Abstract
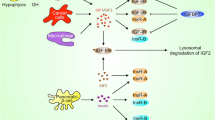
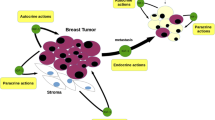
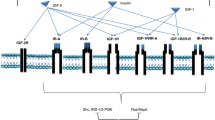
Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women worldwide. Although patients are often diagnosed in the early and curable stages, the treatment of metastatic breast cancer remains a major clinical challenge. The combination of chemotherapy with new targeting agents, such as bevacizumab, is helpful in improving patient survival; however, novel treatment strategies are required to improve clinical outcomes. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) is a tyrosine kinase cell surface receptor which is involved in the regulation of cell growth and metabolism. Previous studies have shown that activation of the IGF-IR signaling pathway promotes proliferation, survival, and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Additionally, overexpression of IGF-IR is associated with breast cancer cell resistance to anticancer therapies. Recently, IGF-IR has been introduced as a marker of stemness in breast cancer cells and there is also accumulating evidence that IGF-IR contributes to the establishment and maintenance of breast cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Therefore, pharmacological or molecular targeting of IGF-IR could be a promising strategy, in the treatment of patients with breast cancer, particularly in order to circumvent the therapeutic resistance and targeting breast cancer stem/progenitors. Currently, many strategies have been developed for targeting IGF-IR, some have entered clinical trials and some are in preclinical stages for breast cancer therapy. In this review, we will first discuss on the biology of IGF-IR in an attempt to find the role of this receptor in breast cancer and then discuss about therapeutic strategies to target this receptor.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcotte R, Sayad A, Iorio C, Moffat J, Neel BG. Abstract PR14: integrative functional genomics of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:PR14-PR.
Yang Y, Yee D. Targeting insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2012;17:251–61.
Motallebnezhad M, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Qamsari ES, Bagheri S, Gharibi T, Yousefi M. The immunobiology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015:1–20.
Kazemi T, Younesi V, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Yousefi M. Immunotherapeutic approaches for cancer therapy: an updated review. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2015:1–11.
Garcia-Closas M, Hall P, Nevanlinna H, Pooley K, Morrison J, Richesson DA, et al. Heterogeneity of breast cancer associations with five susceptibility loci by clinical and pathological characteristics. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000054.
Mauro L, Naimo GD, Ricchio E, Panno ML, Andò S. Cross-talk between adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Front Oncol. 2015;5.
Kaleko M, Rutter W, Miller A. Overexpression of the human insulin-like growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:464–73.
Pietrzkowski Z, Lammers R, Carpenter G, Soderquist A, Limardo M, Phillips P, et al. Constitutive expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor abrogates all requirements for exogenous growth factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1992;3:199–205.
Seccareccia E, Brodt P. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in malignancy: an update. Growth Hormon IGF Res. 2012;22:193–9.
Law JH, Habibi G, Hu K, Masoudi H, Wang MY, Stratford AL, et al. Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-i/insulin receptor is present in all breast cancer subtypes and is related to poor survival. Cancer Res. 2008;68:10238–46.
Stewart AJ, Johnson MD, May F, Westley B. Role of insulin-like growth factors and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor in the estrogen-stimulated proliferation of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:21172–8.
Christopoulos PF, Msaouel P, Koutsilieris M. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:1.
Farabaugh SM, Boone DN, Lee AV. Role of IGF1R in breast cancer subtypes, stemness, and lineage differentiation. Front Endocrinol. 2015;6.
Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:915–28.
Brahmkhatri VP, Prasanna C, Atreya HS. Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer: novel targeted therapies. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015.
Fürstenberger G, Senn H-J. Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:298–302.
Danielsen A, Larsen E, Gammeltoft S. Chromaffin cells express two types of insulin-like growth factor receptors. Brain Res. 1990;518:95–100.
Casa AJ, Dearth RK, Litzenburger BC, Lee AV, Cui X. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway: a key player in cancer therapeutic resistance. Front Biosci. 2007;13:3273–87.
Tao Y, Pinzi V, Bourhis J, Deutsch E. Mechanisms of disease: signaling of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathway—therapeutic perspectives in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2007;4:591–602.
Iams WT, Lovly CM. Molecular pathways: clinical applications and future direction of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor pathway blockade. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:4270–7.
Kooijman R, Lauf JJ, Kappers AC, Rijkers GT. Insulin-like growth factor induces phosphorylation of immunoreactive insulin receptor substrate and its association with phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in human thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1995;182:593–7.
Soon L, Flechner L, Gutkind JS, Wang L-H, Baserga R, Pierce JH, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I synergizes with interleukin 4 for hematopoietic cell proliferation independent of insulin receptor substrate expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:3816–28.
