Abstract
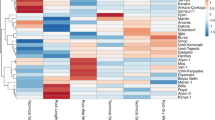
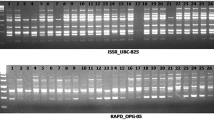
The objective of this study was to analyze the genetic relationships, using PCR-based ISSR markers, among 70 Indian flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) genotypes actively utilized in flax breeding programs. Twelve ISSR primers were used for the analysis yielding 136 loci, of which 87 were polymorphic. The average number of amplified loci and the average number of polymorphic loci per primer were 11.3 and 7.25, respectively, while the percent loci polymorphism ranged from 11.1 to 81.8 with an average of 63.9 across all the genotypes. The range of polymorphism information content scores was 0.03–0.49, with an average of 0.18. A dendrogram was generated based on the similarity matrix by the Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA), wherein the flax genotypes were grouped in five clusters. The Jaccard’s similarity coefficient among the genotypes ranged from 0.60 to 0.97. When the omega-3 alpha linolenic acid (ALA) contents of the individual genotypes were correlated with the clusters in the dendrogram, the high ALA containing genotypes were grouped in two clusters. This study identified SLS 50, Ayogi, and Sheetal to be the most diverse genotypes and suggested their use in breeding programs and for developing mapping populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zohary, D., & Hopf, M. (1993). Domestication of plants in the old world (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford Science publications, Claredon Press.
Caston, L., & Leeson, S. (1990). Research note: Dietary flaxseed and egg composition. Poultry Science, 69, 1617–1620.
Thiessen, D. (2002). Flax as a feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Effects on growth, carcass composition and microbial populations. Saskatchewan Flax Grower, 4, 5.
Fu, Y. B., Diederichsen, A., Richards, K. W., & Peterson, G. (2002). Genetic diversity within a range of cultivars and landraces of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) as revealed by RAPDs. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 49(2), 167–174.
Diederichsen, A. (2001). Comparison of genetic diversity of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) between Canadian cultivars and a world collection. Plant Breeding, 120, 360–362.
Diederichsen, A., & Fu, Y. B. (2006). Phenotypic and molecular (RAPD) differentiation of four infraspecific groups of cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L. subsp. usitatissimum). Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 53, 77–90.
von Kulpa, W., & Danert, S. (1962). Zur Systematik von Linum usitatissimum L. Die Kulturpflanze 3 (pp. 341–388). Berlin: Akademie Verlag.
Månsby, E., Díaz, O., & von Bothmer, R. (2000). Preliminary study of genetic diversity in Swedish flax (Linum usitatissimum). Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 47, 417–424.
Oh, T. J., Gorman, M., & Cullis, C. A. (2000). RFLP and RAPD mapping in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 101, 590–593.
Fu, Y. B., Rowland, G. G., Duguid, S. D., & Richards, K. W. (2003). RAPD analysis of 54 North American flax cultivars. Crop Science, 43, 1510–1515.
van Treuren, R., van Soest, L. J. M., & van Hintum, T. J. L. (2001). Marker-assisted rationalisation of genetic resource collections: A case study in flax using AFLPs. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 103, 144–152.
Wiesner, I., & Wiesnerova, D. (2003). Insertion of a reamplification round into the ISSR-PCR protocol gives new flax fingerprinting patterns. Cellular and Molecular Biology Letters, 8, 743–748.
Wiesner, I., & Wiesnerova, D. (2004). Statistical correlations of primer thermodynamic stability Delta G degree for enhanced flax ISSR-PCR cultivar authentication. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 52, 2568–2571.
Zietkiewicz, E., Rafalaski, A., & Labuda, D. (1994). Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics, 20, 176–183.
Murray, M. G., & Thompson, W. F. (1980). Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 8(19), 4321–4325.
Manku, M. S., Horrobin, D. F., Huang, Y. S., & Morse, N. (1983). Fatty acids in plasma and red cell membranes in normal humans. Lipids, 18, 906–908.
Yap, I. V., & Nelson, R. J. (1996). Winboot: A program for performing bootstrap analysis of binary data to determine the confidence limits of UPGMA-based dendrograms. IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 14. Manila, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute.
