Abstract
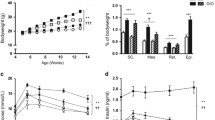
Several studies have investigated the beneficial effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on lipid and glucose metabolism. However, many of these studies are inconclusive about the effects of DHEA administration on metabolic disorders, and there appear to be sex-related differences in the effects of DHEA treatment. Few animal studies have addressed the effects of DHEA on diet-induced metabolic disorders. The present study sought to ascertain whether sex differences exist in the effects of a high-fat diet (HFD) on weight gain, adiposity, and biochemical and hormonal parameters in DHEA-treated rats. Rats were fed a HFD for 4 weeks and simultaneously received treatment with DHEA (10 mg/kg by subcutaneous injection) once weekly. Body weight, retroperitoneal fat depot weight, serum glucose, insulin, and leptin levels, and hepatic lipids were measured. HFD exposure increased the adiposity index in both sexes, the hepatic triglyceride content in both sexes, and the hepatic total cholesterol level in males. Moreover, the HFD induced an increase in blood glucose levels in both sexes, and hyperinsulinemia in males. In this experimental model, DHEA treatment reduced hepatic triglyceride levels only in females, regardless of HFD exposure. Exposure to a HFD, even if it does not cause obesity, may enhance risk factors for metabolic disorders, and males are more sensitive to this effect. DHEA treatment can help prevent metabolic derangements, but its effect varies with sex.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Hariri, L. Thibault, High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23, 270–299 (2010)
M.L. Fernandez, The metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Rev. 65, S30–S34 (2007)
M. Bergman, Inadequacies of current approaches to prediabetes and diabetes prevention. Endocrine 44, 623–633 (2013)
T. Priego, J. Sánchez, C. Picó, A. Palou, Sex-differential expression of metabolism- related genes in response to a high-fat diet. Obesity 16, 819–826 (2008)
O.D. Taraschenko, I.M. Maisonneuve, S.D. Glick, Sex differences in high fat-induced obesity in rats: effects of 18-methoxycoronaridine. Physiol. Behav. 103, 308–314 (2011)
K. Michalakis, G. Mintziori, A. Kaprara, B.C. Tarlatzis, D.G. Goulis, The complex interaction between obesity, metabolic syndrome and reproductive axis: a narrative review. Metabolism 62, 457–478 (2013)
J. Avruch, Insulin signal transduction through protein kinase cascades. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 182, 31–48 (1998)
A.R. Saltiel, J.E. Pessin, Insulin signaling pathways in time and space. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 65–71 (2002)
R.V. Farese, M.P. Sajan, M.L. Standaert, Insulin-sensitive protein kinases (atypical protein kinase C and protein kinase B/Akt): actions and defects in obesity and type II diabetes. Exp. Biol. Med. 230, 593–605 (2005)
C.A. Lalli, J.R. Pauli, P.O. Prada, D.E. Cintra, E.R. Ropelle, L.A. Velloso, M.J. Saad, Statin modulates insulin signaling and insulin resistance in liver and muscle of rats fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism 57, 57–65 (2008)
G.D. Ferreira, A. Germeyer, A. de Barros Machado, T.L. do Nascimento, T. Strowitzki, I.S. Brum, H. Von Eye Corleta, E. Capp, Metformin modulates PI3K and GLUT4 expression and Akt/PKB phosphorylation in human endometrial stromal cells after stimulation with androgen and insulin. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 175, 157–162 (2014)
J. Karbowska, Z. Kochan, Fat-reducing effects of dehydroepiandrosterone involve upregulation of ATGL and HSL expression, and stimulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue. Steroids 77, 1359–1365 (2012)
N. Orentreich, J.L. Brind, J.H. Vogelman, R. Andres, H. Baldwin, Long-term longitudinal measurements of plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in normal men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75, 1002–1004 (1992)
J. Sánchez, F. Pérez-Heredia, T. Priego, M.P. Portillo, S. Zamora, M. Garaulet, A. Palou, Dehydroepiandrosterone prevents age-associated alterations, increasing insulin sensitivity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 19, 809–818 (2008)
M. Garaulet, F. Pérex-Llamas, T. Fuente, S. Zamora, F.J. Tebar, Anthropometric, computed tomography and fat cell data in an obese population: relationship with insulin, leptin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, sex hormone-binding globulin and sex hormones. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 143, 657–666 (2000)
