Abstract
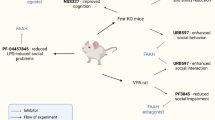
The purpose of this review is to summarize the current knowledge regarding the reciprocal associations between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and immune-inflammatory pathways and how these links may explain the involvement of this neurotrophin in the immune pathophysiology of mood disorders and schizophrenia. Toward this end, we delineated the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network centered around BDNF and searched PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Science Direct for papers dealing with the involvement of BDNF in the major psychosis, neurodevelopment, neuronal functions, and immune-inflammatory and related pathways. The PPI network was built based on the significant interactions of BDNF with neurotrophic (NTRK2, NTF4, and NGFR), immune (cytokines, STAT3, TRAF6), and cell–cell junction (CTNNB, CDH1) DEPs (differentially expressed proteins). Enrichment analysis shows that the most significant terms associated with this PPI network are the tyrosine kinase receptor (TRKR) and Src homology region two domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP2) pathways, tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathways, positive regulation of kinase and transferase activity, cytokine signaling, and negative regulation of the immune response. The participation of BDNF in the immune response and its interactions with neuroprotective and cell–cell adhesion DEPs is probably a conserved regulatory process which protects against the many detrimental effects of immune activation and hyperinflammation including neurotoxicity. Lowered BDNF levels in mood disorders and schizophrenia (a) are associated with disruptions in neurotrophic signaling and activated immune-inflammatory pathways leading to neurotoxicity and (b) may interact with the reduced expression of other DEPs (CTNNB1, CDH1, or DISC1) leading to multiple aberrations in synapse and axonal functions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BD:
-
Bipolar disorder
- CDH:
-
Cadherin gene/protein
- CDC:
-
Cell division cycle gene/protein
- ChIP analysis:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis
- CIRS:
-
Compensatory immune regulatory system
- CPE:
-
Carboxypeptidase E
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CRK:
-
CRK proto-oncogene
- CREB:
-
CAMP response element-binding protein
- CTNNB:
-
Catenin beta protein
- CTBBB1:
-
Catenin beta 1 gene
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- DISC1:
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 protein
- DEPs:
-
Differentially expressed proteins
- FEP:
-
First-episode psychosis
- FES:
-
First-episode schizophrenia
- GABA:
-
Gamma aminobutyric acid
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- GSK:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase
- GRB2:
-
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HMGB1:
-
High mobility group box 1 DNA-binding nuclear protein
- HRAS:
-
GTPase HRas
- Hp:
-
Haptoglobin
- hESC-NSCs:
-
Human embryonic spinal cord NSCs
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IRS:
-
Inflammatory response system
- JAK-STAT:
-
Janus kinases/signal transducer and activator of transcription
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- LIMK1:
-
LIM domain kinase 1
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LTD:
-
Long-term depression
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- MAPK:
-
Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MDD:
-
Major depressive disorder
- MECP2:
-
Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2
- MFB:
-
Medial forebrain bundle
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- NMDAR:
-
N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor
- NGF:
-
Beta-nerve growth factor
- NGFR:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16
- NPC:
-
Intracellular cholesterol transporter
- NSC:
-
Neural stem cells
- NTF:
-
Neurotrophin
- NTRK1:
-
High affinity nerve growth factor receptor
- NTRK2:
-
BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- PIK3R:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase receptor
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- PPI:
-
Protein-protein interaction
- qRT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative reverse transcription
- RAGE:
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- RIP2:
-
Serine/threonine protein kinase 2
- SHP2:
-
Two domain-containing phosphatase-2
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- STRING:
-
Significant database-annotated interactions
- SORT:
-
Sortilin
- Th:
-
T helper cells
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- TNFR:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor
- TP53:
-
Tumor protein p53
- TRAF6:
-
Tumor necrosis factor 6 receptor factor
- T reg:
-
T regulatory cells
- TRK:
-
Tropomyosin receptor kinase
- TRKR:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptor
- TRYCAT:
-
Tryptophan catabolite
References
Maes M, Smith R, Scharpe S (1995) The monocyte-T-lymphocyte hypothesis of major depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20(2):111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4530(94)00066-j
Smith RS, Maes M (1995) The macrophage-T-lymphocyte theory of schizophrenia: additional evidence. Med Hypotheses 45(2):135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-9877(95)90062-4
Maes M, Carvalho AF (2018) The compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in depression and bipolar disorder. Mol Neurobiol 55(12):8885–8903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1016-x
Roomruangwong C, Noto C, Kanchanatawan B, Anderson G, Kubera M, Carvalho AF, Maes M (2020) The role of aberrations in the immune-inflammatory response system (IRS) and the compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in different phenotypes of schizophrenia: the IRS-CIRS theory of schizophrenia. Mol Neurobiol 57(2):778–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01737-z
Maes M, Vojdani A, Sirivichayakul S, Barbosa DS, Kanchanatawan B (2021) Inflammatory and oxidative pathways are new drug targets in multiple episode schizophrenia and leaky gut, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and c1q immune complexes are additional drug targets in first episode schizophrenia. Mol Neurobiol 58(7):3319–3334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02343-8
Simeonova D, Stoyanov D, Leunis JC, Murdjeva M, Maes M (2021) Construction of a nitro-oxidative stress-driven, mechanistic model of mood disorders: a nomothetic network approach. Nitric Oxide 106:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.11.001
Maes M, Berk M, Goehler L, Song C, Anderson G, Galecki P, Leonard B (2012) Depression and sickness behavior are Janus-faced responses to shared inflammatory pathways. BMC Med 10:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-10-66
Lu B, Nagappan G, Lu Y (2014) BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. Handb Exp Pharmacol 220:223–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45106-5_9
Bjorkholm C, Monteggia LM (2016) BDNF - a key transducer of antidepressant effects. Neuropharmacology 102:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.10.034
Kowianski P, Lietzau G, Czuba E, Waskow M, Steliga A, Morys J (2018) BDNF: a key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(3):579–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0510-4
Lima Giacobbo B, Doorduin J, Klein HC, Dierckx R, Bromberg E, de Vries EFJ (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: focus on neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 56(5):3295–3312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1283-6