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:505–18.
Wu J, Yu E. Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-IR) as a target for prostate cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33:607–17.
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D, Brodt P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:20–47.
DeAngelis T, Wu K, Pestell R, Baserga R. The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor and resistance to DACH1. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:1956–9.
Goel HL, Sayeed A, Breen M, Zarif MJ, Garlick DS, Leav I, et al. β1 integrins mediate resistance to ionizing radiation in vivo by inhibiting c-Jun amino terminal kinase 1. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228:1601–9.
Papa V, Gliozzo B, Clark GM, McGuire WL, Moore D, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3736–40.
Jones R, Campbell C, Gunther E, Chodosh L, Petrik J, Khokha R, et al. Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene. 2007;26:1636–44.
Gross JM, Yee D. The type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: biology and therapeutic relevance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:327–36.
Karey KP, Sirbasku DA. Differential responsiveness of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and T47D to growth factors and 17β-estradiol. Cancer Res. 1988;48:4083–92.
Karamouzis MV, Papavassiliou AG. Targeting insulin-like growth factor in breast cancer therapeutics. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;84:8–17.
Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490:61–70.
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G, et al. Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:7203–15.
Samani A, Brodt P. The receptor for the type I insulin-like growth factor and its ligands regulate multiple cellular functions that impact on metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2001;10:289–312 .viii
Long L, Navab R, Brodt P. Regulation of the Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3243–7.
Dunn SE, Ehrlich M, Sharp NJ, Reiss K, Solomon G, Hawkins R, et al. A dominant negative mutant of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3353–61.
Zhu C, Qi X, Chen Y, Sun B, Dai Y, Gu Y. PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:1587–94.
Sachdev D, Hartell JS, Lee AV, Zhang X, Yee D. A dominant negative type I insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits metastasis of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5017–24.
Saldana SM, Lee H-H, Lowery FJ, Khotskaya YB, Xia W, Zhang C, et al. Inhibition of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling attenuates the development of breast cancer brain metastasis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73406.
Chang W-W, Lin R-J, Yu J, Chang W-Y, C-H F, Lai AC-Y, et al. The expression and significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its pathway on breast cancer stem/progenitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15:R39.
Malaguarnera R, Belfiore A. The emerging role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling in cancer stem cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5.
Guvakova MA, Surmacz E. The activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin. Exp Cell Res. 1999;251:244–55.
Taliaferro-Smith L, Oberlick E, Liu T, McGlothen T, Alcaide T, Tobin R, et al. FAK activation is required for IGF1R-mediated regulation of EMT, migration, and invasion in mesenchymal triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:4757.
Stewart A, Westley B, May F. Modulation of the proliferative response of breast cancer cells to growth factors by oestrogen. Br J Cancer. 1992;66:640.
Oesterreich S, Zhang P, Guler RL, Sun X, Curran EM, Welshons WV, et al. Re-expression of estrogen receptor α in estrogen receptor α-negative MCF-7 cells restores both estrogen and insulin-like growth factor-mediated signaling and growth. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5771–7.
Vignon F, Bouton M-M, Rochefort H. Antiestrogens inhibit the mitogenic effect of growth factors on breast cancer cells in the total absence of estrogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;146:1502–8.
Brockdorff B, Heiberg I, Lykkesfeldt A. Resistance to different antiestrogens is caused by different multi-factorial changes and is associated with reduced expression of IGF receptor Ialpha. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003;10:579–90.
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Barrow D, Gee JMW, Nicholson RI. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Endocrinology. 2005;146:4609–18.
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, Qin L, Tsimelzon A, Huang S, et al. Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 2008;68:826–33.
Arnedos M, Drury S, Afentakis M, A’hern R, Hills M, Salter J, et al. Biomarker changes associated with the development of resistance to aromatase inhibitors (AIs) in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:605–10.
Miller TW, editor Endocrine resistance: what do we know? American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2013.
De Marco P, Bartella V, Vivacqua A, Lappano R, Santolla M, Morcavallo A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I regulates GPER expression and function in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2013;32:678–88.
De Marco P, Romeo E, Vivacqua A, Malaguarnera R, Abonante S, Romeo F, et al. GPER1 is regulated by insulin in cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21:739–53.
Ignatov A, Ignatov T, Weißenborn C, Eggemann H, Bischoff J, Semczuk A, et al. G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPR30 and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;128:457–66.
Mo Z, Liu M, Yang F, Luo H, Li Z, Tu G, et al. GPR30 as an initiator of tamoxifen resistance in hormone-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15:1–15.
Sjöström M, Hartman L, Grabau D, Fornander T, Malmström P, Nordenskjöld B, et al. Lack of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) in the plasma membrane is associated with excellent long-term prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;145:61–71.