Kovach, W. L. (1998). Multivariate statistical package for Windows, ver. 3.0. Wales. United Kingdom: Kovach company services.
Smith, J. S. C., Chin, E. C. L., Shu, H., Smith, O. S., Wall, S. J., Senior, M. L., et al. (1997). An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): Comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 95, 163–173.
Ghislain, M., Zhang, D., Fajardo, D., Huamann, Z., & Hijmans, R. (1999). Marker-assisted sampling of the cultivated Andean potato Solanum phureja collection using RAPD markers. Genetics Resources and Crop Evolution, 46, 547–555.
Wetton, J. H., Carter, R. E., Parkin, D. T., & Walters, D. C. (1987). Demographic study of a wild house sparrow population by DNA fingerprinting. Nature, 327, 147–149.
Nei, M. (1978). Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics, 89, 583–590.
Li, Z., & Nelson, R. L. (2001). Genetic diversity among soybean accessions from three countries measured by RAPDs. Crop Science, 41, 1337–1347.
Messmer, M. M., Melchinger, A. E., Boppenmaier, J., Herrmann, R. G., & Brunklans-Jung, E. (1992). RFLP analyses of early-maturing European maize germplasm: Genetic diversity among Flint and dent inbreds. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 83, 1003–1020.
Charters, Y. M., Robertson, A., Wilkinson, M. J., & Ramsey, G. (1996). PCR analysis of oilseed rape cultivars (Brassica napus L. Ssp. oleifera) using 5′ A-anchored simple sequence repeat (SSR) primers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 92, 442–447.
Huang, J. C., & Sun, M. (2000). Genetic diversity and relationships of sweetpotato and its wild relatives in Ipomoea series Batatas (Convolvlaceae) as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and restriction analysis of chloroplast DNA. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 100, 1050–1060.
Wiesnerova, D., & Wiesner, I. (2004). ISSR-based clustering of cultivated flax germplasm is statistically correlated to thousand seed mass. Molecular Biotechnology, 26(3), 207–214.
Xiao, J., Li, J., Yuan, L., McCouch, S. R., & Tanksley, S. D. (1996). Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance and heterosis in rice as revealed by PCR-based markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 92, 637–643.
Lanza, L. L. B., De Souza, C. L., Jr, Ottoboni, L. M. M., Vieira, M. L. C., & De Souza, A. P. (1997). Genetic distance of inbred lines and prediction of maize single-cross performance using RAPD markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 94(8), 1023–1030.
Paz, M. M., & Veilleux, R. E. (1997). Genetic diversity based on randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and its relationship with the performance of diploid potato hybrids. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 122(6), 740–747.
Chowdari, K. V., Venkatachalam, S. R., Davierwala, A. P., Gupta, V. S., Ranjekar, P. K., & Govila, O. P. (1998). Hybrid performance and genetic distance as revealed by the (GATA)4 microsatellite and RAPD markers in pearl millet. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 97(1–2), 163–169.
Sant, V. J., Patankar, A. G., Sarode, N. D., Mhase, L. B., Sainani, M. N., Deshmukh, R. B., et al. (1999). Potential of DNA markers in detecting divergence and in analysing heterosis in Indian elite chickpea cultivars. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 98(8), 1217–1225.
Riaz, A., Li, G., Quresh, Z., Swati, M. S., & Quiros, C. F. (2001). Genetic diversity of oilseed Brassica napus inbred lines based on sequence-related amplified polymorphism and its relation to hybrid performance. Plant Breeding, 120(5), 411–415.
Joshi, S. P., Bhave, S. G., Chowdari, K. V., Apte, G. S., Dhonukshe, B. L., Lalitha, K., et al. (2001). Use of DNA markers in prediction of hybrid performance and heterosis for a three-line hybrid system in rice. Biochemical Genetics, 39(5–6), 179–200.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director, NCL and the Director, IRSHA for providing the lab facilities to conduct the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajwade, A.V., Arora, R.S., Kadoo, N.Y. et al. Relatedness of Indian Flax Genotypes (Linum usitatissimum L.): An Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) Primer Assay. Mol Biotechnol 45, 161–170 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9256-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9256-7