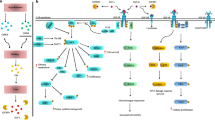
Abstract
Gastric cancer is a major cause of treatment-related mortality and morbidity worldwide, it ranks as the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death in males and fifth most common cause of cancer-related death in women. The prognosis of advanced cases with gastric cancer looks poor with the majority dying within 1 year of diagnosis of metastatic disease. Thus, intensive search for new innovative treatments has been a major focus of current oncology research. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) pathway has been evaluated extensively in preclinical settings of gastric cancer. Initially, a number of studies have shown a potential role for aberrant tissue expression of IGFR-related markers in the process of gastric carcinogenesis, and a number of other studies have shown a clear association between IGFR expression and aggressive histopathological subtypes. However, clinical introduction of IGFR inhibitors into gastric cancer treatment has been delayed compared to other solid tumors. This review provides concise evaluation of prognostic significance of IGF pathway-related markers in gastric cancer with assessment of potential therapeutic strategies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Fitzgerald R, Hardwick R, Huntsman D. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: updated consensus guidelines for clinical management and directions for future research. J Med Genet. 2010;47:436–44.
Kordes S, Cats A, Meijer SL, van Laarhoven HW. Targeted therapy for advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;90:68–76.
Abdel-Rahman O. Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/mesenchymal epithelial transition pathway in gastric cancer: biological rationale and clinical applications. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014. doi:10.1586/14737140.2014.974564.
Abdel-Rahman O. Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway in gastric cancer: preclinical and clinical aspects. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.05.012.
Miller BS, Yee D. Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(22):10123–7.
Rosenthal SM, Cheng ZQ. Opposing early and late effects of insulin-like growth factor I on differentiation and the cell cycle regulatory retinoblastoma protein in skeletal myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92(22):10307–11. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10307.
Hamelers IH, van Schaik RF, Sipkema J, Sussenbach JS, Steenbergh PH. Insulin-like growth factor I triggers nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 in MCF-7S breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(49):47645–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208727200.
Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995;16(1):3–34. doi:10.1210/er.16.1.3.
Hewish M, Chau I, Cunningham D. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor targeted therapeutics: novel compounds and novel treatment strategies for cancer medicine. Recent Pat Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery. 2009;4(1):54–72.
Ennishi D, Shitara K, Ito H, Hosono S, Watanabe M, Ito S, et al. Association between insulin-like growth factor-1 polymorphisms and stomach cancer risk in a Japanese population. Cancer Sci. 2011;102(12):2231–5.
Wang HB, Zhou CJ, Song SZ, Chen P, Xu WH, Liu B, et al. Evaluation of Nrf2 and IGF-1 expression in benign, premalignant and malignant gastric lesions. Pathol Res Pract. 2011;207(3):169–73.
Liu WD, Yu R, Zhou GR. [Expression and significance of IGF-1R and VEGF in gastric carcinoma]. Xi bao yu fen zi mian yi xue za zhi=. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;25(6):529–30.
Pham TM, Fujino Y, Kikuchi S, Tamakoshi A, Yatsuya H, Matsuda S, Yoshimura T. A nested case-control study of stomach cancer and serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-2 and IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-3. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43(10):1611–6.
Gryko M, Kiśluk J, Cepowicz D, Zińczuk J, Kamocki Z, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 correlate with lymphatic metastases in human gastric cancer. Pol J Pathol. 2014;65(2):135–40.
Kuang RG, Wu HX, Hao GX, Wang JW, Zhou CJ. Expression and significance of IGF-2, PCNA, MMP-7, and α-actin in gastric carcinoma with Lauren classification. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2013;24(2):99–108.
Shitara K, Ito S, Misawa K, Ito Y, Ito H, Hosono S, et al. Genetic polymorphism of IGF-I predicts recurrence in patients with gastric cancer who have undergone curative gastrectomy. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(3):659–64.
Shou ZX, He QJ, Chu YQ, Zhao ZS. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor-1 in gastric carcinoma and their clinicopathological significance. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;48(10):774–9.
Ge J, Chen Z, Wu S, Chen J, Li X, Li J, Yin J. Expression levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 indicate poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Digestion. 2009;80(3):148–58.
Oh SY, Kwon HC, Kim SH, Lee S, Lee JH, Graves CA, et al. Prognostic significance of serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with FOLFOX chemotherapy. Chemotherapy 2013;58(6):426–34.
Matsubara J, Hirashima Y, Yamada Y. Impact of HER2, EGFR, IGF-1R, and VEGFR expressions on the outcome of chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Gan to kagaku ryoho. Cancer Chemother. 2010;37(8):1489–96.
