Abstract
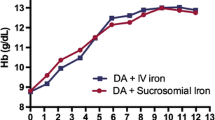
Anemia is a common complication of chemotherapy, and its presence affects the quality of life of cancer patients. Recombinant human erythropitein (rHuEPO) is the mainstay of treatment in patients suffering from chemotherapy-induced anemia. Since rHuEPO is a costly treatment, development of biogeneric products with equivalent efficacy and safety is an essential requirement. This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of a biogeneric rHuEPO (Epolyrec®) with those of the original brand-name product (Eprex®). Seventy-seven cancer patients with hemoglobin levels <11 g/dL, serum ferritin >100 ng/dL, and a life expectancy of at least 6 months were recruited into the trial. Included subjects were randomly assigned to either Epolyrec® (n = 37) or Eprex® (n = 40) at a weekly dose of 100 IU/kg (divided in three doses), for a period of 8 weeks. Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels were significantly increased by week 4 in the Epolyrec® group (p < 0.001), while remained statistically constant from weeks 4 to 8. In the Eprex® group, increases in hemoglobin levels did not reach significance by week 4, but the values at week 8 were significantly increased (p = 0.001). In spite of increase, no significant change in hematocrit values was observed in the Eprex® group. Comparison of the magnitude of changes in hemoglobin concentrations between the study groups revealed a significantly greater increase from baseline to week 4 in the Epolyrec® group (p = 0.02), while the change from week 4 to week 8 was greater in the Eprex® group (p = 0.005). As to hematocrit values, the magnitude of changes at both study periods was comparable between the study groups (p > 0.05). There was no report of severe adverse events in either of the study groups. The present findings support equivalent efficacy and safety of Epolyrec® and Eprex® in the management of chemotherapy-induced anemia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beiraghdar F, Panahi Y, Einollahi B, Torkaman M, Mohammadi R, Marzony ET, Sahebkar A (2012a) Investigation of the efficacy of a biogeneric recombinant human erythropoietin alfa in the correction of post-transplantation anemia: a randomized comparative trial with Eprex. Clin Lab 58(11-12):1179–1185
Beiraghdar F, Panahi Y, Einollahi B, Nemati E, Ghadiani MH, Sahebkar A, Maghsoudi N, Marzony ET (2012b) Investigation of the efficacy of a biogeneric recombinant human erythropoietin alfa in the management of renal anemia in patients on hemodialysis: a multi-center clinical trial. Clin Lab 58(7-8):737–745
Bennett CL, Spiegel DM, Macdougall IC, Norris L, Qureshi ZP, Sartor O, Lai SY, Tallman MS, Raisch DW, Smith SW, Silver S, Murday AS, Armitage JO, Goldsmith D (2012) A review of safety, efficacy, and utilization of erythropoietin, darbepoetin, and peginesatide for patients with cancer or chronic kidney disease: a report from the Southern Network on Adverse Reactions (SONAR). Semin Thromb Hemost 38(8):783–796
Bezwoda WR, Seymour L, Dansey RD (1995) High-dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic rescue as primary treatment for metastatic breast cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 13(10):2483–2489
Bohlius J, Weingart O, Trelle S, Engert A (2006) Cancer-related anemia and recombinant human erythropoietin--an updated overview. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3(3):152–164
Boogaerts M, Coiffier B, Kainz C (2003) Epoetin beta QOL Working Group. Impact of epoetin beta on quality of life in patients with malignant disease. Br J Cancer 88(7):988–995
Cantrell LA, Westin SN, Van Le L (2011) The use of recombinant erythropoietin for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced anemia in patients with ovarian cancer does not affect progression-free or overall survival. Cancer 117(6):1220–1226
Chavez-MacGregor M, Zhao H, Fang S, Srokowski TP, Hortobagyi GN, Giordano SH (2011) Complications associated with erythropoietin-stimulating agents in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-Medicare study. Cancer 117(16):3641–3649
Demetri GD, Kris M, Wade J, Degos L, Cella D (1998) Quality-of-life benefit in chemotherapy patients treated with epoetin alfa is independent of disease response or tumor type: results from a prospective community oncology study. Procrit Study Group. J Clin Oncol 16(10):3412–3425
Durmaz O, Demirkaya M, Sevinir B (2011) Recombinant human erythropoietin β: the effect of weekly dosing on anemia, quality of life, and long-term outcomes in pediatric cancer patients. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 28(6):461–468
Engert A (2000) Recombinant human erythropoietin as an alternative to blood transfusion in cancer-related anaemia. Dis Manag Health Outcome 8:259–272
Glaspy J, Bukowski R, Steinberg D, Taylor C, Tchekmedyian S, Vadhan-Raj S (1997) Impact of therapy with epoetin alfa on clinical outcomes in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies during cancer chemotherapy in community oncology practice. Procrit Study Group. J Clin Oncol 15(3):1218–1234
Kelada O, Marignol L (2014) Erythropoietin-stimulating agents and clinical outcomes in metastatic breast cancer patients with chemotherapy-induced anemia: a closed debate? Tumour Biol 35(6):5095–5100
Ludwig H, Fritz E, Leitgeb C, Krainer M, Kührer I, Sagaster P, Umek H (1993) Erythropoietin treatment for chronic anemia of selected hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Ann Oncol 4(2):161–167
Ludwig H (1999) Epoetin in cancer-related anemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(suppl 2):S 85–S 92
Miller CB, Jones RJ, Piantadosi S, Abeloff MD, Spivak JL (1990) Decreased erythropoietin response in patients with the anemia of cancer. N Engl J Med 322(24):1689–1692
Osterborg A, Brandberg Y, Molostova V, Iosava G, Abdulkadyrov K, Hedenus M, Messinger D, Epoetin Beta Hematology Study Group (2002) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of recombinant human erythropoietin, epoetin Beta, in hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 20(10):2486–2494
Rizzo JD, Lichtin AE, Woolf SH, Seidenfeld J, Bennett CL, Cella D, Djulbegovic B, Goode MJ, Jakubowski AA, Lee SJ, Miller CB, Rarick MU, Regan DH, Browman GP, Gordon MS, American Society of Clinical Oncology, American Society of Hematology (2002) Use of epoetin in patients with cancer: evidence-based clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and the American Society of Hematology. J Clin Oncol 20(19):4083–4107
Sazama K (1990) Reports of 355 transfusion-associated deaths: 1976 through 1985. Transfusion 30(7):583–590
Spivak JL (2005) The anaemia of cancer: death by a thousand cuts. Nat Rev Cancer 5(7):543–555
Thomaidis T, Weinmann A, Sprinzl M, Kanzler S, Raedle J, Ebert M, Schimanski CC, Galle PR, Hoehler T, Moehler M (2014) Upper-GI-Group of AIO (Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie), Germany. Erythropoietin treatment in chemotherapy-induced anemia in previously untreated advanced esophagogastric cancer patients. Int J Clin Oncol 19(2):288–296
Voravud N, Sriuranpong V (2005) Clinical benefits of epoetin alfa (Eprex) 10000 units subcutaneously thrice weekly in Thai cancer patients with anemia receiving chemotherapy. J Med Assoc Thai 88:607–612
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institute of Hematology and Clinical Trial Research Center, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panahi, Y., Saadat, A., Imani, S. et al. Efficacy and safety of a biogeneric recombinant human erythropoietin in the management of chemotherapy-induced anemia: a randomized double-blind active-comparator trial. Comp Clin Pathol 25, 155–160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-015-2158-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-015-2158-0