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB, Bekinschtein P (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci 13:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00363
Wu SY, Pan BS, Tsai SF, Chiang YT, Huang BM, Mo FE, Kuo YM (2020) BDNF reverses aging-related microglial activation. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01887-1
Colucci-D’Amato L, Cimaglia G (2020) Ruta graveolens as a potential source of neuroactive compounds to promote and restore neural functions. J Tradit Complement Med 10(3):309–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.05.002
Lin CC, Huang TL (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mental disorders. Biomed J 43(2):134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2020.01.001
Pruunsild P, Kazantseva A, Aid T, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Dissecting the human BDNF locus: bidirectional transcription, complex splicing, and multiple promoters. Genomics 90(3):397–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.05.004
Colucci-D'Amato L, Speranza L, Volpicelli F (2020) Neurotrophic factor BDNF, physiological functions and therapeutic potential in depression, neurodegeneration and brain cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21 (20). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207777
Friedman WJ (2010) Proneurotrophins, seizures, and neuronal apoptosis. Neuroscientist 16(3):244–252. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858409349903
Minichiello L (2009) TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(12):850–860. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2738
Yang J, Harte-Hargrove LC, Siao CJ, Marinic T, Clarke R, Ma Q, Jing D, Lafrancois JJ et al (2014) proBDNF negatively regulates neuronal remodeling, synaptic transmission, and synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. Cell Rep 7(3):796–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.040
Volosin M, Song W, Almeida RD, Kaplan DR, Hempstead BL, Friedman WJ (2006) Interaction of survival and death signaling in basal forebrain neurons: roles of neurotrophins and proneurotrophins. J Neurosci 26(29):7756–7766. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1560-06.2006
Haapasalo A, Sipola I, Larsson K, Akerman KE, Stoilov P, Stamm S, Wong G, Castren E (2002) Regulation of TRKB surface expression by brain-derived neurotrophic factor and truncated TRKB isoforms. J Biol Chem 277(45):43160–43167. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205202200
Chen ZY, Patel PD, Sant G, Meng CX, Teng KK, Hempstead BL, Lee FS (2004) Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type BDNF in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. J Neurosci 24(18):4401–4411. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0348-04.2004
Lohia R, Salari R, Brannigan G (2019) Sequence specificity despite intrinsic disorder: how a disease-associated Val/Met polymorphism rearranges tertiary interactions in a long disordered protein. PLoS Comput Biol 15(10):e1007390. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007390
Hempstead BL (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: three ligands, many actions. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc 126:9–19
Takei N, Inamura N, Kawamura M, Namba H, Hara K, Yonezawa K, Nawa H (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent local activation of translation machinery and protein synthesis in neuronal dendrites. J Neurosci 24(44):9760–9769. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1427-04.2004
Marini AM, Jiang X, Wu X, Tian F, Zhu D, Okagaki P, Lipsky RH (2004) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and survival: from genes to phenotype. Restor Neurol Neurosci 22(2):121–130
Messaoudi E, Ying SW, Kanhema T, Croll SD, Bramham CR (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor triggers transcription-dependent, late phase long-term potentiation in vivo. J Neurosci 22(17):7453–7461
Bernd P (2008) The role of neurotrophins during early development. Gene Expr 14(4):241–250. https://doi.org/10.3727/105221608786883799
Mou K, Hunsberger CL, Cleary JM, Davis RL (1997) Synergistic effects of BDNF and NT-3 on postnatal spiral ganglion neurons. J Comp Neurol 386(4):529–539
Paris AJ, Hayer KE, Oved JH, Avgousti DC, Toulmin SA, Zepp JA, Zacharias WJ, Katzen JB et al (2020) STAT3-BDNF-TrkB signalling promotes alveolar epithelial regeneration after lung injury. Nat Cell Biol 22(10):1197–1210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-020-0569-x
Jansen P, Giehl K, Nyengaard JR, Teng K, Lioubinski O, Sjoegaard SS, Breiderhoff T, Gotthardt M et al (2007) Roles for the pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin in neuronal development, aging and brain injury. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1449–1457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2000
Aid T, Kazantseva A, Piirsoo M, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited. J Neurosci Res 85(3):525–535. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21139
Antonakopoulos N, Iliodromiti Z, Mastorakos G, Iavazzo C, Valsamakis G, Salakos N, Papageorghiou A, Margeli A et al (2018) Association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in 2(nd) trimester amniotic fluid and fetal development. Mediators Inflamm 2018:8476217. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8476217
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Sato W, Fukuda J, Kumagai J, Tanaka T (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes implantation and subsequent placental development by stimulating trophoblast cell growth and survival. Endocrinology 150(8):3774–3782. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-0213
Kawamura K, Kawamura N, Fukuda J, Kumagai J, Hsueh AJ, Tanaka T (2007) Regulation of preimplantation embryo development by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev Biol 311(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.08.026
Klein R, Parada LF, Coulier F, Barbacid M (1989) trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J 8(12):3701–3709
Barbacid M (1994) The Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol 25(11):1386–1403. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.480251107
Deinhardt K, Chao MV (2014) Shaping neurons: long and short range effects of mature and proBDNF signalling upon neuronal structure. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt C:603–609. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.054
Anastasia A, Deinhardt K, Chao MV, Will NE, Irmady K, Lee FS, Hempstead BL, Bracken C (2013) Val66Met polymorphism of BDNF alters prodomain structure to induce neuronal growth cone retraction. Nat Commun 4:2490. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3490
Teng HK, Teng KK, Lee R, Wright S, Tevar S, Almeida RD, Kermani P, Torkin R et al (2005) ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci 25(22):5455–5463. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5123-04.2005
Reichardt LF (2006) Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361(1473):1545–1564. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1894
Gonzalez A, Moya-Alvarado G, Gonzalez-Billaut C, Bronfman FC (2016) Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating neuronal growth by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 73(10):612–628. https://doi.org/10.1002/cm.21312
Sasi M, Vignoli B, Canossa M, Blum R (2017) Neurobiology of local and intercellular BDNF signaling. Pflugers Arch 469(5–6):593–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-1964-4
Foltran RB, Diaz SL (2016) BDNF isoforms: a round trip ticket between neurogenesis and serotonin? J Neurochem 138(2):204–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13658
