Abstract
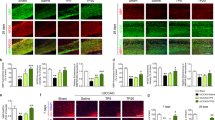
Andrographolide is a medical herbal compound with documented anti-inflammatory activity and therapeutic efficacy in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and ischemic stroke. The present study examined the potential therapeutic effects of andrographolide on chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH)–induced hippocampal neuronal damage and cognitive dysfunction. A CCH model was established in male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats using 2-vessel occlusion (2VO). After 4 weeks of CCH, spatial learning and memory were assessed in the Morris water maze and structural damage to the hippocampus by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Astrocyte activation was examined by immunohistochemical staining and Western blotting for glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP), while expression levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), the apoptosis effector cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-3 (caspase-3), and the neuroprotectant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the TrkB receptor were estimated by Western blotting. After 4 weeks of CCH, the hippocampus of 2VO rats exhibited marked neurodegeneration as well as elevated GFAP, TNF-α, IL-1β, and caspase-3 compared to Sham controls. In addition, spatial learning was impaired compared to Sham controls. Andrographolide treatment during CCH suppressed astrocyte activation as evidenced by reduced GFAP expression, enhanced expression of BDNF and TrkB, improved impaired spatial learning and memory, and reversed upregulated TNF-α, IL-1β, and caspase-3 expression. These results reveal a potential neuroprotective effect of andrographolide on hippocampal neuronal damage and cognitive impairment from CCH due to suppression of astrocyte activation and enhancement of BDNF-TrkB signaling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertoglio JC, Baumgartner M, Palma R, Ciampi E, Carcamo C, Cáceres DD, Acosta-Jamett G, Hancke JL, Burgos RA (2016) Andrographis paniculata decreases fatigue in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 12-month double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. BMC Neurol 16:77
Chan SJ, Wong WS, Wong PT et al (2010) Neuroprotective effects of andrographolide in a rat model of permanent cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol 161(3):668–679
Chern CM, Liou KT, Wang YH, Liao JF, Yen JC, Shen YC (2011) Andrographolide inhibits PI3K/AKT-dependent NOX2 and iNOS expression protecting mice against hypoxia/ischemia-induced oxidative brain injury. Planta Med 77(15):1669–1679
Das S, Mishra KP, Ganju L, Singh SB (2017) Andrographolide - a promising therapeutic agent, negatively regulates glial cell derived neurodegeneration of prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and working memory impairment. J Neuroimmunol 313:161–175
de Pins B, Cifuentes-Diaz C, Thamila Farah A et al (2019) Conditional BDNF delivery from astrocytes rescues memory deficits, spine density and synaptic properties in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Neurosci
Du J, Zhang C, Na X et al (2018) Andrographolide protects mouse astrocytes against hypoxia injury by promoting autophagy and S100B expression. Braz J Med Biol Res 51(6):e7061
Duncombe J, Kitamura A, Hase Y, Ihara M, Kalaria RN, Horsburgh K (2017) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a key mechanism leading to vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Closing the translational gap between rodent models and human vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Clin Sci (Lond) 131(19):2451–2468
El Hayek L, Khalifeh M, Zibara V et al (2019) Lactate mediates the effects of exercise on learning and memory through SIRT1-dependent activation of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). J Neurosci
Fletcher JL, Murray SS, Xiao J (2018) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in central nervous system myelination: a new mechanism to promote myelin plasticity and repair. Int J Mol Sci 19(12)
Geng J, Liu W, Xiong Y, Ding H, Jiang C, Yang X, Li X, Elgehama A, Sun Y, Xu Q, Guo W, Gao J (2018) Andrographolide sulfonate improves Alzheimer-associated phenotypes and mitochondrial dysfunction in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Biomed Pharmacother 97:1032–1039