Graziano F, Ruzzo A, Canestrari E, Catalano V, Santini D, Galluccio N, et al. Host genetic variants in the IGF binding protein-3 impact on survival of patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with palliative chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics 2010;11(9):1247–56.
Ozkan EE. Plasma and tissue insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) as a prognostic marker for prostate cancer and anti-IGF-IR agents as novel therapeutic strategy for refractory cases: a review. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;344(1):1–24.
Li H, Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Min Y, Ohashi H, Ii M, et al. Insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor blockade reduces tumor angiogenesis and enhances the effects of bevacizumab for a human gastric cancer cell line, MKN45. Cancer 2011;117(14):3135–47.
Wang Y, Adachi Y, Imsumran A, Yamamoto H, Piao W, Li H, et al. Targeting for insulin-like growth factor-I receptor with short hairpin RNA for human digestive/gastrointestinal cancers. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(2):159–70.
Adachi Y, Li R, Yamamoto H, Min Y, Piao W, Wang Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor blockade reduces the invasiveness of gastrointestinal cancers via blocking production of matrilysin. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(8):1305–13.
Becerra CR, Salazar R, Garcia-Carbonero R, Thomas AL, Vázquez-Mazón FJ, Cassidy J, et al. Figitumumab in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with standard therapies: a nonrandomized, open-label, phase II trial. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73(4):695–702.
Kindler HL, Richards DA, Garbo LE, Garon EB, Stephenson JJ, Rocha-Lima CM, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 study of ganitumab (AMG 479) or conatumumab (AMG 655) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(11):2834–42.
Harzstark AL, Ryan C, Diamond M, Jones J, Zavodovskaya M, Maddux B, et al. A phase I trial of nordihydroguareacetic acid (NDGA) in patients with non-metastatic prostate cancer and rising PSA. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007;25(18 suppl):15500.
Langer CJ, Novello S, Park K, Krzakowski M, Karp DD, Mok T, et al. Randomized, phase III trial of first-line figitumumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin versus paclitaxel and carboplatin alone in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(19):2059–66.
Scagliotti GV, Bondarenko I, Blackhall F, Barlesi F, Hsia TC, Jassem J et al. Randomized, phase III trial of figitumumab in combination with erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in patients with non-adenocarcinoma non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014. pii: mdu517.
De Bono JS, Piulats JM, Pandha HS, Petrylak DP, Saad F, Aparicio LMA, et al. Phase II randomized study of figitumumab plus docetaxel and docetaxel alone with crossover for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(7):1925–34.
Schmitz S, Kaminsky-Forrett MC, Henry S, Zanetta S, Geoffrois L, Bompas E, et al. Phase II study of figitumumab in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: clinical activity and molecular response (GORTEC 2008-02). Ann Oncol. 2012;23(8):2153–61.
Zhang Z, Wang J, Ji D, Wang C, Liu R, Wu Z, et al. Functional genetic approach identifies MET, HER3, IGF1R, INSR pathways as determinants of lapatinib unresponsiveness in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(17):4559–73.
Pavlicek A, Lira ME, Lee NV, Ching KA, Ye J, Cao J, et al. Molecular predictors of sensitivity to the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor figitumumab (CP-751,871). Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(12):2929–39.
McCaffery I, Tudor Y, Deng H, Tang R, Suzuki S, Badola S, et al. Putative predictive biomarkers of survival in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma treated with gemcitabine and ganitumab, an IGF1R inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(15):4282–9.
Kim JG, Kang MJ, Yoon YK, Kim HP, Park J, Song SH, et al. Heterodimerization of glycosylated insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and insulin receptors in cancer cells sensitive to anti-IGF1R antibody. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(3):e33322.
Abou-Alfa GK, Capanu M, O’Reilly EM, Ma J, Chou JF, Gansukh B, et al. A phase II study of cixutumumab (IMC-A12, NSC742460) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2014;60(2):319–24.
Bendell JC, Jones SF, Hart L, Spigel DR, Lane CM, Earwood C, et al. A phase Ib study of linsitinib (OSI-906), a dual inhibitor of IGF-1R and IR tyrosine kinase, in combination with everolimus as treatment for patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Investig New Drugs. 2014. doi:10.1007/s10637-014-0177-3.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Rahman, O. Insulin-like growth factor pathway aberrations and gastric cancer; evaluation of prognostic significance and assessment of therapeutic potentials. Med Oncol 32, 431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0431-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0431-8