Abstract
Anaemia is a frequent complication in cancer patients and may be multifactorial in origin. Treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) is an alternative to red blood cell transfusion. The evidence from clinical trials has established that patients with chemotherapy-induced anaemia with a haemoglobin concentration below 10 g/dl benefit from epoetin therapy. The native glycoprotein hormone consists of 165 amino acids with three N-glycosylation and one O-glycosylation sites. Epoetin and darbepoetin bind to the EPO receptor to induce intracellular signalling by the same intracellular molecules as native EPO. There are some differences in the glycosylation pattern which lead to variations in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics profiles. Pharmacokinetic and therapeutic studies have examined the use of rHuEPO administered intravenously and subcutaneously and there is accumulating evidence that the latter route has several advantages in cancer patients. After subcutaneous administration, the bioavailability of epoetin is about 20–30% and has a plasma half-life of >24 h. Darbepoetin has a longer half-life after subcutaneous administration of 48 h. The general recommendations are based on evidence from trials in which epoetin was administered 150 U/kg thrice weekly. The recommended initial dose for darbepoetin alpha is 2.25 μg/kg per week. The most serious adverse effects are hypertension, bleeding and increased risk of thrombotic complications. Caution is advised when used in patients who are at high risk for thromboembolic events. In the management of anaemic cancer patients, physicians should closely follow the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)/American Society of Hematology (ASH) guidelines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carnot P, Deflandre C (1906) Sur l’activite hemopoietique de serum au tours de la regeneration du sang. C R Acad Sci Paris 143:384–386
Ng T, Marx G, Littlewood T et al (2003) Recombinant erythropoietin in clinical practice. Postgrad Med J 79:367–376
Groopman JE, Itri LM (1999) Chemotherapy-induced anemia in adults: incidence and treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1616–1634
Cella D, Kallich J, McDermott A et al (2004) The longitudinal relationship of hemoglobin, fatigue and quality of life in anemic cancer patients: results from five randomized clinical trials. Ann Oncol 15:979–986
Bohlius J, Langensiepen S, Schwarzer G et al (2006) Eritropoyetina para los pacientes con enfermedades malignas: La Biblioteca Cochrane Plus, Número 4. Oxford: Update Software Ltd. http://www.update-software.com
Sazama K (1990) Reports of 355 transfusion-associated deaths: 1976 through 1985. Transfusion 30:583–590
Eschbach JW, Abdulhadi MH, Browne JK et al (1989) Recombinant human erythropoietin in anemic patient with end-stage renal disease. Results of a phase III multicenter clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 111:992–1000
Jelkmann W (1992) Erythropoietin: structure, control of production and function. Physiol Rev 72:449–489
Farrell F, Lee A (2004) The erythropoietin receptor and its expression in tumor cells and other tissues. Oncologist 9[Suppl 5]:18–30
Verdier F, Walrafen P, Hubert N et al (2000) Proteasomes regulate the duration of erythropoietin receptor activation by controlling down-regulation of cell surface receptors. J Biol Chem 275: 18375–18381
Jelkmann W (2004) Molecular biology of erythropoietin. Intern Med 43:649–656
Priyadarshi A, Shapiro J (2006) Erythropoietin resistance in the treatment of the anemia of chronic renal failure. Semin Dial 19:273–278
Annable L, Cotes PM, Musset MV et al (1972) The second international reference preparation of erythropoietin, human urinary, for bioassay. Bull WHO 47:99–112
Mason Garcia MB, Beckman JW, Brookins JS et al (1990) Development of a new radioimmunoassay for erythropoietin. Kidney Int 38: 969–975
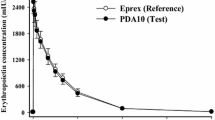
Pérez-Oliva JF, Casanova M, García I et al (2005) Comparison of two recombinant erythropoietin formulations in patients with anemia due to end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis: a parallel, randomized, double blind study. BMC Nephrol 6:5
Engert A (2005) Recombinant human erythropoietin in oncology: current status and further developments. Ann Oncol 16:1584–1595
Egrie JC, Dwyer E, Browne JC et al (2003) Darbepoetin alfa has a longer half-life and greater in vivo potency than recombinant human erythropoietin. Exp Hematol 31:290–299
Sweetman S, Bpharm, MR Pharm S. Martindale A (2004). Guia completa de consulta farmacoterapeútica. Hemoderivados, expansores del plasma y hemostáticos. Epoetinas. 2nd Edición. 1422–1425
Macdougall IC, Gray SJ, Elston O (1999) Pharmacokinetics of novel erythropoiesis stimulating protein compared with epoetin alfa in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2392–2395
Macdougall IC, Roberts DE, Neubert P et al (1989) Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human erythropoietin in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Lancet 25:425–427
Allon M, Kleinman K, Walczyk M et al (2002) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of darbepoetin alfa and epoetin in patients undergoing dialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:546–555
Agoram B, Sutjandra L, Sullivan J et al (2005) Development and evaluation of a population pharmacokinetic (PK) model for darbepoetin alfa in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 77:P76
Heatherington AC, Schuller J, Mercer AJ et al (2001) Pharmacokinetics of novel erythropoiesis stimulating protein (NESP) in cancer patients: preliminary report. Br J Cancer 84[Suppl 1]:11–16