M.K. Shelby, D.J. Crouch, D.L. Black, T.A. Robert, R. Heltsley, Screening indicators of dehydroepiandosterone, androstenedione, and dihydrotestosterone use: a literature review. J. Anal. Toxicol. 35, 638–655 (2011)
C. Gómez-Santos, J.J. Hernández-Morante, F.J. Tébar, E. Granero, M. Garaulet, Differential effect of oral dehydroepiandrosterone-sulphate on metabolic syndrome features in pre- and postmenopausal obese women. Clin. Endocrinol. 77, 548–554 (2012)
P.A. Hansen, D.H. Han, L.A. Nolte, M. Chen, J.O. Holloszy, DHEA protects against visceral obesity and muscle insulin resistance in rats fed a high-fat diet. Am. J. Physiol. 273, R1704–R1708 (1997)
Z. Magyar, G. Bekesi, K. Racz, J. Feher, Z. Schaff, G. Lengyel, A. Blazovics, G. Illyes, D. Szombath, A. Hrabak, B. Szekacs, P. Gergics, I. Marczell, E. Dinya, J. Rigo Jr, Z. Tulassay, Increased total scavenger capacity and decreased liver fat content in rats fed dehydroepiandrosterone and its sulphate on a high-fat diet. Gerontology 57, 343–349 (2011)
C.S. Campbell, L.C. Caperuto, A.E. Hirata, E.P. Araujo, L.A. Velloso, M.J. Saad, C.R. Carvalho, The phosphatidylinositol/AKT/atypical PKC pathway is involved in the improved insulin sensitivity by DHEA in muscle and liver of rats in vivo. Life Sci. 76, 57–70 (2004)
M. Aragno, R. Mastrocola, G. Alloatti, I. Vercellinatto, P. Bardini, S. Geuna, M.G. Catalano, O. Danni, G. Boccuzzi, Oxidative stress triggers cardiac fibrosis in the heart of diabetic rats. Endocrinology 149, 380–388 (2008)
J.J. Hernández-Morante, F. Pérez-de-Heredia, J.A. Luján, S. Zamora, M. Garaulet, Role of DHEA-S on body fat distribution: gender- and depot specific stimulation of adipose tissue lipolysis. Steroids 73, 209–215 (2008)
M. Pesaresi, S. Giatti, G. Cavaletti, F. Abbiati, D. Calabrese, R. Lombardi, R. Bianchi, G. Lauria, D. Caruso, L.M. Garcia-Segura, R.C. Melcangi, Sex-dimorphic effects of dehydroepiandrosterone in diabetic neuropathy. Neuroscience 199, 401–409 (2011)
M.H.V.M. Jacob, D.R. Janner, A. Bello´-Klein, S.F. Llesuy, M.F.M. Ribeiro, Dehydroepiandrosterone modulates antioxidant enzymes and Akt signaling in healthy Wistar rat hearts. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 112, 138–144 (2008)
M.H.V.M. Jacob, D.R. Janner, M.P. Jahn, L.C.R. Kucharski, A. Belló-Klein, M.F.M. Ribeiro, DHEA effects on myocardial Akt signaling modulation and oxidative stress changes in aged rats. Steroids 74, 1045–1050 (2009)
M.H.V.M. Jacob, D.R. Janner, A.S.R. Araújo, M.P. Jahn, L.C.R. Kucharski, T.B. Moraes, C.S. Dutra Filho, M.F.M. Ribeiro, A. Belló-Klein, Dehydroepiandrosterone improves hepatic antioxidant reserve and stimulates Akt signaling in young and old rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 127, 331–336 (2011)
M.P. Jahn, L.F. Gomes, M.H. Jacob, D. da Rocha Janner, A.S. Araújo, A. Belló-Klein, M.F. Ribeiro, L.C. Kucharski, The effect of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on renal function and metabolism in diabetic rats. Steroids 76, 564–570 (2011)
M.C. Castro, F. Francini, J.J. Gagliardino, M.L. Massa, Lipoic acid prevents fructose-induced changes in liver carbohydrate metabolism: role of oxidative stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840, 1145–1151 (2013)
A.G. Ferreira, A.A. da Cunha, F.R. Machado, C.D. Pederzolli, G.R. Dalazen, A.M. de Assis, M.L. Lamers, M.F. dos Santos, C.S. Dutra-Filho, A.T. Wyse, Experimental hyperprolinemia induces mild oxidative stress, metabolic changes and tissue adaptation in rat liver. J. Cell. Biochem. 113, 174–183 (2012)
D.R. Janner, M.H.V.M. Jacob, M.P. Jahn, L.C. Kucharski, M.F.M. Ribeiro, Dehydroepiandrosterone effects on Akt signaling modulation in central nervous system of young and aged healthy rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 122, 142–148 (2010)
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976)
L.M. Brown, D.J. Clegg, Central effects of estradiol in the regulation of food intake, body weight, and adiposity. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 122, 65–73 (2010)
M.W. Schwartz, D. Porte Jr, Diabetes, obesity, and the brain. Science 307, 375–379 (2005)
K. Esposito, A. Capuano, D. Giugliano, Metabolic syndrome and cancer: holistic or reductionist? Endocrine 45, 362–364 (2014)
