Abstract
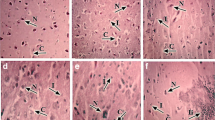
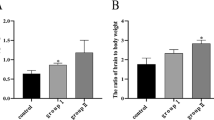
There were many studies about the effect of excess manganese (Mn) on nervous system apoptosis; however, Mn-induced apoptosis in chicken cerebrums and embryonic neurocytes was unclear. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of excess Mn on chicken cerebrum and embryonic neurocyte apoptosis. Seven-day-old Hyline male chickens were fed either a commercial diet or three levels of manganese chloride (MnCl2)-added commercial diets containing 600-, 900-, and 1800-mg/kg-Mn diet, respectively. On the 30th, 60th, and 90th days, cerebrums were collected. Fertilized Hyline chicken eggs were hatched for 6–8 days and were selected. Embryonic neurocytes with 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, and 3 mM Mn were collected and were cultured for 12, 24, 36, and 48 h, respectively. The following research contents were performed: superoxide dismutase (SOD) and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) activities; tumor protein p53 (p53), B cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), B cell lymphoma extra large (Bcl-x), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer (Bak), fas, and caspase-3 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression; and morphologic observation. The results indicated that excess Mn inhibited SOD and T-AOC activities; induced p53, Bax, Bak, fas, and caspase-3 mRNA expression; and inhibited Bcl-2 and Bcl-x mRNA expression in chicken cerebrums and embryonic neurocytes. There were dose-dependent manners on all the above factors at all the time points and time-dependent manners on SOD activity of 1800-mg/kg-Mn group, T-AOC activity, and apoptosis-related gene mRNA expression in all the treatment groups in chicken cerebrums. Excess Mn induced chicken cerebrum and embryonic neurocyte apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang FF, Zou YF, Shen YF, Zhong YQ, Lv YN, Huang DM, Chen KC, Li Q, Qing L, Xia B, Su C, Ma SY, Yang XB (2015a) Synergistic impaired effect between smoking and manganese dust exposure on pulmonary ventilation function in Guangxi manganese-exposed workers healthy cohort (GXMEWHC). PLoS One 10(2):e0116558. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0116558
Gong QQ, Jin ZM, Zou HF (2012) Concentrations of copper, zinc and manganese in tree sparrow (Passer montanus) at Jixi, Heilongjiang Province, China. J For Res 23(2):319–322. doi:10.1007/s11676-012-0259-z
Krishna S, Dodd CA, Hekmatyar SK, Filipov NM (2014) Brain deposition and neurotoxicity of manganese in adult mice exposed via the drinking water. Arch Toxicol 88(1):47–64. doi:10.1007/s00204-013-1088-3
Liu XF, Zuo N, Guan HN, Han CR, Xu SW (2013a) Manganese-induced effects on cerebral trace element and nitric oxide of Hyline cocks. Biol Trace Elem Res 154(2):202–209. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9692-x
Wang T, Li XH, Yang DX, Zhang HT, Zhao P, Fu JL, Yao BY, Zhou ZC (2015b) ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis are involved in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in the rat striatum in vivo. NeurotToxicology 48:109–119. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2015.02.007
Liu XF, Li ZP, Tie F, Liu N, Zhang ZW, Xu SW (2013b) Effects of manganese-toxicity on immune-related organs of cocks. Chemosphere 90(7):2085–2100. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.072
Chen K, Albano A, Ho A, Keaney JF (2003) Activation of p53 by oxidative stress involves platelet-derived growth factor-β receptor-mediated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase activation. J Biol Chem 278(41):39527–39533. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304423200
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Li S, Wang XL, Lei XG, Xu SW (2013a) Selenoprotein W serves as an antioxidant in chicken myoblasts. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1830(4):3112–3120. doi:10.3945/jn.112.172395
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang JL, Li S, Huang JQ, Ren FZ, Xu SW, Wang XL, Lei XG (2013b) Gene expression of endoplasmic reticulum resident selenoproteins correlates with apoptosis in various muscles of Se-deficient chick. Biochemical, molecular, and genetic mechanisms. J Nutr 143(5):613–619. doi:10.3945/jn.112.172395
Maroto R, Perez-Polo JR (1997) BCL-2-related protein expression in apoptosis: oxidative stress versus serum deprivation in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 69(2):514–523. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69020514.x
Denning TL, Takaishi H, Crowe SE, Boldogh I, Jevnikar A, Ernst PB (2002) Oxidative stress induces the expression of fas and fas ligand and apoptosis in murine intestinal epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 33(12):1641–1650. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01141-3
Wang L, Wang H, Li JG, Chen DW, Liu ZP (2011) Simultaneous effects of lead and cadmium on primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells: interaction of apoptosis and oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61(3):500–511. doi:10.1007/s00244-011-9644-4