Goncalves CA, Rodrigues L, Bobermin LD et al (2018) Glycolysis-derived compounds from astrocytes that modulate synaptic communication. Front Neurosci 12:1035
Graverini G, Piazzini V, Landucci E, Pantano D, Nardiello P, Casamenti F, Pellegrini-Giampietro DE, Bilia AR, Bergonzi MC (2018) Solid lipid nanoparticles for delivery of andrographolide across the blood-brain barrier: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 161:302–313
Gu L, Yu Q, Li Q, Zhang L, Lu H, Zhang X (2018) Andrographolide protects PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced autophagy-associated cell death through activation of the Nrf2-mediated p62 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19(9)
Hancke JL, Srivastav S, Caceres DD et al (2019) A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy of andrographis paniculata standardized extract (ParActin(R)) on pain reduction in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Phytother Res 33:1469–1479
Hase Y, Ding R, Harrison G, Hawthorne E, King A, Gettings S, Platten C, Stevenson W, Craggs LJL, Kalaria RN (2019) White matter capillaries in vascular and neurodegenerative dementias. Acta Neuropathol Commun 7(1):16
Huang L, Nakamura Y, Lo EH, Hayakawa K (2019) Astrocyte signaling in the neurovascular unit after central nervous system injury. Int J Mol Sci 20(2)
Iadecola C (2017) The neurovascular unit coming of age: a journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron. 96(1):17–42
Kim JH, Ko PW, Lee HW, Jeong JY, Lee MG, Kim JH, Lee WH, Yu R, Oh WJ, Suk K (2017) Astrocyte-derived lipocalin-2 mediates hippocampal damage and cognitive deficits in experimental models of vascular dementia. Glia. 65(9):1471–1490
Lin HC, Li CC, Yang YC, Chiu TH, Liu KL, Lii CK, Chen HW (2019) Andrographis paniculata diterpenoids and ethanolic extract inhibit TNFalpha-induced ICAM-1 expression in EA.hy926 cells. Phytomedicine. 52:157–167
Liu Y, Fassbender K (2018) Deficiency of TLR4 ameliorates hypoperfusion-induced brain pathology. Theranostics. 8(22):6355–6356
Liu W, Li R, Yin J, Guo S, Chen Y, Fan H, Li G, Li Z, Li X, Zhang X, He X, Duan C (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the early brain injury of subarachnoid hemorrhage partly by suppression of Notch1-dependent neuroinflammation: involvement of Botch. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):8
Lu B, Nagappan G, Lu Y (2014) BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. Handb Exp Pharmacol 220:223–250
Mansour A, Niizuma K, Rashad S, Sumiyoshi A, Ryoke R, Endo H, Endo T, Sato K, Kawashima R, Tominaga T (2018) A refined model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion resulting in cognitive impairment and a low mortality rate in rats. J Neurosurg:1–11
Ojha CR, Rodriguez M, Karuppan MKM, Lapierre J, Kashanchi F, el-Hage N (2019) Toll-like receptor 3 regulates Zika virus infection and associated host inflammatory response in primary human astrocytes. PLoS One 14(2):e0208543
Paemanee A, Hitakarun A, Wintachai P, Roytrakul S, Smith DR (2019) A proteomic analysis of the anti-dengue virus activity of andrographolide. Biomed Pharmacother 109:322–332
Piazzini V, Landucci E, Graverini G, Pellegrini-Giampietro D, Bilia A, Bergonzi M (2018) Stealth and cationic nanoliposomes as drug delivery systems to increase andrographolide BBB permeability. Pharmaceutics 10(3)
Ray AK, DuBois JC, Gruber RC et al (2017) Loss of Gas6 and Axl signaling results in extensive axonal damage, motor deficits, prolonged neuroinflammation, and less remyelination following cuprizone exposure. Glia. 65(12):2051–2069
Seo EJ, Klauck SM, Efferth T, Panossian A (2019) Adaptogens in chemobrain (part I): plant extracts attenuate cancer chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment - transcriptome-wide microarray profiles of neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine. 55:80–91
Serrano FG, Tapia-Rojas C, Carvajal FJ, Hancke J, Cerpa W, Inestrosa NC (2014) Andrographolide reduces cognitive impairment in young and mature AbetaPPswe/PS-1 mice. Mol Neurodegener 9:61
Siuda J, Patalong-Ogiewa M, Zmuda W et al (2017) Cognitive impairment and BDNF serum levels. Neurol Neurochir Pol 51(1):24–32
Trias E, Barbeito L, Yamanaka K (2018) Phenotypic heterogeneity of astrocytes in motor neuron disease. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol 9(4):225–234