Maor S, Mayer D, Yarden RI, Lee AV, Sarfstein R, Werner H, et al. Estrogen receptor regulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in breast tumor cells: involvement of transcription factor Sp1. J Endocrinol. 2006;191:605–12.
Kolacinska A, Chalubinska J, Zawlik I, Szymanska B, Borowska-Garganisz E, Nowik M, et al. Apoptosis-, proliferation, immune function-, and drug resistance-related genes in ER positive, HER2 positive and triple negative breast cancer. Neoplasma. 2011;59:424–32.
Yerushalmi R, Gelmon KA, Leung S, Gao D, Cheang M, Pollak M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) in breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;132:131–42.
Shin S-J, Gong G, Lee HJ, Kang J, Bae YK, Lee A, et al. Positive expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is associated with a positive hormone receptor status and a favorable prognosis in breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2014;17:113–20.
Corcoran C, Rani S, Breslin S, Gogarty M, Ghobrial IM, Crown J, et al. miR-630 targets IGF1R to regulate response to HER-targeting drugs and overall cancer cell progression in HER2 over-expressing breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:1.
Zimon D, Pizon M, Pachmann U, Pachmann K. Abstract P4-15-20: insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) expression is highly correlated with HER2 amplification on circulating epithelial tumor cells (CETCs) in breast cancer-this may be the reason for resistance to trastuzumab. Cancer Res. 2015;75:P4-15-20-P4-15-20.
Ye X-M, Zhu H-Y, Bai W-D, Wang T, Wang L, Chen Y, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-375 induces trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:1.
Sanabria-Figueroa E, Donnelly SM, Foy KC, Buss MC, Castellino RC, Paplomata E, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling increases the invasive potential of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-overexpressing breast cancer cells via Src-focal adhesion kinase and Forkhead box protein M1. Mol Pharmacol. 2015;87:150–61.
Chen C, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Tsao SW, Zhang M-Y. Superior antitumor activity of a novel bispecific antibody cotargeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:90–100.
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Yang X, Lind SE, Thor AD. Potent anti-proliferative effects of metformin on trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells via inhibition of erbB2/IGF-1 receptor interactions. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:2959–66.
Hartog H, Horlings HM, van der Vegt B, Kreike B, Ajouaou A, van de Vijver MJ, et al. Divergent effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression on prognosis of estrogen receptor positive versus triple negative invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;129:725–36.
Girgert R, Emons G, Gründker C. Inactivation of GPR30 reduces growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells: possible application in targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;134:199–205.
Steiman J, Peralta EA, Louis S, Kamel O. Biology of the estrogen receptor, GPR30, in triple negative breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2013;206:698–703.
Litzenburger BC, Creighton CJ, Tsimelzon A, Chan BT, Hilsenbeck SG, Wang T, et al. High IGF-IR activity in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines and tumorgrafts correlates with sensitivity to anti-IGF-IR therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2314–27.
Mancini M, Gariboldi M, Taiana E, Bonzi M, Craparotta I, Pagin M, et al. Co-targeting the IGF system and HIF-1 inhibits migration and invasion by (triple-negative) breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2014;110.
Abramovitch S, Glaser T, Ouchi T, Werner H. BRCA1-Sp1 interactions in transcriptional regulation of the IGF-IR gene. FEBS Lett. 2003;541:149–54.
Maor S, Yosepovich A, Papa MZ, Yarden RI, Mayer D, Friedman E, et al. Elevated insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) levels in primary breast tumors associated with BRCA1 mutations. Cancer Lett. 2007;257:236–43.
Kang H, Yi Y, Kim H, Hong Y, Seong Y, Bae I. BRCA1 negatively regulates IGF-1 expression through an estrogen-responsive element-like site. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e336.
Denduluri SK, Idowu O, Wang Z, Liao Z, Yan Z, Mohammed MK, et al. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in tumorigenesis and the development of cancer drug resistance. Genes Diseases. 2015;2:13–25.
Heskamp S, Boerman OC, Molkenboer-Kuenen JD, Wauters CA, Strobbe LJ, Mandigers CM, et al. Upregulation of IGF-1R expression during neoadjuvant therapy predicts poor outcome in breast cancer patients. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0117745.
Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D. Minireview: IGF, insulin, and cancer. Endocrinology. 2011;152:2546–51.
Winder T, Giamas G, Wilson P, Zhang W, Yang D, Bohanes P, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor polymorphism defines clinical outcome in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014;14:28–34.
Liu S, Meng X, Chen H, Liu W, Miller T, Murph M, et al. Targeting tyrosine-kinases and estrogen receptor abrogates resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:9049.
