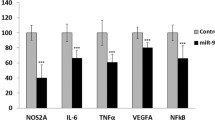
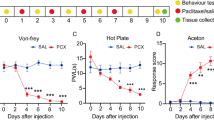
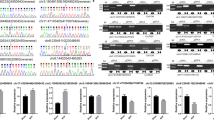
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) remain stable in circulation and have been identified as potential biomarkers for a variety of conditions. We report miRNA changes in blood from multiple rodent models of pain, including spinal nerve ligation and spared nerve injury models of neuropathic pain; a complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) model of inflammatory pain; and a chemotherapy-induced model of pain using the histone deacetylase inhibitor JNJ-26481585. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, was investigated in the CFA model as proof of principle for assessing the utility of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers in determining treatment response. Each study resulted in a unique miRNA expression profile. Despite differences in miRNAs identified from various models, computational target prediction and functional enrichment have identified biological pathways common among different models. The Wnt signaling pathway was affected in all models, suggesting a crucial role for this pathway in the pathogenesis of pain. Our studies demonstrate the utility of circulating miRNAs as pain biomarkers and suggest the potential for rigorous forward and reverse translational approaches. Evaluating alterations in miRNA fingerprints under different pain conditions and after administering therapeutic agents may be beneficial in evaluating clinical trial outcomes, predicting treatment response, and developing correlational outcomes between preclinical and human studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gereau IV RW, Sluka KA, Maixner W, Savage SR, Price TJ, Murinson BB, Sullivan MD and Fillingim RB A Pain Research Agenda for the 21st Century. J. Pain
Borsook D, Becerra L, Hargreaves R (2011) Biomarkers for chronic pain and analgesia. Part 1: the need, reality, challenges, and solutions. Discov Med 11:197–207
Strimbu K, Tavel JA (2010) What are biomarkers? Curr Opin HIV AIDS 5:463–466
DeVon HA, Piano MR, Rosenfeld AG, Hoppensteadt DA (2014) The association of pain with protein inflammatory biomarkers: a review of the literature. Nurs Res 63:51–62. doi:10.1097/NNR.0000000000000013
Marchi A, Vellucci R, Mameli S, Rita Piredda A, Finco G (2009) Pain biomarkers. Clin Drug Investig 29(Suppl 1):41–46
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M, Zhang X, Li M, Wang G, Liu Y (2009) miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D98–104
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D and Wang, K (2011) Extracellular microRNA: a new source of biomarkers. Mutat Res
Kynast KL, Russe OQ, Geisslinger G, Niederberger E (2013) Novel findings in pain processing pathways: implications for miRNAs as future therapeutic targets. Expert Rev Neurother 13:515–525
Kress M, Hüttenhofer A, Landry M, Kuner R, Favereaux A, Greenberg DS, Bednarik J, Heppenstall P, Kronenberg F, Malcangio M et al (2013) MicroRNAs in nociceptive circuits as predictors of future clinical applications. Front Mol Neurosci 6:33
Bali KK, Kuner R (2014) Noncoding RNAs: key molecules in understanding and treating pain. Trends Mol Med 20:437–448
Tan P-H, Pao Y-Y, Cheng J-K, Hung K-C, Liu C-C (2013) MicroRNA-based therapy in pain medicine: current progress and future prospects. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 51:171–176
Elramah S, Landry M, Favereaux A (2014) MicroRNAs regulate neuronal plasticity and are involved in pain mechanisms. Front Cell Neurosci 8:31
Sakai A and Suzuki H (2014) Emerging roles of microRNAs in chronic pain. Neurochem Int
Mogil JS, Davis KD, Derbyshire SW (2010) The necessity of animal models in pain research. Pain 151:12–17
Gregory NS, Harris AL, Robinson CR, Dougherty PM, Fuchs PN, Sluka KA (2013) An overview of animal models of pain: disease models and outcome measures. J Pain 14:1255–1269
Percie du Sert N, Rice AS (2014) Improving the translation of analgesic drugs to the clinic: animal models of neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol 171:2951–2963
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A, Burwinkel B (2011) Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 39:7223–7233
Boon RA, Vickers KC (2013) Intercellular transport of microRNAs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:186–192