Zheng LR, Zhu XQ, Huang XM, Gu Q, Xie DH (2013) Morphological study on early development of brain derived neurophic factor-positive neurons in the frontal lobe of human fetus. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 35(3):260–264. https://doi.org/10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2013.03.004
Yao L, Zhang D, Bernd P (1994) The onset of neurotrophin and trk mRNA expression in early embryonic tissues of the quail. Dev Biol 165(2):727–730. https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1994.1288
Jungbluth S, Koentges G, Lumsden A (1997) Coordination of early neural tube development by BDNF/trkB. Development 124(10):1877–1885
Zhang D, Yao L, Bernd P (1996) Expression of neurotrophin trk and p75 receptors in quail embryos undergoing gastrulation and neurulation. Dev Dyn 205(2):150–161. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199602)205:2%3c150::AID-AJA6%3e3.0.CO;2-H
Li H, Lin LY, Zhang Y, Lim Y, Rahman M, Beck A, Al-Hawwas M, Feng S et al (2020) Pro-BDNF knockout causes abnormal motor behaviours and early death in mice. Neuroscience 438:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.05.007
Conover JC, Erickson JT, Katz DM, Bianchi LM, Poueymirou WT, McClain J, Pan L, Helgren M et al (1995) Neuronal deficits, not involving motor neurons, in mice lacking BDNF and/or NT4. Nature 375(6528):235–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/375235a0
Johnson EM, Craig ET, Yeh HH (2007) TrkB is necessary for pruning at the climbing fibre-Purkinje cell synapse in the developing murine cerebellum. J Physiol 582(Pt 2):629–646. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2007.133561
Maisonpierre PC, Belluscio L, Friedman B, Alderson RF, Wiegand SJ, Furth ME, Lindsay RM, Yancopoulos GD (1990) NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron 5(4):501–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(90)90089-x
Almeida LE, Roby CD, Krueger BK (2014) Increased BDNF expression in fetal brain in the valproic acid model of autism. Mol Cell Neurosci 59:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2014.01.007
Murray PS, Holmes PV (2011) An overview of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and implications for excitotoxic vulnerability in the hippocampus. Int J Pept 2011:654085. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/654085
Deuschle M, Hendlmeier F, Witt S, Rietschel M, Gilles M, Sanchez-Guijo A, Fananas L, Hentze S et al (2018) Cortisol, cortisone, and BDNF in amniotic fluid in the second trimester of pregnancy: effect of early life and current maternal stress and socioeconomic status. Dev Psychopathol 30(3):971–980. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579418000147
Kodomari I, Wada E, Nakamura S, Wada K (2009) Maternal supply of BDNF to mouse fetal brain through the placenta. Neurochem Int 54(2):95–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2008.11.005
DM Halepoto S Bashir L ALA 2014 Possible role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in autism spectrum disorder: current status J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 24 4 274 278 04.2014/JCPSP.274278
Kimiwada T, Sakurai M, Ohashi H, Aoki S, Tominaga T, Wada K (2009) Clock genes regulate neurogenic transcription factors, including NeuroD1, and the neuronal differentiation of adult neural stem/progenitor cells. Neurochem Int 54(5–6):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.005
Ohmiya M, Shudai T, Nitta A, Nomoto H, Furukawa Y, Furukawa S (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor alters cell migration of particular progenitors in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 317(1):21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(01)02412-0
Buchman VL, Davies AM (1993) Different neurotrophins are expressed and act in a developmental sequence to promote the survival of embryonic sensory neurons. Development 118(3):989–1001
Fukumitsu H, Ohtsuka M, Murai R, Nakamura H, Itoh K, Furukawa S (2006) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor participates in determination of neuronal laminar fate in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 26(51):13218–13230. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4251-06.2006
Bartkowska K, Paquin A, Gauthier AS, Kaplan DR, Miller FD (2007) Trk signaling regulates neural precursor cell proliferation and differentiation during cortical development. Development 134(24):4369–4380. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.008227
Kertes DA, Bhatt SS, Kamin HS, Hughes DA, Rodney NC, Mulligan CJ (2017) BNDF methylation in mothers and newborns is associated with maternal exposure to war trauma. Clin Epigenetics 9:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-017-0367-x
Braithwaite EC, Kundakovic M, Ramchandani PG, Murphy SE, Champagne FA (2015) Maternal prenatal depressive symptoms predict infant NR3C1 1F and BDNF IV DNA methylation. Epigenetics 10(5):408–417. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2015.1039221
Gilmore JH, Jarskog LF, Vadlamudi S (2003) Maternal infection regulates BDNF and NGF expression in fetal and neonatal brain and maternal-fetal unit of the rat. J Neuroimmunol 138(1–2):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5728(03)00095-x
Wang JM, Pei LX, Zhang YY, Cheng YX, Niu CL, Cui Y, Feng WS, Wang GF (2018) Ethanol extract of Rehmannia glutinosa exerts antidepressant-like effects on a rat chronic unpredictable mild stress model by involving monoamines and BDNF. Metab Brain Dis 33(3):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0202-x
Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R, Post RM (1995) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 15(3 Pt 1):1768–1777
Buchmann AF, Hellweg R, Rietschel M, Treutlein J, Witt SH, Zimmermann US, Schmidt MH, Esser G et al (2013) BDNF Val 66 Met and 5-HTTLPR genotype moderate the impact of early psychosocial adversity on plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and depressive symptoms: a prospective study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23(8):902–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.09.003
Kundakovic M, Gudsnuk K, Herbstman JB, Tang D, Perera FP, Champagne FA (2015) DNA methylation of BDNF as a biomarker of early-life adversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(22):6807–6813. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408355111
Branchi I (2009) The mouse communal nest: investigating the epigenetic influences of the early social environment on brain and behavior development. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33(4):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.03.011
Lippmann M, Bress A, Nemeroff CB, Plotsky PM, Monteggia LM (2007) Long-term behavioural and molecular alterations associated with maternal separation in rats. Eur J Neurosci 25(10):3091–3098. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05522.x
Mateos-Aparicio P, Rodriguez-Moreno A (2019) The impact of studying brain plasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 13:66. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00066
Kee N, Teixeira CM, Wang AH, Frankland PW (2007) Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 10(3):355–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1847
Castren E, Pitkanen M, Sirvio J, Parsadanian A, Lindholm D, Thoenen H, Riekkinen PJ (1993) The induction of LTP increases BDNF and NGF mRNA but decreases NT-3 mRNA in the dentate gyrus. NeuroReport 4(7):895–898. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199307000-00014
