Abstract
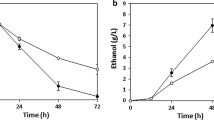
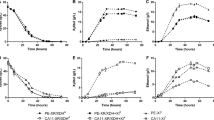
The absence of pentose-utilizing enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an obstacle for efficiently converting lignocellulosic materials to ethanol. In the present study, the genes coding xylose reductase (XYL1) and xylitol dehydrogenase (XYL2) from Pichia stipitis were successfully engineered into S. cerevisae. As compared to the control transformant, engineering of XYL1 and XYL2 into yeasts significantly increased the microbial biomass (8.1 vs. 3.4 g/L), xylose consumption rate (0.15 vs. 0.02 g/h) and ethanol yield (6.8 vs. 3.5 g/L) after 72 h fermentation using a xylose-based medium. Interestingly, engineering of XYL1 and XYL2 into yeasts also elevated the ethanol yield from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate (SUBH). This study not only provides an effective approach to increase the xylose utilization by yeasts, but the results also suggest that production of ethanol by this recombinant yeasts using unconventional nutrient sources, such as components in SUBH deserves further attention in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe S, Saleh AA, Pack SP, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein engineered NADP+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 130:316–319
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II: inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresour Technol 74:25–33
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Galbe M, Gorwa-Grauslund G, Liden G, Zacchi G (2006) Bio-ethanol. the fuel of tomorrow from the residues of today. Trends Biotechnol 24:549–556
McMillan JD, Boynton BL (1994) Arabinose utilization by xylose-fermenting yeasts and fungi. Appl Biochem Biotehcnol 45–46:569–584
Smiley KL, Bolen PL (1982) Demonstration of d-xylose reductase and d-xylitol dehydrogenase in Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol Lett 4:607–610
Aristidou A, Penttilä M (2000) Metabolic engineering applications to renewable resource utilization. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:187–198
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Wahlbom CF, Gardonyi M, Van Zyl WH, Cordero Otero RR, Jönsson LJ (2001) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for xylose utilization. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 73:53–84
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhumaa K, Jeppsson M, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Metabolic engineering for pentose utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:147–177
Amore R, Kötter P, Küster C, Ciriacy M, Hollenberg CP (1991) Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the NAD(P)H-dependent xylose reductase-encoding gene (XYL1) from the xylose-assimilating yeast Pichia stipitis. Gene 109:89–97
Shi NQ, Prahl K, Hendrick J, Cruz J, Lu P, Cho JY, Jones S, Jeffries T (2000) Characterization and complementation of a Pichia stipitis mutant unable to grow on d-xylose or l-arabinose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84–86:201–216
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Watanabe S, Kodaki T, Makino K (2005) Complete reversal of coenzyme specificity of xylitol dehydrogenase and increase of thermostability by the introduction of structural zinc. J Biol Chem 280:10340–10349
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Martin C, Alriksson B, Sjöde A, Nilvebrant NO, Jönsson LJ (2007) Dilute-sulphuric acid prehydrolysis of agricultural and agro-industrial residues for ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137–140:339–352
Alriksson B, Rose SH, Van Zyl WH, Sjöde A, Nilvebrant NO, Jönsson LJ (2009) Cellulase production from spent lignocellulose hydrolysates by recombinant Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2366–2374
Lang X, Macdonald DG, Hill GA (2001) Recycle bioreactor for bioethanol production from wheat starchII. Fermentation and economics. Energy Sour 23:427–436
Demirbas A (2005) Bioethanol from cellulosic materials: a renewable motor fuel from biomass. Energy Sour 27:327–337
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2009) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Roca C, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2003) Metabolic engineering of ammonium assimilation in xylose fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves ethanol production. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4732–4736
Pitkänen JP, Aristidou A, Salusjärvi L, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2003) Metabolic flux analysis of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using continuous culture. Metab Eng 5:16–31
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MS, de Laat WT, den Ridder JJ, Op den Camp HJ, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylsoe isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 4:69–78
Zaldivar J, Borges A, Johansson B, Smits HP, Villas-Boas SG, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2002) Fermentation performance and intracellular metabolite patterns in laboratory and industrial xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:436–442
Sellick CA, Campbell RN, Reece RJ (2008) Galactose metabolism in yeast-structure and regulation of the leloir pathway enzymes and the genes encoding them. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 269:111–150
Bruinenberg PM, De Bot PHM, Van Dijken JP, Scheffers TW (1984) NADH-linked aldose reductase: the key to anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:256–260
Bruinenberg PM, De Bot PHM, Van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1983) The role of redox balances in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:287–292
Jeffries TW, Jin YS (2004) Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:495–509
Cornish-Bowden A, Hofmeyr JHS, Cardenas ML (1995) Strategies for manipulating metabolic fluxes in biotechnology. Bioorg Chem 23:439–449
Eliasson A, Hofmeyr JHS, Pedler S, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2001) The xylose reductase/xylitol dehydrogenase/xylulokinase ratio affects product formation in recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:288–297
De Robichion-Szulmajster H (1958) Induction of enzymes of galactose pathway in mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 127:19–28
Bhat PJ, Murthy TVS (2001) Transcriptional control of the GAL/MEL regulation of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mechanism of galactose mediated signal transduction. Mol Microbiol 40:1059–1066
Acknowledgments
This work was granted by Prominent Youthfund Project of Sichuan Agricultural University with grant. No. 00924201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, H., Jiayi, C. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for increased bioconversion of lignocellulose to ethanol. Indian J Microbiol 52, 442–448 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-012-0259-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-012-0259-x