El Andaloussi S, Mager I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJA (2013) Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:347–357
Bjersing JL, Lundborg C, Bokarewa MI, Mannerkorpi K (2013) Profile of cerebrospinal microRNAs in fibromyalgia. PLoS ONE 8, e78762
Ammari M, Jorgensen C, Apparailly F (2013) Impact of microRNAs on the understanding and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25:225–233
Shen N, Liang D, Tang Y, de Vries N, Tak PP (2012) MicroRNAs–novel regulators of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:701–709
Fourie NH, Peace RM, Abey SK, Sherwin LB, Rahim-Williams B, Smyser PA, Wiley JW, Henderson WA (2014) Elevated circulating miR-150 and miR-342-3p in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Exp Mol Pathol 96:422–425
Orlova IA, Alexander GM, Qureshi RA, Sacan A, Graziano A, Barrett JE, Schwartzman RJ, Ajit SK (2011) MicroRNA modulation in complex regional pain syndrome. J Transl Med 9:195
Gheinani A, Burkhard F, Monastyrskaya K (2013) Deciphering microRNA code in pain and inflammation: lessons from bladder pain syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:3773–3789
Ohlsson Teague EMC, Print CG, Hull ML (2010) The role of microRNAs in endometriosis and associated reproductive conditions. Hum Reprod Update 16:142–165
Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R, Croce CM (2013) A new role for microRNAs, as ligands of toll-like receptors. RNA Biol 10:169–174
Park CK, Xu ZZ, Berta T, Han Q, Chen G, Liu XJ, Ji RR (2014) Extracellular microRNAs activate nociceptor neurons to elicit pain via TLR7 and TRPA1. Neuron 82:47–54
Decosterd I, Woolf CJ (2000) Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 87:149–158
Kim SH, Chung JM (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50:355–363
Capasso K, Manners M, Quershi R, Tian Y, Gao R, Hu H, Barrett J, Sacan A and Ajit S (2014) Effect of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor JNJ-26481585 in Pain. J Mol Neurosci 1–9
Qureshi R, Sacan A (2013) A novel method for the normalization of microRNA RT-PCR data. BMC Med Genet 6:S14
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 57:289–300
Friedman RC, Farh KK-H, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1–13
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2008) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57
Mogil JS (2009) Animal models of pain: progress and challenges. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:283–294
Kawaguchi M, Satoh Y, Otsubo Y, Kazama T (2014) Molecular hydrogen attenuates neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS ONE 9, e100352
von Schack D, Agostino MJ, Murray BS, Li Y, Reddy PS, Chen J, Choe SE, Strassle BW, Li C, Bates B et al (2011) Dynamic changes in the microRNA expression profile reveal multiple regulatory mechanisms in the spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. PLoS One 6, e17670
Kusuda R, Cadetti F, Ravanelli M, Sousa T, Zanon S, De Lucca F, Lucas G (2011) Differential expression of microRNAs in mouse pain models. Mol Pain 7:17
Aldrich BT, Frakes EP, Kasuya J, Hammond DL, Kitamoto T (2009) Changes in expression of sensory organ-specific microRNAs in rat dorsal root ganglia in association with mechanical hypersensitivity induced by spinal nerve ligation. Neuroscience 164:711–723
Strickland IT, Richards L, Holmes FE, Wynick D, Uney JB, Wong L-F (2011) Axotomy-induced miR-21 promotes axon growth in adult dorsal root ganglion neurons. PLoS ONE 6, e23423
Tan P-H and Liu C-C (2013) 39th annual regional anesthesiology and acute pain medicine meeting. American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine
Strickland ER, Hook MA, Balaraman S, Huie JR, Grau JW, Miranda RC (2011) MicroRNA dysregulation following spinal cord contusion: implications for neural plasticity and repair. Neuroscience 186:146–160
Curtale G, Renzi TA, Locati M (2012) P142 miR-146b: IL-10-dependent negative regulator of inflammation. Cytokine 59:565
Sisignano M, Baron R, Scholich K and Geisslinger G (2014) Mechanism-based treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Neurol, advance online publication
Seretny M, Currie GL, Sena ES, Ramnarine S, Grant R, MacLeod MR, Colvin LA and Fallon M Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PAIN®
Chiechio S, Zammataro M, Morales ME, Busceti CL, Drago F, Gereau RWT, Copani A, Nicoletti F (2009) Epigenetic modulation of mGlu2 receptors by histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory pain. Mol Pharmacol 75:1014–1020