Patterson SL, Grover LM, Schwartzkroin PA, Bothwell M (1992) Neurotrophin expression in rat hippocampal slices: a stimulus paradigm inducing LTP in CA1 evokes increases in BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs. Neuron 9(6):1081–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(92)90067-n
Figurov A, Pozzo-Miller LD, Olafsson P, Wang T, Lu B (1996) Regulation of synaptic responses to high-frequency stimulation and LTP by neurotrophins in the hippocampus. Nature 381(6584):706–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/381706a0
Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T (1995) Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(19):8856–8860. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.19.8856
Patterson SL, Abel T, Deuel TA, Martin KC, Rose JC, Kandel ER (1996) Recombinant BDNF rescues deficits in basal synaptic transmission and hippocampal LTP in BDNF knockout mice. Neuron 16(6):1137–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80140-3
Baj G, Pinhero V, Vaghi V, Tongiorgi E (2016) Signaling pathways controlling activity-dependent local translation of BDNF and their localization in dendritic arbors. J Cell Sci 129(14):2852–2864. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.177626
Barbacid M (1993) Nerve growth factor: a tale of two receptors. Oncogene 8(8):2033–2042
Dinsmore CJ, Soriano P (2018) MAPK and PI3K signaling: at the crossroads of neural crest development. Dev Biol 444(Suppl 1):S79–S97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.02.003
Chapleau CA, Pozzo-Miller L (2012) Divergent roles of p75NTR and Trk receptors in BDNF’s effects on dendritic spine density and morphology. Neural Plast 2012:578057. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/578057
Einat H, Yuan P, Gould TD, Li J, Du J, Zhang L, Manji HK, Chen G (2003) The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation. J Neurosci 23(19):7311–7316
Peng CH, Chiou SH, Chen SJ, Chou YC, Ku HH, Cheng CK, Yen CJ, Tsai TH et al (2008) Neuroprotection by Imipramine against lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in hippocampus-derived neural stem cells mediated by activation of BDNF and the MAPK pathway. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18(2):128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.05.002
Kuzniewska B, Rejmak E, Malik AR, Jaworski J, Kaczmarek L, Kalita K (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in neurons via the serum response factor/c-Fos pathway. Mol Cell Biol 33(11):2149–2162. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00008-13
Bramham CR, Wells DG (2007) Dendritic mRNA: transport, translation and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(10):776–789. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2150
Van Horck FP, Holt CE (2008) A cytoskeletal platform for local translation in axons. Sci Signal 1(8):pe11. https://doi.org/10.1126/stke.18pe11
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439(7074):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04367
Troca-Marin JA, Alves-Sampaio A, Tejedor FJ, Montesinos ML (2010) Local translation of dendritic RhoA revealed by an improved synaptoneurosome preparation. Mol Cell Neurosci 43(3):308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.12.004
Messaoudi E, Kanhema T, Soule J, Tiron A, Dagyte G, da Silva B, Bramham CR (2007) Sustained Arc/Arg3.1 synthesis controls long-term potentiation consolidation through regulation of local actin polymerization in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci 27(39):10445–10455. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2883-07.2007
Gooney M, Messaoudi E, Maher FO, Bramham CR, Lynch MA (2004) BDNF-induced LTP in dentate gyrus is impaired with age: analysis of changes in cell signaling events. Neurobiol Aging 25(10):1323–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.01.003
Panja D, Bramham CR (2014) BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: a synthesis and breakdown. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt C:664–676. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024
Lessmann V, Heumann R (1998) Modulation of unitary glutamatergic synapses by neurotrophin-4/5 or brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal microcultures: presynaptic enhancement depends on pre-established paired-pulse facilitation. Neuroscience 86(2):399–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00035-9
Stoop R, Poo MM (1996) Synaptic modulation by neurotrophic factors: differential and synergistic effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and ciliary neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci 16(10):3256–3264
Vicario-Abejon C, Collin C, McKay RD, Segal M (1998) Neurotrophins induce formation of functional excitatory and inhibitory synapses between cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 18(18):7256–7271
Takei N, Numakawa T, Kozaki S, Sakai N, Endo Y, Takahashi M, Hatanaka H (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces rapid and transient release of glutamate through the non-exocytotic pathway from cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 273(42):27620–27624. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.42.27620
Levine ES, Crozier RA, Black IB, Plummer MR (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates hippocampal synaptic transmission by increasing N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(17):10235–10239. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.17.10235
Lau CG, Takeuchi K, Rodenas-Ruano A, Takayasu Y, Murphy J, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2009) Regulation of NMDA receptor Ca2+ signalling and synaptic plasticity. Biochem Soc Trans 37(Pt 6):1369–1374. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0371369
Yamada MK, Nakanishi K, Ohba S, Nakamura T, Ikegaya Y, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes the maturation of GABAergic mechanisms in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 22(17):7580–7585
Rutherford LC, DeWan A, Lauer HM, Turrigiano GG (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates the activity-dependent regulation of inhibition in neocortical cultures. J Neurosci 17(12):4527–4535
Sairanen M, Lucas G, Ernfors P, Castren M, Castren E (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 25(5):1089–1094. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3741-04.2005
Scharfman H, Goodman J, Macleod A, Phani S, Antonelli C, Croll S (2005) Increased neurogenesis and the ectopic granule cells after intrahippocampal BDNF infusion in adult rats. Exp Neurol 192(2):348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.11.016
Yang T, Nie Z, Shu H, Kuang Y, Chen X, Cheng J, Yu S, Liu H (2020) The role of BDNF on neural plasticity in depression. Front Cell Neurosci 14:82. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00082
Kuipers SD, Trentani A, Tiron A, Mao X, Kuhl D, Bramham CR (2016) BDNF-induced LTP is associated with rapid Arc/Arg3.1-dependent enhancement in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Sci Rep 6:21222. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21222
Leal G, Bramham CR, Duarte CB (2017) BDNF and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Vitam Horm 104:153–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2016.10.004
Bamji SX, Rico B, Kimes N, Reichardt LF (2006) BDNF mobilizes synaptic vesicles and enhances synapse formation by disrupting cadherin-beta-catenin interactions. J Cell Biol 174(2):289–299. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200601087
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K (2012) The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J 31(12):2714–2736. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.150
