Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of 18–27-nucleotides single-stranded RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. It has been demonstrated that miRNAs regulate a variety of physiological functions, including development, cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. There are growing evidence showed that miRNAs can affect the genesis and development of tumor and play a kind of tumor suppressor or oncogenic function by regulating its targetted gene-related signal pathway. miRNA-21 is one of the early discovered miRNAs in human cells, and the expression of miRNA-21 is significantly upregulated in different kinds of solid tumors. Its abnormal expression levels are closely associated with pathogenesis of cancers. This review summarizes the recent study on the field of miRNA-21 and its association with cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006;66(15):7390–4.
Schanen BC, Li X. Transcriptional regulation of mammalian miRNA genes. Genomics. 2011;97(1):1–6.
Asirvatham AJ, Magner WJ, Tomasi TB. miRNA regulation of cytokine genes. Cytokine. 2009;45(2):58–69.
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(9):597–610.
Kent OA, Mullendore M, Wentzel EA, Lopez-Romero P, Tan AC, Alvarez H, West K, Ochs MF, Hidalgo M, Arking DE, et al. A resource for analysis of microRNA expression and function in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8(21):2013–24.
Lu YC, Chen YJ, Wang HM, Tsai CY, Chen WH, Huang YC, Fan KH, Tsai CN, Huang SF, Kang CJ, et al. Oncogenic function and early detection potential of miRNA-10b in oral cancer as identified by microRNA profiling. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012;5(4):665–74.
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK. MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(3–4):369–78.
Luo X, Burwinkel B, Tao S, Brenner H. MicroRNA signatures: novel biomarker for colorectal cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20(7):1272–86.
Skrzypski M, Dziadziuszko R, Jassem J. MicroRNA in lung cancer diagnostics and treatment. Mutat Res. 2011;717(1–2):25–31.
Zhao L, Chen X, Cao Y. New role of microRNA: carcinogenesis and clinical application in cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(11):831–9.
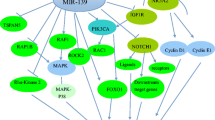
Moore LM, Zhang W. Targeting miR-21 in glioma: a small RNA with big potential. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010;14(11):1247–57.
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Spillane C. miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(Pt 4):918–25.
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G. miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(1):39–53.
Rossi S, Shimizu M, Barbarotto E, Nicoloso MS, Dimitri F, Sampath D, Fabbri M, Lerner S, Barron LL, Rassenti LZ, et al. microRNA fingerprinting of CLL patients with chromosome 17p deletion identify a miR-21 score that stratifies early survival. Blood. 2010;116(6):945–52.
Rask L, Balslev E, Jorgensen S, Eriksen J, Flyger H, Moller S, Hogdall E, Litman T, Nielsen BS. High expression of miR-21 in tumor stroma correlates with increased cancer cell proliferation in human breast cancer. APMIS. 2011;119(10):663–73.
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008;14(11):2348–60.
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K, Yang GH. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(11–12):846–52.
Wei J, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Mei Z, Cheng T, Shu YQ. Identification of plasma microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer. 2011;30(6):407–14.
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L, Fotinou M, Georgoulias V, Lianidou ES. Prognostic value of mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem. 2008;54(10):1696–704.
Ying SY, Chang DC, Lin SL. The microRNA (miRNA): overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol Biotechnol. 2008;38(3):257–68.
Perera RJ, Ray A. Epigenetic regulation of miRNA genes and their role in human melanomas. Epigenomics. 2012;4(1):81–90.
Pillai RS. MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 2005;11(12):1753–61.
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12(12):580–7.
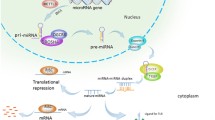
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(4):605–10.
Murchison EP, Hannon GJ. miRNAs on the move: miRNA biogenesis and the RNAi machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16(3):223–9.
Krol J, Sobczak K, Wilczynska U, Drath M, Jasinska A, Kaczynska D, Krzyzosiak WJ. Structural features of microRNA (miRNA) precursors and their relevance to miRNA biogenesis and small interfering RNA/short hairpin RNA design. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(40):42230–9.
He JF, Luo YM, Wan XH, Jiang D. Biogenesis of MiRNA-195 and its role in biogenesis, the cell cycle, and apoptosis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2011;25(6):404–8.
Chaulk SG, Thede GL, Kent OA, Xu Z, Gesner EM, Veldhoen RA, Khanna SK, Goping IS, MacMillan AM, Mendell JT, et al. Role of pri-miRNA tertiary structure in miR-17 ~ 92 miRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2011;8(6):1105–14.
Yang JS, Lai EC. Alternative miRNA biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway mutants. Mol Cell. 2011;43(6):892–903.
