Abstract
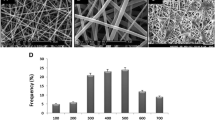
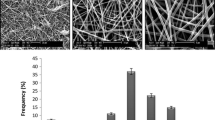
Electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) have great potential for applications in neural tissue regeneration due to their electrical conductivity, biocompatibility, and morphological similarity to natural extracellular matrix. In this study, we cultured human endometrial stem cells (hEnSCs) on electrospun CNFs with random and aligned topographies and demonstrated that hEnSCs could attach, proliferate, and differentiate into neural cells on both random and aligned CNFs. However, the proliferation, differentiation, and morphology of cells were affected by CNF morphology. Under the proliferative condition, hEnSCs showed lower proliferation on aligned CNFs than on random CNFs and on tissue culture plate (TCP) control. When cultured on aligned CNFs in neural induction media, hEnSCs showed significant upregulation of neuronal markers, NF-H and Tuj-1, and downregulation of neural progenitor marker (nestin) compared to that on random CNFs and on TCP. In contrast, hEnSCs showed higher expression of nestin and slight upregulation of oligodendrocyte marker (OLIG-2) on random CNFs compared to that on aligned CNFs and on TCP. SEM imaging revealed that differentiated cells extended along the CNF main axis on aligned CNFs but stretched multidirectionally on random CNFs. These findings suggest electrospun CNFs as proper substrate for stem cell differentiation into specific neural cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nunes A, Al-Jamal K, Nakajima T, Hariz M, Kostarelos K (2012) Application of carbon nanotubes in neurology: clinical perspectives and toxicological risks. Arch Toxicol 86(7):1009–1020
Tran PA, Zhang L, Webster TJ (2009) Carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(12):1097–1114
Wilkinson AE, McCormick AM, Leipzig ND (2011) Central nervous system tissue engineering: current considerations and strategies. Synthesis Lectures on Tissue Eng 3(2):1–120
Silva GA (2006) Neuroscience nanotechnology: progress, opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(1):65–74
Lee W, Parpura V (2009) Carbon nanotubes as substrates/scaffolds for neural cell growth. Prog Brain Res 180:110–125
Fraczek-Szczypta A (2014) Carbon nanomaterials for nerve tissue stimulation and regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C 34:35–49
Galvan-Garcia P, Keefer EW, Yang F, Zhang M, Fang S, Zakhidov AA, Baughman RH, Romero MI (2007) Robust cell migration and neuronal growth on pristine carbon nanotube sheets and yarns. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 18(10):1245–1261
Hu H, Ni Y, Montana V, Haddon RC, Parpura V (2004) Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes as substrates for neuronal growth. Nano Lett 4(3):507–511
Matsumoto K, Sato C, Naka Y, Kitazawa A, Whitby RL, Shimizu N (2007) Neurite outgrowths of neurons with neurotrophin-coated carbon nanotubes. J Biosci Bioeng 103(3):216–220
Ni Y, Hu H, Malarkey EB, Zhao B, Montana V, Haddon RC, Parpura V (2005) Chemically functionalized water soluble single-walled carbon nanotubes modulate neurite outgrowth. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5(10):1707–1712
Tay CY, Gu H, Leong WS, Yu H, Li HQ, Heng BC, Tantang H, Loo SCJ et al (2010) Cellular behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on single-walled carbon nanotube film. Carbon 48(4):1095–1104
Mattson MP, Haddon RC, Rao AM (2000) Molecular functionalization of carbon nanotubes and use as substrates for neuronal growth. J Mol Neurosci 14(3):175–182
Lovat V, Pantarotto D, Lagostena L, Cacciari B, Grandolfo M, Righi M, Spalluto G, Prato M et al (2005) Carbon nanotube substrates boost neuronal electrical signaling. Nano Lett 5(6):1107–1110
Chao T-I, Xiang S, Chen C-S, Chin W-C, Nelson A, Wang C, Lu J (2009) Carbon nanotubes promote neuron differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384(4):426–430
Kam NWS, Jan E, Kotov NA (2008) Electrical stimulation of neural stem cells mediated by humanized carbon nanotube composite made with extracellular matrix protein. Nano Lett 9(1):273–278
Dalby MJ, Gadegaard N, Tare R, Andar A, Riehle MO, Herzyk P, Wilkinson CD, Oreffo RO (2007) The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nat Mater 6(12):997–1003
Christopherson GT, Song H, Mao H-Q (2009) The influence of fiber diameter of electrospun substrates on neural stem cell differentiation and proliferation. Biomaterials 30(4):556–564
Malarkey EB, Fisher KA, Bekyarova E, Liu W, Haddon RC, Parpura V (2008) Conductive single-walled carbon nanotube substrates modulate neuronal growth. Nano Lett 9(1):264–268
Nguyen-Vu TB, Chen H, Cassell AM, Andrews RJ, Meyyappan M, Li J (2007) Vertically aligned carbon nanofiber architecture as a multifunctional 3-D neural electrical interface. Biomed Eng IEEE Trans on 54(6):1121–1128