Seong E, Yuan L, Arikkath J (2015) Cadherins and catenins in dendrite and synapse morphogenesis. Cell Adh Migr 9(3):202–213. https://doi.org/10.4161/19336918.2014.994919
Arikkath J, Reichardt LF (2008) Cadherins and catenins at synapses: roles in synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 31(9):487–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2008.07.001
Zhang L, Yang X, Yang S, Zhang J (2011) The Wnt /beta-catenin signaling pathway in the adult neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 33(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.7483.x
Wuhanqimuge AM (2013) Lysophosphatidylcholine potentiates BDNF-induced TrkB phosphorylation and downstream signals in cerebellar granule neurons. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77(12):2510–2513. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.130622
Shimizu T, Kagawa T, Inoue T, Nonaka A, Takada S, Aburatani H, Taga T (2008) Stabilized beta-catenin functions through TCF/LEF proteins and the Notch/RBP-Jkappa complex to promote proliferation and suppress differentiation of neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Biol 28(24):7427–7441. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01962-07
Maguschak KA, Ressler KJ (2008) Beta-catenin is required for memory consolidation. Nat Neurosci 11(11):1319–1326. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2198
Umschweif G, Alexandrovich AG, Trembovler V, Horowitz M, Shohami E (2013) The role and dynamics of beta-catenin in precondition induced neuroprotection after traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 8(10):e76129. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076129
Chen BY, Wang X, Wang ZY, Wang YZ, Chen LW, Luo ZJ (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, possibly by triggering the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res 91(1):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23138
Liyanli WM, Yang J, Jin R, Ren Z, Gao W, Li X, Wang T, Luo T et al (2016) The relationship between BDNF and the Wnt signaling pathway in the growth of human neural stem. Neurology 86(16 Supplement):5148
Yang JW, Ru J, Ma W, Gao Y, Liang Z, Liu J, Guo JH, Li LY (2015) BDNF promotes the growth of human neurons through crosstalk with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway via GSK-3beta. Neuropeptides 54:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2015.08.005
Zhang F, Liu CL, Tong MM, Zhao Z, Chen SQ (2019) Both Wnt/beta-catenin and ERK5 signaling pathways are involved in BDNF-induced differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett 708:134345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134345
Zhang W, Shi Y, Peng Y, Zhong L, Zhu S, Zhang W, Tang SJ (2018) Neuron activity-induced Wnt signaling up-regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the pain neural circuit. J Biol Chem 293(40):15641–15651. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002840
Gomes C, Smith SC, Youssef MN, Zheng JJ, Hagg T, Hetman M (2011) RNA polymerase 1-driven transcription as a mediator of BDNF-induced neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem 286(6):4357–4363. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.170134
Li XT, Liang Z, Wang TT, Yang JW, Ma W, Deng SK, Wang XB, Dai YF et al (2017) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes growth of neurons and neural stem cells possibly by triggering the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/ AKT/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16(7):828–836. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527316666170518170422
Cohen-Cory S, Kidane AH, Shirkey NJ, Marshak S (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the development of structural neuronal connectivity. Dev Neurobiol 70(5):271–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.20774
Lin G, Bella AJ, Lue TF, Lin CS (2006) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) acts primarily via the JAK/STAT pathway to promote neurite growth in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat: part 2. J Sex Med 3(5):821–829. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00292.x
Lin G, Zhang H, Sun F, Lu Z, Reed-Maldonado A, Lee YC, Wang G, Banie L et al (2016) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes nerve regeneration by activating the JAK/STAT pathway in Schwann cells. Transl Androl Urol 5(2):167–175. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2016.02.03
Hixson KM, Cogswell M, Brooks-Kayal AR, Russek SJ (2019) Evidence for a non-canonical JAK/STAT signaling pathway in the synthesis of the brain’s major ion channels and neurotransmitter receptors. BMC Genomics 20(1):677. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6033-2
Yoshimatsu T, Kawaguchi D, Oishi K, Takeda K, Akira S, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2006) Non-cell-autonomous action of STAT3 in maintenance of neural precursor cells in the mouse neocortex. Development 133(13):2553–2563. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02419
Oatley JM, Kaucher AV, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL (2010) Regulation of mouse spermatogonial stem cell differentiation by STAT3 signaling. Biol Reprod 83(3):427–433. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.109.083352
Yadav A, Kalita A, Dhillon S, Banerjee K (2005) JAK/STAT3 pathway is involved in survival of neurons in response to insulin-like growth factor and negatively regulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. J Biol Chem 280(36):31830–31840. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M501316200
Selvaraj BT, Frank N, Bender FL, Asan E, Sendtner M (2012) Local axonal function of STAT3 rescues axon degeneration in the pmn model of motoneuron disease. J Cell Biol 199(3):437–451. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201203109
Quarta S, Baeumer BE, Scherbakov N, Andratsch M, Rose-John S, Dechant G, Bandtlow CE, Kress M (2014) Peripheral nerve regeneration and NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth of adult sensory neurons converge on STAT3 phosphorylation downstream of neuropoietic cytokine receptor gp130. J Neurosci 34(39):13222–13233. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1209-13.2014
Bouret SG, Bates SH, Chen S, Myers MG Jr, Simerly RB (2012) Distinct roles for specific leptin receptor signals in the development of hypothalamic feeding circuits. J Neurosci 32(4):1244–1252. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2277-11.2012
Tang QP, Shen Q, Wu LX, Feng XL, Liu H, Wu B, Huang XS, Wang GQ et al (2016) STAT3 signal that mediates the neural plasticity is involved in willed-movement training in focal ischemic rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 17(7):493–502. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500297
Radin DP, Patel P (2017) BDNF: an oncogene or tumor suppressor? Anticancer Res 37(8):3983–3990. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11783
Batista CM, Mariano ED, Barbosa BJ, Morgalla M, Marie SK, Teixeira MJ, Lepski G (2014) Adult neurogenesis and glial oncogenesis: when the process fails. Biomed Res Int 2014:438639. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/438639
Li Z, Zhang Y, Tong Y, Tong J, Thiele CJ (2015) Trk inhibitor attenuates the BDNF/TrkB-induced protection of neuroblastoma cells from etoposide in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 16(3):477–483. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2015.1016659
Lv X, Gu C, Guo S (2020) Activation of BDNF-AS/ADAR/p53 positive feedback loop inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation. Neurochem Res 45(2):508–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02943-w
Lai PC, Chiu TH, Huang YT (2010) Overexpression of BDNF and TrkB in human bladder cancer specimens. Oncol Rep 24(5):1265–1270. https://doi.org/10.3892/or_00000981