Cheloufi S, Dos Santos CO, Chong MM, Hannon GJ. A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature. 2010;465(7298):584–9.
Heale BS, Keegan LP, O’Connell MA. The effect of RNA editing and ADARs on miRNA biogenesis and function. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;700:76–84.
Azzam G, Smibert P, Lai EC, Liu JL. Drosophila Argonaute 1 and its miRNA biogenesis partners are required for oocyte formation and germline cell division. Dev Biol. 2012;365(2):384–94.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–31.
Ketting RF. microRNA biogenesis and function: an overview. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;700:1–14.
Liu Y, Liu Q. ATM signals miRNA biogenesis through KSRP. Mol Cell. 2011;41(4):367–8.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(7):2257–61.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(2):647–58.
Lima RT, Busacca S, Almeida GM, Gaudino G, Fennell DA, Vasconcelos MH. MicroRNA regulation of core apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(2):163–74.
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY, Yan M. microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 2012;27(4):1019–26.
Xu Y, Sun J, Xu J, Li Q, Guo Y, Zhang Q. miR-21 Is a promising novel biomarker for lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:640168.
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 2008;299(4):425–36.
Xie L, Qian X, Liu B. MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for gastrointestinal carcinomas. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;341(1–2):291–9.
Yang L, Belaguli N, Berger DH. MicroRNA and colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2009;33(4):638–46.
Yu Y, Kanwar SS, Patel BB, Oh PS, Nautiyal J, Sarkar FH, Majumdar AP. MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFbetaR2) in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(1):68–76.
Ventura A, Jacks T. MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 2009;136(4):586–91.
Rossbach M. MicroRNAs in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16(8):743–5.
Lee YS, Dutta A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:199–227.
Valeri N, Gasparini P, Braconi C, Paone A, Lovat F, Fabbri M, Sumani KM, Alder H, Amadori D, Patel T, et al. MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(49):21098–103.
Rossi L, Bonmassar E, Faraoni I. Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 2007;56(3):248–53.
Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Taniguchi H, Kunimoto H, Nosho K, Suzuki H, Shinomura Y. Interrelationship between microsatellite instability and microRNA in gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(22):2745–55.
Corte H, Manceau G, Blons H, Laurent-Puig P. MicroRNA and colorectal cancer. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;44(3):195–200.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2128–36.
Qian B, Katsaros D, Lu L, Preti M, Durando A, Arisio R, Mu L, Yu H. High miR-21 expression in breast cancer associated with poor disease-free survival in early stage disease and high TGF-beta1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;117(1):131–40.
Ferracin M, Querzoli P, Calin GA, Negrini M. MicroRNAs: toward the clinic for breast cancer patients. Semin Oncol. 2011;38(6):764–75.
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Kerin MJ, Spillane C. Regulatory interplay between miR-21, JAG1 and 17beta-estradiol (E2) in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;423(2):234–9.
Huang TH, Wu F, Loeb GB, Hsu R, Heidersbach A, Brincat A, Horiuchi D, Lebbink RJ, Mo YY, Goga A, et al. Up-regulation of miR-21 by HER2/neu signaling promotes cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(27):18515–24.
Song B, Wang C, Liu J, Wang X, Lv L, Wei L, Xie L, Zheng Y, Song X. MicroRNA-21 regulates breast cancer invasion partly by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:29.
Shi M, Liu D, Duan H, Shen B, Guo N. Metastasis-related miRNAs, active players in breast cancer invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29(4):785–99.
Huang GL, Zhang XH, Guo GL, Huang KT, Yang KY, Shen X, You J, Hu XQ. Clinical significance of miR-21 expression in breast cancer: SYBR-Green I-based real-time RT-PCR study of invasive ductal carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009;21(3):673–9.
Wu Q, Lu Z, Li H, Lu J, Guo L, Ge Q. Next-generation sequencing of microRNAs for breast cancer detection. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:597145.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(4):225–49.
Lan H, Lin CY, Yuan HY, Xiong B. Overexpression of miR-21 promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011;33(10):742–6.
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH, Zhang YK. High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2011;29(2):618–26.
Liu X, Sempere LF, Guo Y, Korc M, Kauppinen S, Freemantle SJ, Dmitrovsky E. Involvement of microRNAs in lung cancer biology and therapy. Transl Res. 2011;157(4):200–8.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(2):1026–33.
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008;18(3):350–9.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14328–36.
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(4):1290–7.
Hatley ME, Patrick DM, Garcia MR, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, van Rooij E, Olson EN. Modulation of K-Ras-dependent lung tumorigenesis by MicroRNA-21. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(3):282–93.
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH, Li Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene. 2008;27(31):4373–9.
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6029–33.
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG. Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334(4):1351–8.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(16):7065–70.