Johnson CA, Wakeen M, Taylor CA et al (1999) Comparison of intraperitoneal and subcutaneous epoetin alfa in peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit Dial Int 19:578–582
Locatelli F, Canaud B, Giacardy F et al (2003) Treatment of anaemia in dialysis patients with unit dosing of darbepoetin alfa at a reduced dose frequency relative to recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEpo). Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:362–369
Littlewood TJ, Bajetta E, Nortier JW et al (2001) Effects of epoetin alfa on hematologic parameters and quality of life in cancer patients receiving nonplatinum chemotherapy: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 19:2865–2874
Vansteenkiste J, Pirker R, Massuti B et al (2002) Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase III trial of darbepoetin alfa in lung cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:1211–1220
Cascinu S, Fedeli A, Del Ferro E et al (1994) Recombinant human erythropoietin treatment in cisplatin-associated anemia: a randomized, double-blind trial with placebo. J Clin Oncol 12: 1058–1062
Österborg A, Boogaerts MA, Cimino R et al (1996) Recombinant human erythropoietin in transfusion-dependent anemic patients with multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma-a randomized multicenter study. Blood 87:2675–2682
Del Mastro L, Venturini M, Lionetto R et al (1997) Randomized phase III trial evaluating the role of erythropoietin in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced anemia. J Clin Oncol 15: 2715–2721
Seidenfeld J, Piper M, Flamm C et al (2001) Epoetin treatment of anemia associated with cancer therapy: a systematic review and metaanalysis of controlled clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1204–1214
Glaspy J, Bukowsky R, Steinberg D et al (1997) Impact of therapy with Epoetin alfa on clinical outcomes in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies during cancer chemotherapy in community oncology practice. J Clin Oncol 15: 1218–1234
Gabrilove JL, Cleeland CS, Livingston RB et al (2001) Clinical evaluation of once-weekly dosing of epoetin alfa in chemotherapy patients: improvements in hemoglobin and quality of life are similar to three-times-weekly dosing. J Clin Oncol 19:2875–2882
Glaspy JA, Jadeja JS, Justice G (2002) Darbepoetin alfa given every 1 or 2 weeks alleviates anaemia associated with cancer chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 87:268–276
Kotasek D, Steger G, Faught W et al (2003) Darbepoetin alfa administered every 3 weeks alleviates anaemia in patients with solid tumours receiving chemotherapy; results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised study. Eur J Cancer 39:2026–2034
Bocciaa R, Malikb IA, Rajac V et al (2006) Darbepoetin alfa administered every three weeks is effective for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced anemia. Oncologist 11:409–417
Hesketh PJ, Arena F, Patel D et al (2004) A randomized controlled trial of darbepoetin alfa administered as a fixed or weight-based dose using a front-loading schedule in patients with anemia who have nonmyeloid malignancies. Cancer 100:859–868
Canon J, Vansteenkiste J, Bodoky G et al (2006) Randomized double-blind, active controlled trial of every-3-week darbepoetin alfa for the treatment to chemotherapy induced anemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:273–284
Rizzo JD, Lichtin AE, Woolf SH et al (2002) Use of epoetin in patients with cancer: evidence-based clinical practice guide-lines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the American Society of Hematology. J Clin Oncol 20: 4083–4107
Thames WA, Smith SL, Scheifele AC et al (2004) Evaluation of the US Oncology Networks recommended guidelines for therapeutic substitution with darbepoetin alfa 200 mcg every 2 weeks in both naïve patients and patients switched from epoetin alfa. Pharmacotherapy 24: 313–323
Goram AL (2006) Every-three-week administration of darbepoetin alfa in women with chemotherapy-associated anemia. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63:1522–1527
Peeters HR, Jongen-Lavrencic M, Bakkar CH et al (1999) Recombinant human erythropoietin improves health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and anaemia of chronic disease; utility measures correlate strongly with disease activity measures. Rheumatol Int 18: 201–206
Wurnig C, Schatz K, Noske H et al (2001) Subcutaneous low-dose epoetin beta for the avoidance of transfusion in patients scheduled for elective surgery not eligible for autologous blood donation. Eur Surg Res 33:303–310
Van Iperen CE, Gaillard CA, Kraaijenhagen RJ et al (2000) Response of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism to recombinant human erythropoietin in intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med 28:2773–2778
Ekblom BT (2000) Blood boosting and sport. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 14:89–98
Bohlius J, Wison J, Seidenfeld J et al (2006) Recombinant human erythropoietins and cancer patients: updated meta-analysis of 57 studies including 9353 patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:708–714
Zhu X, Perazella M (2006) Nonhematologic complications of erythropoietin therapy. Semin Dial 19:279–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurado García, J.M., Torres Sánchez, E., Olmos Hidalgo, D. et al. Erythropoietin pharmacology. Clin Transl Oncol 9, 715–722 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-007-0128-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-007-0128-y