Vanhecke E, Adriaenssens E, Verbeke S, Meignan S, Germain E, Berteaux N, Nurcombe V, Le Bourhis X et al (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-4/5 are expressed in breast cancer and can be targeted to inhibit tumor cell survival. Clin Cancer Res 17(7):1741–1752. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1890
Yin B, Ma ZY, Zhou ZW, Gao WC, Du ZG, Zhao ZH, Li QQ (2015) The TrkB+ cancer stem cells contribute to post-chemotherapy recurrence of triple-negative breast cancers in an orthotopic mouse model. Oncogene 34(6):761–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.8
Au CW, Siu MK, Liao X, Wong ES, Ngan HY, Tam KF, Chan DC, Chan QK et al (2009) Tyrosine kinase B receptor and BDNF expression in ovarian cancers - effect on cell migration, angiogenesis and clinical outcome. Cancer Lett 281(2):151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.025
Lam CT, Yang ZF, Lau CK, Tam KH, Fan ST, Poon RT (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes tumorigenesis via induction of neovascularization: implication in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17(10):3123–3133. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2802
Guo D, Hou X, Zhang H, Sun W, Zhu L, Liang J, Jiang X (2011) More expressions of BDNF and TrkB in multiple hepatocellular carcinoma and anti-BDNF or K252a induced apoptosis, supressed invasion of HepG2 and HCCLM3 cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-30-97
Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kawamura M, Kawamoto A, Hiro J, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y et al (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B pathway in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 108(1):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.499
Fujikawa H, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Saigusa S, Inoue Y, Uchida K, Kusunoki M (2012) High TrkB expression levels are associated with poor prognosis and EMT induction in colorectal cancer cells. J Gastroenterol 47(7):775–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0532-0
Tanaka K, Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Saigusa S, Kawamura M, Araki T, Uchida K et al (2014) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced tropomyosin-related kinase B (Trk B) signaling is a potential therapeutic target for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 9(5):e96410. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096410
Li Z, Oh DY, Nakamura K, Thiele CJ (2011) Perifosine-induced inhibition of Akt attenuates brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB-induced chemoresistance in neuroblastoma in vivo. Cancer 117(23):5412–5422. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26133
Lee J, Jiffar T, Kupferman ME (2012) A novel role for BDNF-TrkB in the regulation of chemotherapy resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7(1):e30246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030246
Zhang S, Guo D, Luo W, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Li C, Lu Y, Cui Z et al (2010) TrkB is highly expressed in NSCLC and mediates BDNF-induced the activation of Pyk2 signaling and the invasion of A549 cells. BMC Cancer 10:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-43
Yuan Y, Ye HQ, Ren QC (2018) Upregulation of the BDNF/TrKB pathway promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, as well as the migration and invasion of cervical cancer. Int J Oncol 52(2):461–472. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4230
Jia S, Wang W, Hu Z, Shan C, Wang L, Wu B, Yang Z, Yang X et al (2015) BDNF mediated TrkB activation contributes to the EMT progression and the poor prognosis in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol 51(1):64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.10.008
Brunelli A, Dimauro I, Sgro P, Emerenziani GP, Magi F, Baldari C, Guidetti L, Di Luigi L et al (2012) Acute exercise modulates BDNF and pro-BDNF protein content in immune cells. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44(10):1871–1880. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31825ab69b
Moalem G, Gdalyahu A, Shani Y, Otten U, Lazarovici P, Cohen IR, Schwartz M (2000) Production of neurotrophins by activated T cells: implications for neuroprotective autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 15(3):331–345. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaut.2000.0441
Camara ML, Corrigan F, Jaehne EJ, Jawahar MC, Anscomb H, Baune BT (2015) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and its receptors in behaviour and neurobiology of adult mice, in the absence of an immune challenge. Behav Brain Res 290:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.040
Xu D, Lian D, Wu J, Liu Y, Zhu M, Sun J, He D, Li L (2017) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces inflammation and hippocampal apoptosis in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):156. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0930-6
Han R, Liu Z, Sun N, Liu S, Li L, Shen Y, Xiu J, Xu Q (2019) BDNF alleviates neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of type 1 diabetic mice via blocking the aberrant HMGB1/RAGE/NF-kappaB pathway. Aging Dis 10(3):611–625. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.0707
Stillman J, Martin A, Miguez MJ, McDaniel HR, Konefal J, Woolger JM, Lewis JE (2020) Relationship between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and immune function during dietary supplement treatment of elderly with Alzheimer’s dementia. J Clin Transl Res 5(2):68–75
Weinstock-Guttman B, Zivadinov R, Tamano-Blanco M, Abdelrahman N, Badgett D, Durfee J, Hussein S, Feichter J et al (2007) Immune cell BDNF secretion is associated with white matter volume in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 188(1–2):167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.06.003
Linker RA, Lee DH, Demir S, Wiese S, Kruse N, Siglienti I, Gerhardt E, Neumann H et al (2010) Functional role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuroprotective autoimmunity: therapeutic implications in a model of multiple sclerosis. Brain 133(Pt 8):2248–2263. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq179
Islas-Hernandez A, Aguilar-Talamantes HS, Bertado-Cortes B, Mejia-delCastillo GJ, Carrera-Pineda R, Cuevas-Garcia CF, Garcia-delaTorre P (2018) BDNF and Tau as biomarkers of severity in multiple sclerosis. Biomark Med 12(7):717–726. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2017-0374
Hu ZL, Luo C, Hurtado PR, Li H, Wang S, Hu B, Xu JM, Liu Y et al (2021) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor in the immune system is a novel target for treating multiple sclerosis. Theranostics 11(2):715–730. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.51390
Yoshimura S, Ochi H, Isobe N, Matsushita T, Motomura K, Matsuoka T, Minohara M, Kira J (2010) Altered production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by peripheral blood immune cells in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 16(10):1178–1188. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458510375706
Li L, Shui QX, Zhao ZY (2003) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression following antibiotic treatment of experimental bacterial meningitis. J Child Neurol 18(12):828–834. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307380301801202
Alvin Z, Laurence GG, Coleman BR, Zhao A, Hajj-Moussa M, Haddad GE (2011) Regulation of L-type inward calcium channel activity by captopril and angiotensin II via the phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase pathway in cardiomyocytes from volume-overload hypertrophied rat hearts. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 89(3):206–215. https://doi.org/10.1139/Y11-011
