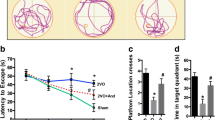
Abstract
The hippocampus, a brain region vital for memory and learning, is sensitive to the damage caused by ischemic/hypoxic stroke and is one of the main regions affected by Alzheimer’s disease. The pathological changes that might occur in the hippocampus and its connections, because of cerebral injury in a distant brain region, such as the striatum, have not been examined. Therefore, in the present study, we evaluated the combined effects of endothelin-1-induced ischemia (ET1) in the striatum and β-amyloid (Aβ) toxicity on hippocampal pathogenesis, dictated by the anatomical and functional intra- and inter-regional hippocampal connections to the striatum. The hippocampal pathogenesis induced by Aβ or ET1 alone was not severe enough to significantly affect the entire circuit of the hippocampal network. However, the combination of the two pathological states (ET1 + Aβ) led to an exacerbated increase in neuroinflammation, deposition of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) fragments with the associated appearance of degenerating cells, and blood-brain-barrier disruption. This was observed mainly in the hippocampal formation (CA2 and CA3 regions), the dentate gyrus as well as distinct regions with synaptic links to the hippocampus such as entorhinal cortex, thalamus, and basal forebrain. In addition, ET1 + Aβ-treated rats also demonstrated protracted loss of AQP4 depolarization, dissolution of β-dystroglycan, and basement membrane laminin with associated IgG and dysferlin leakage. Spatial dynamics of hippocampal injury in ET1 + Aβ rats may provide a valuable model to study new targets for clinical therapeutic applications, specifically when areas remotely connected to hippocampus are damaged.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
amyloid precursor protein
- Aβ:
-
β-amyloid
- ICV:
-
intracerebroventricular
- ET1:
-
endothelin-1
- ABC:
-
avidin-biotin complex
- DAB:
-
3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride
- FJB:
-
fluorojade B
References
Amaral DG, Insausti R (1990) Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G (ed) The Human Nervous System. Academic Press Inc, San Diego, p 711–755
Rosene D (1987) Cerebral cortex. In: Jones E (ed) Cerebral cortex. Plenun Pre, New York, pp. 345–456
Amtul Z, Atta-Ur-Rahman (2015) Neural plasticity and memory: molecular mechanism. Rev Neurosci 26:253–268
Amtul Z, Rahman A (2016) Neural plasticity and memory: is memory encoded in hydrogen bonding patterns? Neuroscientist 22:9–18
Poucet B, Benhamou S (1997) The neuropsychology of spatial cognition in the rat. Crit Rev Neurobiol 11:101–120
Hasselmo M (1999) Neuromodulation: acetylcholine and memory consolidation. Trends Cogn Sci 3:351–359
Schmidt-Kastner R, Szymas J, Hossmann KA (1990) Immunohistochemical study of glial reaction and serum-protein extravasation in relation to neuronal damage in rat hippocampus after ischemia. Neuroscience 38:527–540
Nikonenko AG, Radenovic L, Andjus PR, Skibo G (2009) Structural feautures of ischemic damage in the hippocampus. Anat Rec 292:1914–1921
Eberling JL, Jagust WJ, Reed BR, Baker M (1992) Reduced temporal lobe blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 13:483–491
Altman R, Ruttledge J (2010) The vascular contribution to Alzeheimer’s disease. Clin Sci 119:407–421
Honig LS, Tang MX, Albert S, Costa R, Luchsinger J, Manly J, Stern Y, Mayeux R (2003) Stroke and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 60:1707–1712
Amtul Z (2016) Why therapies for Alzheimer’s disease do not work: do we have consensus over the path to follow? Ageing Res Rev 25:70–84
Amtul Z, Nikolova S, Gao L, Keeley RJ, Bechberger JF, Fisher AL, Bartha R, Munoz DG et al (2014) Comorbid Aβ toxicity and stroke: hippocampal atrophy, pathology, and cognitive deficit. Neurobiol Aging 35:1605–1614
Amtul Z, Whitehead SN, Keeley RJ, Bechberger J, Fisher AL, McDonald RJ, Naus CC, Munoz DG et al (2015) Comorbid rat model of ischemia and β-amyloid toxicity: striatal and cortical degeneration. Brain Pathol 25:24–32
Amtul Z, Hepburn JD (2014) Protein markers of cerebrovascular disruption of neurovascular unit: immunohistochemical and imaging approaches. Rev Neurosci 25:481–507
Yang J, D’Esterre CD, Amtul Z et al (2014) Hemodynamic effects of combined focal cerebral ischemia and amyloid protein toxicity in a rat model: a functional CT study. PLoS One 9:e100575
Amtul Z, Hill DJ, Arany EJ, Cechetto DF (2018) Altered insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in a comorbid rat model of ischemia and β-amyloid toxicity. Sci Rep 8:5136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22985-4
Amtul Z, Yang J, Nikolova S, Lee TY, Bartha R, Cechetto DF (2018) The dynamics of impaired blood-brain barrier restoration in a rat model of co-morbid injury. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0904-4
Klunk W, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt D (2004) Imaging brain amyloid in Alzeheimer’s disease with Pittsburg Compound-B. Am Neurol 55:306–319
