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(6):2609–14.
Zhou Q, Chen J, Feng J, Wang J. E4BP4 promotes thyroid cancer proliferation by modulating iron homeostasis through repression of hepcidin. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(10):987.
Keniry M, Pires MM, Mense S, Lefebvre C, Gan B, Justiano K, et al. Survival factor NFIL3 restricts FOXO-induced gene expression in cancer. Genes Dev. 2013;27(8):916–27.
Jiramongkol Y, Lam EW. FOXO transcription factor family in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020;39(3):681–709.
Chaudhry GE, Akim AM, Sung YY, Muhammad TST. Cancer and apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2543:191–210.
Karthik IP, Desai P, Sukumar S, Dimitrijevic A, Rajalingam K, Mahalingam S. E4BP4/NFIL3 modulates the epigenetically repressed RAS effector RASSF8 function through histone methyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(15):5624–35.
Edlich F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: recent insights and unknowns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(1):26–34.
Lin SC, Lin CH, Shih NC, Liu HL, Wang WC, Lin KY, et al. Cellular prion protein transcriptionally regulated by NFIL3 enhances lung cancer cell lamellipodium formation and migration through JNK signaling. Oncogene. 2020;39(2):385–98.
Hayashi M, Kawakubo H, Fukuda K, Mayanagi S, Nakamura R, Suda K, et al. THUMP domain containing 2 protein possibly induces resistance to cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in in vitro human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells as revealed by transposon activation mutagenesis. J Gene Med. 2019;21(12): e3135.
Hosseini K, Frenzel A, Fischer-Friedrich E. EMT changes actin cortex rheology in a cell-cycle-dependent manner. Biophys J. 2021;120(16):3516–26.
Tang PM, Zhou S, Meng XM, Wang QM, Li CJ, Lian GY, et al. Smad3 promotes cancer progression by inhibiting E4BP4-mediated NK cell development. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14677.
Peng Z, Zhang C, Zhou W, Wu C, Zhang Y. The STAT3/NFIL3 signaling axis-mediated chemotherapy resistance is reversed by Raddeanin A via inducing apoptosis in choriocarcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(7):5370–82.
Gupta N, Park JE, Tse W, Low JK, Kon OL, McCarthy N, et al. ERO1alpha promotes hypoxic tumor progression and is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2019;10(57):5970–82.
Progatzky F, Taylor H, Bugeon L, Cassidy S, Radbruch A, Dallman MJ, et al. The role of Nfil3 in zebrafish hematopoiesis. Dev Comp Immunol. 2012;38(1):187–92.
Smith AM, Qualls JE, O’Brien K, Balouzian L, Johnson PF, Schultz-Cherry S, et al. A distal enhancer in Il12b is the target of transcriptional repression by the STAT3 pathway and requires the basic leucine zipper (B-ZIP) protein NFIL3. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(26):23582–90.
Li F, Liu J, Jo M, Curry TE Jr. A role for nuclear factor interleukin-3 (NFIL3), a critical transcriptional repressor, in down-regulation of periovulatory gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25(3):445–59.
Dierickx P, Zhu K, Carpenter BJ, Jiang C, Vermunt MW, Xiao Y, et al. Circadian REV-ERBs repress E4bp4 to activate NAMPT-dependent NAD(+) biosynthesis and sustain cardiac function. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022;1(1):45–58.
Tong X, Muchnik M, Chen Z, Patel M, Wu N, Joshi S, et al. Transcriptional repressor E4-binding protein 4 (E4BP4) regulates metabolic hormone fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) during circadian cycles and feeding. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(47):36401–9.
Yu H, Shen Y, Sun J, Xu X, Wang R, Xuan Y, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the NFIL3/E4BP4 transcription factor of grass carp. Ctenopharyngodon idella. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014;47(2):215–22.
Baek YS, Haas S, Hackstein H, Bein G, Hernandez-Santana M, Lehrach H, et al. Identification of novel transcriptional regulators involved in macrophage differentiation and activation in U937 cells. BMC Immunol. 2009;10:18.
Kashiwada M, Pham NL, Pewe LL, Harty JT, Rothman PB. NFIL3/E4BP4 is a key transcription factor for CD8alpha(+) dendritic cell development. Blood. 2011;117(23):6193–7.
Schlenner S, Pasciuto E, Lagou V, Burton O, Prezzemolo T, Junius S, et al. NFIL3 mutations alter immune homeostasis and sensitise for arthritis pathology. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3):342–9.
Zhu C, Sakuishi K, Xiao S, Sun Z, Zaghouani S, Gu G, et al. An IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis drives Tim-3 and IL-10 expression and T-cell dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6072.
Mazzio EA, Lewis CA, Elhag R, Soliman KF. Effects of sepantronium bromide (YM-155) on the whole transcriptome of MDA-MB-231 cells: highlight on impaired ATR/ATM fanconi anemia DNA damage response. Cancer Genom Proteom. 2018;15(4):249–64.
Funding
The work of Weiwei Yang was funded by the Heilongjiang Province Postdoctoral Scientific Research Developmental Fund (Grant No. LBH-Q20046) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (Grant No. LH2022H008) and the work of Minghui Zhang was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Grant No. 2020MS08084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YWW and WYQ offered main direction and significant guidance of this manuscript. ZLX, CDX, XY, and ZMH drafted the manuscript and illustrated the figures for the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that this work does not have any conflict interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
All the participants has written informed consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, L., Chen, D., Xue, Y. et al. A new border for circadian rhythm gene NFIL3 in diverse fields of cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 1940–1948 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03098-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03098-5