Bai G, Wei D, Zou S, Ren K, Dubner R (2010) Inhibition of class II histone deacetylases in the spinal cord attenuates inflammatory hyperalgesia. Mol Pain 6:51
Denk F, Huang W, Sidders B, Bithell A, Crow M, Grist J, Sharma S, Ziemek D, Rice ASC, Buckley NJ et al (2013) HDAC inhibitors attenuate the development of hypersensitivity in models of neuropathic pain. Pain 154:1668–1679
Sun Y, Sahbaie P, Liang DY, Li WW, Li XQ, Shi XY, Clark JD (2013) Epigenetic regulation of spinal CXCR2 signaling in incisional hypersensitivity in mice. Anesthesiology 119:1198–1208
Liang D-Y, Sun Y, Shi X-Y, Sahbaie P, Clark J (2014) Epigenetic regulation of spinal cord gene expression controls opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Mol Pain 10:59
Chen L, Yang G, Grosser T (2013) Prostanoids and inflammatory pain. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat 104–105:58–66
Wei Y, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Chan L, Zhu M, Heyll K, Corbalán-Campos J, Hartmann P, Thiemann A, Weber C, Schober A (2013) The microRNA-342-5p fosters inflammatory macrophage activation through an Akt1- and microRNA-155–dependent pathway during atherosclerosis. Circulation 127:1609–1619
Comer BS, Camoretti-Mercado B, Kogut PC, Halayko AJ, Solway J, Gerthoffer WT (2014) MicroRNA-146a and microRNA-146b expression and anti-inflammatory function in human airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L727–734
Sonkoly E, Ståhle M, Pivarcsi A (2008) MicroRNAs and immunity: novel players in the regulation of normal immune function and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol 18:131–140
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277–D280
Shi Y, Yuan S, Li B, Wang J, Carlton S, Chung K, Chung J, Tang S-J (2012) Regulation of Wnt signaling by nociceptive input in animal models. Mol Pain 8:47
Zhang YK, Huang ZJ, Liu S, Liu YP, Song AA, Song XJ (2013) WNT signaling underlies the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rodents. J Clin Invest 123:2268–2286
Simonetti M, Agarwal N, Stösser S, Bali KK, Karaulanov E, Kamble R, Pospisilova B, Kurejova M, Birchmeier W, Niehrs C et al (2014) Wnt-Fzd signaling sensitizes peripheral sensory neurons via distinct noncanonical pathways. Neuron 83:104–121
Zhao J, Lee MC, Momin A, Cendan CM, Shepherd ST, Baker MD, Asante C, Bee L, Bethry A, Perkins JR et al (2010) Small RNAs control sodium channel expression, nociceptor excitability, and pain thresholds. J Neurosci 30:10860–10871
LaCroix-Fralish ML, Austin JS, Zheng FY, Levitin DJ, Mogil JS (2011) Patterns of pain: meta-analysis of microarray studies of pain. Pain 152:1888–1898
Rosso SB, INESTROSA NC, Rosso SB (2013) WNT signalling in neuronal maturation and synaptogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:103
Kuner R (2010) Central mechanisms of pathological pain. Nat Med 16:1258–1266
Ueno K, Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Dahiya R (2013) Frizzled homolog proteins, microRNAs and Wnt signaling in cancer. Int J Cancer 132:1731–1740
Schepeler T (2013) Emerging roles of MicroRNAs in the Wnt signaling network. Crit Rev Oncog 18:357–371
Zhang L, Wrana JL (2014) The emerging role of exosomes in Wnt secretion and transport. Curr Opin Genet Dev 27:14–19
McDonald MK, Tian Y, Qureshi RA, Gormley M, Ertel A, Gao R, Aradillas Lopez E, Alexander GM, Sacan A, Fortina P et al (2014) Functional significance of macrophage-derived exosomes in inflammation and pain. Pain 155:1527–1539
Squadrito ML, Baer C, Burdet F, Maderna C, Gilfillan GD, Lyle R, Ibberson M, De Palma M (2014) Endogenous RNAs modulate MicroRNA sorting to exosomes and transfer to acceptor cells. Cell Rep 8:1432–1446
Jaggi AS, Jain V, Singh N (2011) Animal models of neuropathic pain. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 25:1–28
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Huijuan Hu for critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Rita Allen Foundation to Seena Ajit.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Drexel University College of Medicine and the experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(XLSX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qureshi, R.A., Tian, Y., McDonald, M.K. et al. Circulating microRNA Signatures in Rodent Models of Pain. Mol Neurobiol 53, 3416–3427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9281-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9281-4