Varela-Nallar L, Arredondo SB, Tapia-Rojas C et al (2015) Andrographolide stimulates neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Neural Plast 2015:935403
Wan Q, Ma X, Zhang ZJ, Sun T, Xia F, Zhao G, Wu YM (2017) Ginsenoside reduces cognitive impairment during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion through brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulated by epigenetic modulation. Mol Neurobiol 54(4):2889–2900
Wang T, Liu B, Zhang W, Wilson B, Hong JS (2004) Andrographolide reduces inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures by inhibiting microglial activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308(3):975–983
Wang L, Wang J, Wang F, Liu C, Yang X, Yang J, Ming D (2017a) VEGF-mediated cognitive and synaptic improvement in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats involves autophagy process. NeuroMolecular Med 19(2–3):423–435
Wang D, Lin Q, Su S, Liu K, Wu Y, Hai J (2017b) URB597 improves cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by inhibiting mTOR-dependent autophagy. Neuroscience. 344:293–304
Wang DP, Liu KJ, Kasper G, Lin Q, Hai J (2017c) Inhibition of SENP3 by URB597 ameliorates neurovascular unit dysfunction in rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Biomed Pharmacother 91:872–879
Wang DP, Yin H, Kang K, Lin Q, Su SH, Hai J (2018a) The potential protective effects of cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 on cognitive dysfunction is associated with the suppression of autophagy and inflammation in an experimental model of vascular dementia. Psychiatry Res 267:281–288
Wang HC, Tsay HS, Shih HN, Chen YA, Chang KM, Agrawal DC, Huang S, Lin YL, Lee MJ (2018b) Andrographolide relieved pathological pain generated by spared nerve injury model in mice. Pharm Biol 56(1):124–131
Wang YH, Yang YL, Cheng X, Zhang J, Li W, du GH (2019) Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction extract regulates differentially expressed proteins in the hippocampus after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neural Regen Res 14(3):470–479
Wurzelmann M, Romeika J, Sun D (2017) Therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and a small molecular mimics of BDNF for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 12(1):7–12
Xie YC, Yao ZH, Yao XL, Pan JZ, Zhang SF, Zhang Y, Hu JC (2018) Glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor is involved in spatial cognitive dysfunction in rats after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Alzheimers Dis 66(4):1559–1576
Xu F, Wu H, Zhang K, Lv P, Zheng L, Zhao J (2016) Proneurogenic effects of andrographolide on RSC96 Schwann cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep 14(4):3573–3580
Yang CH, Yen TL, Hsu CY, Thomas PA, Sheu JR, Jayakumar T (2017) Multi-targeting Andrographolide, a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, as a potential therapeutic agent for stroke. Int J Mol Sci 18(8)
Yen TL, Hsu WH, Huang SK et al (2013) A novel bioactivity of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury through induction of cerebral endothelial cell apoptosis. Pharm Biol 51(9):1150–1157
Yen TL, Chen RJ, Jayakumar T, Lu WJ, Hsieh CY, Hsu MJ, Yang CH, Chang CC, Lin YK, Lin KH, Sheu JR (2016) Andrographolide stimulates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-heme oxygenase 1 signaling in primary cerebral endothelial cells for definite protection against ischemic stroke in rats. Transl Res 170:57–72
Funding
This work received funding from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81771410) and Priority of Shanghai key discipline of medicine (2017ZZ02020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DP. W. wrote the manuscript. H.Y., Q.L., SP. F., and JH. S. prepared the experiments and collected the data. YF. W. and SH. S. analyzed and interpreted the data. DP. W. and J.H. designed the study. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, DP., Yin, H., Lin, Q. et al. Andrographolide enhances hippocampal BDNF signaling and suppresses neuronal apoptosis, astroglial activation, neuroinflammation, and spatial memory deficits in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 1277–1284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01672-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01672-9