Tsenov G, Mátéffyová A, Mares P et al (2007) Intrahippocampal injection of endothelin-1: a new model of ischemia-induced seizures in immature rats. Epilepsia 48(Suppl 5):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01282.x
Dornan WA, Kang DE, McCampbell A, Kang EE (1993) Bilateral injections of beta A(25–35) + IBO into the hippocampus disrupts acquisition of spatial learning in the rat. Neuroreport 5:165–168
Stepanichev MY, Moiseeva YV, Lazareva NA, Onufriev MV, Gulyaeva NV (2003) Single intracerebroventricular administration of amyloid-beta (25–35) peptide induces impairment in short-term rather than long-term memory in rats. Brain Res Bull 61:197–205
Magloczky Z, Freund TF (1993) Selective neuronal death in the contralateral hippocampus following unilateral kainate injections into the CA3 subfield. Neuroscience 56:317–335
Chan RW, Leong ATL, Ho LC, Gao PP, Wong EC, Dong CM, Wang X, He J et al (2017) Low-frequency hippocampal-cortical activity drives brain-wide resting-state functional MRI connectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E6972–E 6981. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1703309114
Kaneko I, Morimoto K, Kubo T (2001) Drastic neuronal loss in vivo by β-amyloid racemized at Ser26 residue: conversion of non-toxic [D-Ser26]β-amyloid 1-40 to toxic and proteinase-resistant fragments. Neuroscience 104:1003–1011
Kubo T, Nishimura S, Kumagae Y, Kaneko I (2002) In vivo conversion of racemized βamyloid ([D-Ser26]Aβ1-40) to truncated and toxic fragments ([D-Ser26]Aβ25-35/40) and fragment presence in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. J Neurosci Res 70:474–483
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. English 7:209
Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA (1987) Blood-brain barrier protein recognized by monoclonal antibody. Pnas 84:8169–8173
Lokkegaard A, Nyengaard JR, West M (2001) Stereological estimates of number and length of capillaries in subdivisions of the human hippocampal region. Hippocampus 11:726–740
Schmued LC, Albertson C, Slikker W (1997) Fluoro-Jade: a novel fluorochrome for the sensitive and reliable histochemical localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 751:37–46
Damjanac M, Bilan AR, Barrier L, Pontcharraud R, Anne C, Hugon J, Page G (2007) Fluoro-Jade® B staining as useful tool to identify activated microglia and astrocytes in a mouse transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1128:40–49
Cunningham LA, Wetzel M, Rosenberg GA (2005) Multiple roles for MMPs and TIMPs in cerebral ischemia. Glia 50:329–339
Wolburg-Buchholz K, Mack AF, Steiner E, Pfeiffer F, Engelhardt B, Wolburg H (2009) Loss of astrocyte polarity marks blood-brain barrier impairment during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol 118:219–233
Kajihara H, Tsutsumi E, Kinoshita A, Nakano J, Takagi K, Takeo S (2001) Activated astrocytes with glycogen accumulation in ischemic penumbra during the early stage of brain infarction: inmunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies. Brain Res 909:92–101
Block F, Dihne M, Loos M (2005) Inflammation in areas of remote changes following focal brain lesion. Prog Neurobiol 75:342–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.03.004
Groenewegen HJ, Vermeulen-Vander Zee A, te Kortschot A, Witter M (1987) Organization of the projections from the subiculum to the ventral striatum in the rat. A study using anterograde transport of Phaseolus vulgaris leucoaglutining. Neuroscience 23:103–120
Pennartz CM, Groenewegen HJ, Lopes da Silva F (1994) The nucleous accumbens as a complex of functionality distinct neuronal ensembles: an integration of behavioural, electrophysiological and anatomical data. Prog Neurobiol 42:719–761
Nyakas C, Luiten PG, Balkan B, Spencer DGJ (1998) Changes in septo-hippocampal projections after lateral enthorhinal or combined enthorhinal-raphe lesions as studied by anterograde tracing methods. Brain Res Bull 21:285–293
Paskavitz JF, Lippa CF, Hamos JE, Pulaski-Salo D, Drachman D (1995) Role of the dorsomedial nucleous of the thalamus in Alzheimer’s disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 8:32–37
Xuereb JH, Perry RH, Candy JM, Perry EK, Marshall E, Bonham J (1991) Nerve loss in the thalamus in Alzeheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 114:1363–1379
Carrera E, Michel P, Bogousslavsky J (2004) Anteromedian, central, and posterolateral infarcts of the thalamus: three variant types. Stroke 35:2826–2831
Swartz RH, Black SE (2006) Anterior-medial thalamic lesions in dementia: frequent, and volume dependently associated with sudden cognitive decline. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:1307–1312. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.091561
Van der Werf YD, Weerts JG, Jolles J, Witter MP, Lindeboom J, Scheltens P (1999) Neuropsycological correlates of a right unilateral lacunar thalamic infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:36–42
Leranth C, Hajszan T (2007) Extrinsic afferent systems to the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:63–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63004-0