Fagan DH, Uselman RR, Sachdev D, Yee D. Acquired resistance to tamoxifen is associated with loss of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor: implications for breast cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3372–80.
Cosaceanu D, Budiu R, Carapancea M, Castro J, Lewensohn R, Dricu A. Ionizing radiation activates IGF-1R triggering a cytoprotective signaling by interfering with Ku-DNA binding and by modulating Ku86 expression via a p38 kinase-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 2007;26:2423–34.
Wen B, Deutsch E, Marangoni E, Frascona V, Maggiorella L, Abdulkarim B, et al. Tyrphostin AG 1024 modulates radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:2017.
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L, Yuan J, Havre PA, Gumbs AA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3079–83.
Li P, Veldwijk MR, Zhang Q, Li Z-b, Xu W-c, Fu S. Co-inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 enhances radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:297.
Beech DJ, Parekh N, Pang Y. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor antagonism results in increased cytotoxicity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin and taxol. Oncol Rep. 2001;8:325–9.
Dunn SE, Hardman RA, Kari FW, Barrett JC. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2687–93.
Guevara-Aguirre J, Balasubramanian P, Guevara-Aguirre M, Wei M, Madia F, Cheng C-W, et al. Growth hormone receptor deficiency is associated with a major reduction in pro-aging signaling, cancer, and diabetes in humans. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:70ra13.
Szereday Z, Schally AV, Varga JL, Kanashiro CA, Hebert F, Armatis P, et al. Antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone inhibit the proliferation of experimental non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7913–9.
Yin D, Vreeland F, Schaaf LJ, Millham R, Duncan BA, Sharma A. Clinical pharmacodynamic effects of the growth hormone receptor antagonist pegvisomant: implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1000–9.
Gao J, Chesebrough JW, Cartlidge SA, Ricketts S-A, Incognito L, Veldman-Jones M, et al. Dual IGF-I/II–neutralizing antibody MEDI-573 potently inhibits IGF signaling and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1029–40.
Adam PJ, Friedbichler K, Hofmann MH, Bogenrieder T, Borges E, Adolf GR, editors. BI 836845, a fully human IGF ligand neutralizing antibody, to improve the efficacy of rapamycin by blocking rapamycin-induced AKT activation. ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings. 2012.
Chitnis MM, Yuen JS, Protheroe AS, Pollak M, Macaulay VM. The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6364–70.
Bohula EA, Playford MP, Macaulay VM. Targeting the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor as anti-cancer treatment. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2003;14:669–82.
Carboni JM, Wittman M, Yang Z, Lee F, Greer A, Hurlburt W, et al. BMS-754807, a small molecule inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1R/IR. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:3341–9.
Hou X, Huang F, Macedo LF, Harrington SC, Reeves KA, Greer A, et al. Dual IGF-1R/InsR inhibitor BMS-754807 synergizes with hormonal agents in treatment of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7597–607.
Durfort T, Tkach M, Meschaninova MI, Rivas MA, Elizalde PV, Venyaminova AG, et al. Small interfering RNA targeted to IGF-IR delays tumor growth and induces proinflammatory cytokines in a mouse breast cancer model. PLoS One. 2012;7:e29213.
Shen K, Liang Q, Xu K, Cui D, Jiang L, Yin P, et al. MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84:320–30.
Wang B, Wang H, Yang Z. MiR-122 inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. PLoS One. 2012;7:e47053.
Bähr C, Groner B. The insulin like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a drug target: novel approaches to cancer therapy. Growth Hormon IGF Res. 2004;14:287–95.
Clark AS, West K, Streicher S, Dennis PA. Constitutive and inducible Akt activity promotes resistance to chemotherapy, trastuzumab, or tamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1:707–17.
Becker MA, Ibrahim YH, Cui X, Lee AV, Yee D. The IGF pathway regulates ERα through a S6K1-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:516–28.
Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, Tkalcevic G, Rossi AM, Miller PE, et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2063–73.
Kurzrock R, Patnaik A, Aisner J, Warren T, Leong S, Benjamin R, et al. A phase I study of weekly R1507, a human monoclonal antibody insulin-like growth factor-I receptor antagonist, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2458–65.
Mahadevan D, Sutton GR, Arteta-Bulos R, Bowden CJ, Miller PJ, Swart RE, et al. Phase 1b study of safety, tolerability and efficacy of R1507, a monoclonal antibody to IGF-1R in combination with multiple standard oncology regimens in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73:467–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motallebnezhad, M., Aghebati-Maleki, L., Jadidi-Niaragh, F. et al. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer: biology and treatment strategies. Tumor Biol. 37, 11711–11721 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5176-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5176-x