Xu D, Lian D, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Sun J, Li L (2017) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated via MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Sci Rep 7(1):3545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03861-z
Mitchell JA, Paul-Clark MJ, Clarke GW, McMaster SK, Cartwright N (2007) Critical role of toll-like receptors and nucleotide oligomerisation domain in the regulation of health and disease. J Endocrinol 193(3):323–330. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0067
Lian D, He D, Wu J, Liu Y, Zhu M, Sun J, Chen F, Li L (2016) Exogenous BDNF increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. J Neuroimmunol 294:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.03.014
Bifrare YD, Kummer J, Joss P, Tauber MG, Leib SL (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against multiple forms of brain injury in bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis 191(1):40–45. https://doi.org/10.1086/426399
Han BH, D’Costa A, Back SA, Parsadanian M, Patel S, Shah AR, Gidday JM, Srinivasan A et al (2000) BDNF blocks caspase-3 activation in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 7(1):38–53. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.1999.0275
Han BH, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury in vivo via the ERK pathway. J Neurosci 20(15):5775–5781
Hisatomi T, Sakamoto T, Murata T, Yamanaka I, Oshima Y, Hata Y, Ishibashi T, Inomata H et al (2001) Relocalization of apoptosis-inducing factor in photoreceptor apoptosis induced by retinal detachment in vivo. Am J Pathol 158(4):1271–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64078-3
Galvin KA, Oorschot DE (2003) Continuous low-dose treatment with brain-derived neurotrophic factor or neurotrophin-3 protects striatal medium spiny neurons from mild neonatal hypoxia/ischemia: a stereological study. Neuroscience 118(4):1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00066-6
Ventimiglia R, Mather PE, Jones BE, Lindsay RM (1995) The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4/5 promote survival and morphological and biochemical differentiation of striatal neurons in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 7(2):213–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01057.x
Qiao LY, Shen S, Liu M, Xia C, Kay JC, Zhang QL (2016) Inflammation and activity augment brain-derived neurotrophic factor peripheral release. Neuroscience 318:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.018
Lai NS, Yu HC, Huang Tseng HY, Hsu CW, Huang HB, Lu MC (2021) Increased serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor contribute to inflammatory responses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 22 (4). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041841
Reddy MS (2010) Depression: the disorder and the burden. Indian J Psychol Med 32(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7176.70510
Ahmed S, Malemud CJ, Koch AE, Athar M, Taub DD (2014) Cytokines and chemokines: disease models, mechanisms, and therapies. Mediators Inflamm 2014:296356. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/296356
Galic MA, Riazi K, Pittman QJ (2012) Cytokines and brain excitability. Front Neuroendocrinol 33(1):116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.12.002
Riazi K, Galic MA, Pittman QJ (2010) Contributions of peripheral inflammation to seizure susceptibility: cytokines and brain excitability. Epilepsy Res 89(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.09.004
Duman RS, Malberg J, Nakagawa S, D’Sa C (2000) Neuronal plasticity and survival in mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 48(8):732–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00935-5
D’Sa C, Duman RS (2002) Antidepressants and neuroplasticity. Bipolar Disord 4(3):183–194. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-5618.2002.01203.x
Calabrese F, Rossetti AC, Racagni G, Gass P, Riva MA, Molteni R (2014) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a bridge between inflammation and neuroplasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 8:430. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00430
Molendijk ML, Bus BA, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW, Kenis G, Prickaerts J, Voshaar RC, Elzinga BM (2011) Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: state-trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Mol Psychiatry 16(11):1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.98
Hsieh MT, Lin CC, Lee CT, Huang TL (2019) Abnormal brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IX promoter methylation, protein, and mRNA levels in patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Med 8 (5). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050568
Schroter K, Brum M, Brunkhorst-Kanaan N, Tole F, Ziegler C, Domschke K, Reif A, Kittel-Schneider S (2020) Longitudinal multi-level biomarker analysis of BDNF in major depression and bipolar disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270(2):169–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01007-y
Chiou YJ, Huang TL (2017) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factors in Taiwanese patients with drug-naive first-episode major depressive disorder: effects of antidepressants. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 20(3):213–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyw096
Chiou YJ, Huang TL (2019) Accuracy of brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels for differentiating between Taiwanese patients with major depressive disorder or schizophrenia and healthy controls. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212373. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212373
Hsieh M, Lin CC, Huang TL (2019) Increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IV histone 3 lysine 9 dimethylation in patients with schizophrenia. Taiwan Journal of Psychiatry 33(2):99–104. https://doi.org/10.4103/TPSY.TPSY_18_19
Caldieraro MA, McKee M, Leistner-Segal S, Vares EA, Kubaski F, Spanemberg L, Brusius-Facchin AC, Fleck MP et al (2018) Val66Met polymorphism association with serum BDNF and inflammatory biomarkers in major depression. World J Biol Psychiatry 19(5):402–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/15622975.2017.1347713
Hosang GM, Shiles C, Tansey KE, McGuffin P, Uher R (2014) Interaction between stress and the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 12:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-12-7
Chen ZY, Bath K, McEwen B, Hempstead B, Lee F (2008) Impact of genetic variant BDNF (Val66Met) on brain structure and function. Novartis Found Symp 289:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470751251.ch14 (discussion 188-195)
Groves JO (2007) Is it time to reassess the BDNF hypothesis of depression? Mol Psychiatry 12(12):1079–1088. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002075
Chai HH, Fu XC, Ma L, Sun HT, Chen GZ, Song MY, Chen WX, Chen YS et al (2019) The chemokine CXCL1 and its receptor CXCR2 contribute to chronic stress-induced depression in mice. FASEB J 33(8):8853–8864. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201802359RR
Walker AK, Budac DP, Bisulco S, Lee AW, Smith RA, Beenders B, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2013) NMDA receptor blockade by ketamine abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(9):1609–1616. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.71