Manikandan J, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD, Pushparaj PN. Oncomirs: the potential role of non-coding microRNAs in understanding cancer. Bioinformation. 2008;2(8):330–4.
Corsten MF, Miranda R, Kasmieh R, Krichevsky AM, Weissleder R, Shah K. MicroRNA-21 knockdown disrupts glioma growth in vivo and displays synergistic cytotoxicity with neural precursor cell delivered S-TRAIL in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 2007;67(19):8994–9000.
Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC, Jung JS. MiR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2009;27(12):3093–102.
Peng X, Guo W, Liu T, Wang X, Tu X, Xiong D, Chen S, Lai Y, Du H, Chen G, et al. Identification of miRs-143 and -145 that is associated with bone metastasis of prostate cancer and involved in the regulation of EMT. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(5):e20341.
Hao Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X, He C, Pang X, Wu TC, Califano JA, Gu X. Improvement of prostate cancer detection by integrating the PSA test with miRNA expression profiling. Cancer Invest. 2011;29(4):318–24.
White NM, Fatoohi E, Metias M, Jung K, Stephan C, Yousef GM. Metastamirs: a stepping stone towards improved cancer management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(2):75–84.
Kuner R, Brase JC, Sultmann H, Wuttig D. microRNA biomarkers in body fluids of prostate cancer patients. Methods. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.05.004.
Yuan SX, Yang F, Yang Y, Tao QF, Zhang J, Huang G, Wang RY, Yang S, Huo XS, Zhang L, et al. Long non-coding RNA-MVIH promotes angiogenesis and serves as a predictor for HCC patients’ poor recurrence-free survival after hepatectomy. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2231–41.
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(5 Suppl 1):S5–16.
Cortez MA, Calin GA. MicroRNA identification in plasma and serum: a new tool to diagnose and monitor diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9(6):703–11.
Pegtel DM, Cosmopoulos K, Thorley-Lawson DA, van Eijndhoven MA, Hopmans ES, Lindenberg JL, de Gruijl TD, Wurdinger T, Middeldorp JM. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(14):6328–33.
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Tanemura M, Tomokuni A, Takemasa I, Umeshita K, et al. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2011;56(1):167–75.
Negrini M, Gramantieri L, Sabbioni S, Croce CM. microRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011;11(6):500–21.
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, Sabbioni S, Lanza G, Croce CM, Bolondi L, Negrini M. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6A):2189–204.
Xu J, Wu C, Che X, Wang L, Yu D, Zhang T, Huang L, Li H, Tan W, Wang C, et al. Circulating microRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50(2):136–42.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300.
Chang SS, Jiang WW, Smith I, Poeta LM, Begum S, Glazer C, Shan S, Westra W, Sidransky D, Califano JA. MicroRNA alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(12):2791–7.
Wong TS, Liu XB, Chung-Wai Ho A, Po-Wing Yuen A, Wai-Man Ng R, Ignace Wei W. Identification of pyruvate kinase type M2 as potential oncoprotein in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue through microRNA profiling. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(2):251–7.
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP, Wei WI. Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(9):2588–92.
Childs G, Fazzari M, Kung G, Kawachi N, Brandwein-Gensler M, McLemore M, Chen Q, Burk RD, Smith RV, Prystowsky MB, et al. Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(3):736–45.
Jung HM, Phillips BL, Patel RS, Cohen DM, Jakymiw A, Kong WW, Cheng JQ, Chan EK. Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(35):29261–72.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21.
Tie Y, Liu B, Fu H, Zheng X. Circulating miRNA and cancer diagnosis. Sci China C Life Sci. 2009;52(12):1117–22.
Resnick KE, Alder H, Hagan JP, Richardson DL, Croce CM, Cohn DE. The detection of differentially expressed microRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;112(1):55–9.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J, Wainscoat JS, et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2008;141(5):672–5.
Zhang J, Zhao H, Gao Y, Zhang W. Secretory miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1826(1):32–43.
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D, Abbruzzesse JL, Frazier ML, Killary AM, Sen S. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009;2(9):807–13.
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, Lu R, Rader JS, Meyers C, Zheng ZM. Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(7):e2557.
Reshmi G, Pillai MR. Beyond HPV: oncomirs as new players in cervical cancer. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(30):4113–6.
Ren J, Zhu D, Liu M, Sun Y, Tian L. Downregulation of miR-21 modulates Ras expression to promote apoptosis and suppress invasion of Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46(18):3409–16.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26(19):2799–803.
Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW, Lin WC. miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 2008;28(2A):907–11.
Yeung ML, Jeang KT. MicroRNAs and cancer therapeutics. Pharm Res. 2012;28(12):3043–9.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Doctoral Science Foundation of He Nan University of Science.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yang, Y.B., Zhang, X.H. et al. MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med Oncol 30, 376 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0376-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0376-8