Riekkinen PJ, LauLumaa V, Sirvio J, Soininen H, Helkala E (1987) Recent progress in the research of Alzheimer’s disease. Med Biol 65:83–88
Di Paola M, Macaluso E, Carlesimo GA et al (2007) Episodic memory impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease is correlated with entorhinal cortex atrophy: a voxel-based morphometry study. J Neurol 254:774–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0435-1
Imdahl A, Hossmann K (1986) Morphometric evaluation of post-ischemic capillary perfusion in selectively vulnerable areas of gerbil brain. Acta Neuropathol 69:267–271
Uchida H, Fujita Y, Matsueda M, Umeda M, Matsuda S, Kato H, Kasahara J, Araki T (2010) Damage to neurons and oligodendrocytes in the hippocampal CA1 sector after transient focal ischemia in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:1125–1134
Bendel O, Bueters T, von Euler M, Ögren SO, Sandin J, von Euler G (2005) Reappearance of hippocampal CA1 neurons after ischemia is associated with recovery of learning and memory. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1586–1595. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600153
Bitting L, Naidu A, Cordell B, Murphy GM (1996) Beta-amyloid peptide secretion by a microglial cell line is induced by beta-amyloid-(25–35) and lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem 271:16084–16089
Pooler AM, Arjona AA, Lee RK, Wurtman RJ (2004) Prostaglandin E2 regulates amyloid precursor protein expression via the EP2 receptor in cultured rat microglia. Neurosci Lett 362:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.03.013
Nagasawa H, Kogure K (1990) Exo-focal postischemic neuronal death in the rat brain. Brain Res 524:196–202
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Harry GJ, Lefebre D (2003) Dentate gyrus: alterations that occur with hippocampal injury. Neurotoxicology 24:343–356
Rosenblum W (1997) Histopathologic clues to the pathways of neuronal death following ischemia/hipoxia. Neurotrauma 14:313–326
Lartey FM, Ahn G-O, Ali R, Rosenblum S, Miao Z, Arksey N, Shen B, Colomer MV et al (2014) The relationship between serial [18 F]PBR06 PET imaging of microglial activation and motor function following stroke in mice. Mol Imaging Biol 16:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0745-0
Hopperton KE, Mohammad D, Trépanier MO, Giuliano V, Bazinet RP (2018) Markers of microglia in post-mortem brain samples from patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Mol Psychiatry 23:177–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.246
Ujie M, Dickenstein DL, Carlow DA, Jefferies WA (2003) Blood-brain barrier permeability precedes senile plaque formation in an Alzheimer disease model. Microcirculation 10:463–470
Rhodin JA, Thomas T (2001) A vascular connection to Alzheimer’s disease. Microcirculation 8(20):207–220
Kalaria RN, Bhatt SU, Lust WD, Perry G (1993) The amiloid precursor protein in ischemic brain injury and chronic hypoperfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 695:190–193
Takahashi A, Park HK, Melgar MA, Alcocer L, Pinto J, Lenzi T, Diaz FG, Rafols JA (1997) Cerebral cortex blood flow and vascular smooth muscle contractility in a rat model of ischemia: a correlative laser Doppler flowmetric and scanning electron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol 93:354–368
Zarow C, Barron E, Chui HC, Perlmutter LS (1997) Vascular basement membrane pathology and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 826:147–160
Leppert D, Waubant E, Galardy R et al (1995) T cell gelatinases mediate basement membrane transmigration in vitro. J Immunol 154:4379–4389
Agrawal S, Anderson P, Durbeej M et al (2006) Dystroglycan is selectively cleaved at the parenchymal basement membrane at sites of leukocyte extravasation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Cell Biol 173:1007–1019
Hochmeister S, Grundtner R, Bauer J, Engelhardt B, Lyck R, Gordon G, Korosec T, Kutzelnigg A et al (2006) Dysferlin is a new marker for leaky brain blood vessels in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:855–865
Schmidt-Kastner R, Meller D, Bellander BM, Strömberg I, Olson L, Ingvar M (1993) A one-step immunohistochemical method for detection of blood-brain barrier disturbances for immunoglobulins in lesioned rat brain with special reference to false-positive labelling in immunohistochemistry. J Neurosci Methods 46:121–132
Palmer JC, Barker R, Kehoe PG, Love S (2012) Endothelin-1 is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease and upregulated by amyloid-β. J Alzheimers Dis 29:853–861
Funding
The funding for this project came from Canadian Institutes of Health Research (R1478A47) and a CIHR Vascular Research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amtul, Z., Frías, C., Randhawa, J. et al. Spatial Dynamics of Vascular and Biochemical Injury in Rat Hippocampus Following Striatal Injury and Aβ Toxicity. Mol Neurobiol 56, 2714–2727 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1225-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1225-3