Francija E, Petrovic Z, Brkic Z, Mitic M, Radulovic J, Adzic M (2019) Disruption of the NMDA receptor GluN2A subunit abolishes inflammation-induced depression. Behav Brain Res 359:550–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.10.011
Crupi R, Cuzzocrea S (2016) Neuroinflammation and immunity: a new pharmacological target in depression. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15(4):464–476. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527315666160321105339
Jeon SW, Kim YK (2016) Neuroinflammation and cytokine abnormality in major depression: cause or consequence in that illness? World J Psychiatry 6(3):283–293. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283
Sen S, Duman R, Sanacora G (2008) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and antidepressant medications: meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry 64(6):527–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.05.005
Autry AE, Monteggia LM (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Rev 64(2):238–258. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.111.005108
Duman RS (2014) Pathophysiology of depression and innovative treatments: remodeling glutamatergic synaptic connections. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 16(1):11–27
Gold PW (2021) The PPARg system in major depression: pathophysiologic and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci 22 (17). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179248
Lee BH, Kim YK (2010) The roles of BDNF in the pathophysiology of major depression and in antidepressant treatment. Psychiatry Investig 7(4):231–235. https://doi.org/10.4306/pi.2010.7.4.231
Kariharan T, Nanayakkara G, Parameshwaran K, Bagasrawala I, Ahuja M, Abdel-Rahman E, Amin AT, Dhanasekaran M et al (2015) Central activation of PPAR-gamma ameliorates diabetes induced cognitive dysfunction and improves BDNF expression. Neurobiol Aging 36(3):1451–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.09.028
Zhou C, Zhang H, Qin Y, Tian T, Xu B, Chen J, Zhou X, Zeng L et al (2018) A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 82:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.11.012
Dandekar MP, Fenoy AJ, Carvalho AF, Soares JC, Quevedo J (2018) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: an integrative review of preclinical and clinical findings and translational implications. Mol Psychiatry 23(5):1094–1112. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2018.2
Martis LS, Wiborg O, Holmes MC, Harris AP (2019) BDNF(+/-) rats exhibit depressive phenotype and altered expression of genes relevant in mood disorders. Genes Brain Behav 18(2):e12546. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12546
Tadic A, Muller-Engling L, Schlicht KF, Kotsiari A, Dreimuller N, Kleimann A, Bleich S, Lieb K et al (2014) Methylation of the promoter of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IV and antidepressant response in major depression. Mol Psychiatry 19(3):281–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.58
Lieb K, Dreimuller N, Wagner S, Schlicht K, Falter T, Neyazi A, Muller-Engling L, Bleich S et al (2018) BDNF plasma levels and BDNF Exon IV promoter methylation as predictors for antidepressant treatment response. Front Psychiatry 9:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00511
Keller S, Sarchiapone M, Zarrilli F, Videtic A, Ferraro A, Carli V, Sacchetti S, Lembo F et al (2010) Increased BDNF promoter methylation in the Wernicke area of suicide subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(3):258–267. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.9
Sakata K, Woo NH, Martinowich K, Greene JS, Schloesser RJ, Shen L, Lu B (2009) Critical role of promoter IV-driven BDNF transcription in GABAergic transmission and synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(14):5942–5947. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0811431106
Castren E (2014) Neurotrophins and psychiatric disorders. Handb Exp Pharmacol 220:461–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45106-5_17
Castren E, Kojima M (2017) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mood disorders and antidepressant treatments. Neurobiol Dis 97(Pt B):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.07.010
Green MJ, Matheson SL, Shepherd A, Weickert CS, Carr VJ (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in schizophrenia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 16(9):960–972. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.88
Noto MN, Maes M, Vargas Nunes SO, Ota VK, Cavalcante D, Oliveira G, Rossaneis AC, Verri WA Jr et al (2021) BDNF in antipsychotic naive first episode psychosis: effects of risperidone and the immune-inflammatory response system. J Psychiatr Res 141:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.07.011
Lin Z, Su Y, Zhang C, Xing M, Ding W, Liao L, Guan Y, Li Z et al (2013) The interaction of BDNF and NTRK2 gene increases the susceptibility of paranoid schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 8(9):e74264. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074264
Dong Z, Sun X, Pan C, Lu T, Han Y, Wang L, Yan H, Dong L et al (2016) Association of DISC1, BDNF, and COMT polymorphisms with exploratory eye movement of schizophrenia in a Chinese Han population. Psychiatr Genet 26(6):258–265. https://doi.org/10.1097/YPG.0000000000000138
Farkas K, Réthelyi J, Polgár P, Benkovits J, Fábián Á, Czobor P, Bitter I (2011) BDNF and DISC1 are associated with cognitive dysfunction but not with schizophrenia in a hungarian sample. Eur Psychiatry 26(S2):805–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-9338(11)72510-X
Yi H, Hu J, Qian J, Hackam AS (2012) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated by the Wnt signaling pathway. NeuroReport 23(3):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e32834fab06
Mallei A, Ieraci A, Corna S, Tardito D, Lee FS, Popoli M (2018) Global epigenetic analysis of BDNF Val66Met mice hippocampus reveals changes in dendrite and spine remodeling genes. Hippocampus 28(11):783–795. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22991
Stoyanov D, Maes MH (2021) How to construct neuroscience-informed psychiatric classification? Towards nomothetic networks psychiatry. World J Psychiatry 11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i1.1
Maes M, Vojdani A, Galecki P, Kanchanatawan B (2020) How to construct a bottom-up nomothetic network model and disclose novel nosological classes by integrating risk resilience and adverse outcome pathways with the phenome of schizophrenia. Brain Sci 10(9):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090645
Maes M, Rachayon M, Jirakran K, Sodsai P, Klinchanhom S, Gałecki P, Sughondhabirom A, Basta-Kaim A (2022) The immune profile of major dysmood disorder: proof of concept and mechanism using the precision nomothetic psychiatry approach. Cells 11(7):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071183
Funding
The work was supported by the National University Complex for Biomedical and Applied Research, with participation in BBMRI-ERIC (NUCBPI-BBMRI.BG), within the national road map for research infrastructure (Contract No. DO1-395/18.12.2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All contributing authors have participated in the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Nikolay Mehterov and Danail Minchev shared first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehterov, N., Minchev, D., Gevezova, M. et al. Interactions Among Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Neuroimmune Pathways Are Key Components of the Major Psychiatric Disorders. Mol Neurobiol 59, 4926–4952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02889-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02889-1