McKenzie JL, Waid MC, Shi R, Webster TJ (2004) Decreased functions of astrocytes on carbon nanofiber materials. Biomaterials 25(7):1309–1317
Nataraj S, Yang K, Aminabhavi T (2012) Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—a state-of-the-art review. Prog Polym Sci 37(3):487–513
Bhardwaj N, Kundu SC (2010) Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv 28(3):325–347
Rahaman M, Ismail AF, Mustafa A (2007) A review of heat treatment on polyacrylonitrile fiber. Polym Degrad Stab 92(8):1421–1432
Jain S, Sharma A, Basu B (2013) In vitro cytocompatibility assessment of amorphous carbon structures using neuroblastoma and Schwann cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 101(4):520–531
Jain S, Webster TJ, Sharma A, Basu B (2013) Intracellular reactive oxidative stress, cell proliferation and apoptosis of Schwann cells on carbon nanofibrous substrates. Biomaterials 34(21):4891–4901
Ebrahimi-Barough S, Javidan AN, Saberi H, Joghataei MT, Rahbarghazi R, Mirzaei E, Faghihi F, Shirian S, Ai A, Ai J (2014) Evaluation of Motor Neuron-Like Cell Differentiation of hEnSCs on Biodegradable PLGA Nanofiber Scaffolds. Mol Neurobiol: 1–10
Mobarakeh ZT, Ai J, Yazdani F, Sorkhabadi SMR, Ghanbari Z, Javidan AN, Mortazavi‐Tabatabaei SAR, Massumi M et al (2012) Human endometrial stem cells as a new source for programming to neural cells. Cell Biol Int Rep 19(1):7–14
Tavakol S, Aligholi H, Gorji A, Eshaghabadi A, Hoveizi E, Tavakol B, Rezayat SM, Ai J (2014) Thermogel nanofiber induces human endometrial‐derived stromal cells to neural differentiation: in vitro and in vivo studies in rat. J Biomed Mater Res A 102(12):4590–4597
Tavakol S, Saber R, Hoveizi E, Aligholi H, Ai J, Rezayat SM (2015) Chimeric Self-assembling Nanofiber Containing Bone Marrow Homing Peptide’s Motif Induces Motor Neuron Recovery in Animal Model of Chronic Spinal Cord Injury; an In Vitro and In Vivo Investigation. Mol Neurobiol: 1–11
Mirzaei E, Ai J, Sorouri M, Ghanbari H, Verdi J, Faridi-Majidi R (2015) Functionalization of PAN-based electrospun carbon nanofibers by acid oxidation: study of structural, electrical and mechanical properties. Fullerenes, Nanotubes, Carbon Nanostruct 23(11):930–937. doi:10.1080/1536383x.2015.1020057
Ebrahimi-Barough S, Kouchesfahani HM, Ai J, Massumi M (2013) Differentiation of human endometrial stromal cells into oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs). J Mol Neurosci 51(2):265–273
Zhang J, Loya P, Peng C, Khabashesku V, Lou J (2012) Quantitative in situ mechanical characterization of the effects of chemical functionalization on individual carbon nanofibers. Adv Funct Mater 22(19):4070–4077
Dongil A, Bachiller-Baeza B, Guerrero-Ruiz A, Rodríguez-Ramos I, Martínez-Alonso A, Tascón J (2011) Surface chemical modifications induced on high surface area graphite and carbon nanofibers using different oxidation and functionalization treatments. J Colloid Interface Sci 355(1):179–189
Zussman E, Chen X, Ding W, Calabri L, Dikin D, Quintana J, Ruoff R (2005) Mechanical and structural characterization of electrospun PAN-derived carbon nanofibers. Carbon 43(10):2175–2185
Zhou Z, Lai C, Zhang L, Qian Y, Hou H, Reneker DH, Fong H (2009) Development of carbon nanofibers from aligned electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber bundles and characterization of their microstructural, electrical, and mechanical properties. Polymer 50(13):2999–3006
Wang G, Pan C, Wang L, Dong Q, Yu C, Zhao Z, Qiu J (2012) Activated carbon nanofiber webs made by electrospinning for capacitive deionization. Electrochim Acta 69:65–70
Yim EK, Pang SW, Leong KW (2007) Synthetic nanostructures inducing differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into neuronal lineage. Exp Cell Res 313(9):1820–1829
Lim SH, Liu XY, Song H, Yarema KJ, Mao H-Q (2010) The effect of nanofiber-guided cell alignment on the preferential differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials 31(34):9031–9039
Gulacsi AA, Anderson SA (2008) β-catenin–mediated Wnt signaling regulates neurogenesis in the ventral telencephalon. Nat Neurosci 11(12):1383–1391
Yamada M, Tanemura K, Okada S, Iwanami A, Nakamura M, Mizuno H, Ozawa M, Ohyama‐Goto R et al (2007) Electrical stimulation modulates fate determination of differentiating embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 25(3):562–570
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS), grant No. 91-04-87-20021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaei, E., Ai, J., Ebrahimi-Barough, S. et al. The Differentiation of Human Endometrial Stem Cells into Neuron-Like Cells on Electrospun PAN-Derived Carbon Nanofibers with Random and Aligned Topographies. Mol Neurobiol 53, 4798–4808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9410-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9410-0