K. Esposito, P. Chiodini, M.I. Maiorino, G. Bellastella, D. Panagiotakos, D. Giugliano, Which diet for prevention of type 2 diabetes? A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Endocrine (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0264-4
L. Velázquez-López, E. González-Figueroa, P. Medina-Bravo, I. Pineda-Del Aguila, L. Avila-Jiménez, R. Ramos-Hernández, M. Klunder-Klunder, J. Escobedo de la Peña, Low calorie and carbohydrate diet:to improve the cardiovascular riskindicators in overweightor obese adults with prediabetes. Endocrine 43, 593–602 (2013)
A.L. Hoefel, F. Hansen, P.D. Rosa, A.M. Assis, S.L. Silveira, C.C. Denardin, L. Pettenuzzo, P.R. Augusti, S. Somacal, T. Emanuelli, M.L. Perry, C.M. Wannmacher, The effects of hypercaloric diets on glucose homeostasis in the rat: influence of saturated and monounsaturated dietary lipids. Cell Biochem. Funct. 29, 569–576 (2011)
Y. Ono, H. Sorimachi, Calpains: an elaborate proteolytic system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1824, 224–236 (2012)
A.M. Baviera, N.M. Zanon, L.C. Carvalho Navegantes, R.H. Migliorini, I. do Carmo Kettelhut, Pentoxifylline inhibits Ca2+ -dependent and ATP proteasome-dependent proteolysis in skeletal muscle from acutely diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292, E702–E708 (2007)
C.T. Montague, S. O’Rahilly, Perspectives in diabetes: the perils of portliness causes and consequences of visceral adiposity. Diabetes 49, 883–888 (2000)
K.F. Petersen, S. Dufour, D. Befroy, M. Lehrke, R.E. Hendler, G.I. Shulman, Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54, 603–608 (2005)
S. Galic, J.S. Oakhill, G.R. Steinberg, Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 316, 129–139 (2010)
S.L. Doyle, C.L. Donohoe, J. Lysaght, J.V. Reynolds, Visceral obesity, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance and cancer. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 71, 181–189 (2012)
B.L. Wajchenberg, Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 21, 697–738 (2000)
S. Klein, The case of visceral fat: argument for the defense. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 1530–1532 (2004)
R. Lomonaco, J. Chen, K. Cusi, An endocrine perspective of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2, 211–225 (2011)
R. Lomonaco, N.E. Sunny, F. Bril, K. Cusi, Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: current issues and novel treatment approaches. Drugs 73, 1–14 (2013)
D. Constantin-Teodosiu, Regulation of muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in insulin resistance: effects of exercise and dichloroacetate. Diabetes Metab. J. 37, 301–314 (2013)
J.O. Lee, S.K. Lee, J.H. Jung, J.H. Kim, G.Y. You, S.J. Kim, S.H. Park, K.O. Uhm, H.S. Kim, Metformin induces Rab4 through AMPK and modulates GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 226, 974–981 (2011)
A. Nadal-Casellas, A.M. Proenza, I. Lladó, M. Gianotti, Sex-dependent differences in rat hepatic lipid accumulation and insulin sensitivity in response to diet-induced obesity. Biochem. Cell Biol. 90, 164–172 (2012)
S. Kumagai, A. Holmäng, P. Björntorp, The effects of oestrogen and progesterone on insulin sensitivity in female rats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 149, 91–97 (1993)
T. Jelenik, M. Roden, How estrogens prevent from lipid-induced insulin resistance. Endocrinology 154, 989–992 (2013)
J.S. Mayes, G.H. Watson, Direct effects of sex steroid hormones on adipose tissues and obesity. Obes. Rev. 5, 197–216 (2004)
S. Stöppeler, D. Palmes, M. Fehr, J.P. Hölzen, A. Zibert, R. Siaj, H.H. Schmidt, H.U. Spiegel, R. Bahde, Gender and strainspecific differences inthe development of steatosis in rats. Lab. Anim. 47, 43–52 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Brazilian research agencies CAPES and CNPq.
Ethical standards
Throughout the experimental procedures, the animals were treated in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals issued by the Brazilian National Council for Animal Experimentation (COBEA). All efforts were made to reduce both animal suffering and the number of animals used. The animal research protocols were approved by the UFRGS Ethics Committee (accredited by the National Research Ethics Commission) under project registration number 19788.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cecconello, A.L., Trapp, M., Hoefel, A.L. et al. Sex-related differences in the effects of high-fat diets on DHEA-treated rats. Endocrine 48, 985–994 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0396-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0396-6