Cao HB, Xia B, Zhang MM, Liao YL, Yang Z, Hu GL, Zhang CY (2015) Changes of antioxidant function and the mRNA expression levels of apoptosis genes in duck ovaries caused by molybdenum or/and cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 171(2):410–418. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0442-0
Huang YH, Shih CM, Huang CJ, Lin CM, Chou CM, Tsai ML, Liu TP, Chiu JF, Chen CT (2006) Effects of cadmium on structure and enzymatic activity of Cu, Zn-SOD and oxidative status in neural cells. J Cell Biochem 98(3):577–589. doi:10.1002/jcb.20772
Zhu YH, Lu XX, Wu D, Cai SH, Li S, Teng XH (2013) The effect of manganese-induced cytotoxicity on mRNA expressions of HSP27, HSP40, HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90 in chicken spleen lymphocytes in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res 156(1):144–152. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9817-2
Zhu YH, Li S, Teng XH (2016) The involvement of the mitochondrial pathway in manganese-induced apoptosis of chicken splenic lymphocytes. Chemosphere 153:462–470. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.081
Lu XX, Zhu YH, Bai RS, Li S, Teng XH (2015) The effect of manganese-induced toxicity on the cytokine mRNA expression of chicken spleen lymphocytes in vitro. Res Vet Sci 101:165–167. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2015.05.009
Liu XF, Li ZP, Han CR, Zhang ZW, Xu SW (2012) Effects of dietary manganese on Cu, Fe, Zn, Ca, Se, IL-1β, and IL-2 changes of immune organs in cocks. Biol Trace Elem Res 148(3):336–344. doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9377-x
Shao JJ, Yao HD, Zhang ZW, Li S, Xu SW (2012) The disruption of mitochondrial metabolism and ion homeostasis in chicken hearts exposed to manganese. Toxicol Lett 214(2):99–108. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.08.011
Du Y, Zhu YH, Teng XJ, Zhang K, Teng XH, Li S (2015) Toxicological effect of manganese on NF-κB/iNOS-COX-2 signaling pathway in chicken testes. Biol Trace Elem Res 168(1):227–234. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0340-5
Klaassen CD, Amdur MO (2007) Casarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons. McGraw-Hill Professional/Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers, New York
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. doi:10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Liu XF, Zhang LM, Guan HN, Zhang ZW, Xu SW (2013c) Effects of oxidative stress on apoptosis in manganese-induced testicular toxicity in cocks. Food Chem Toxicol 60:168–176. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.058
Zhuang Y, Liu P, Wang LQ, Luo JR, Zhang CY, Guo XQ, Hu GL, Cao HB (2016) Mitochondrial oxidative stress-induced hepatocyte apoptosis reflects increased molybdenum intake in caprine. Biol Trace Elem Res 170(1):106–114. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0450-0
Jiao XY, Yang K, An Y, Teng XJ, Teng XH (2017) Alleviation of lead-induced oxidative stress and immune damage by selenium in chicken bursa of Fabricius. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-8329-y
Jin YX, Wang LG, Ruan ML, Liu JW, Yang YF, Zhou C, Xu B, Fu ZW (2011) Cypermethrin exposure during puberty induces oxidative stress and endocrine disruption in male mice. Chemosphere 84(1):124–130. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.034
Ye YY, Liu JW, Xu JH, Sun LJ, Chen MC, Lan MB (2010) Nano-SiO2 induces apoptosis via activation of p53 and Bax mediated by oxidative stress in human hepatic cell line. Toxicol in Vitro 24(3):751–758. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2010.01.001
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ, Morris RG, Bird CC, Hooper ML, Wyllie AH (1993) Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362(6423):849–852. doi:10.1038/362849a0
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B, Reed JC (1994) Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of Bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 9(6):1799–1805
Chen JH, Cao JL, Chu YL, Wang ZL, Yang ZT, Wang HL (2008) T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis involving fas, p53, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in human chondrocytes. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE B 9(6):455–463. doi:10.1631/jzus.B0820013
Qin JC, Chen HG, Yan Q, Deng M, Liu JP, Doerge S, Ma WY, Dong ZG, Li DW (2008) Protein phosphatase-2A is a target of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and modulates p53-Bak apoptotic pathway. Cancer Res 68(11):4150–4162. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0839
Jäättelä M, Benedict M, Tewari M, Shayman JA, Dixit VM (1995) Bcl-x and Bcl-2 inhibit TNF and fas-induced apoptosis and activation of phospholipase A2 in breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 10(12):2297–2305
Wajant H (2002) The fas signaling pathway: more than a paradigm. Science 296(5573):1635–1636. doi:10.1126/science.1071553
Croker BA, O’Donnell JA, Nowell CJ, Metcalf D, Dewson G, Campbell KJ, Rogers KL, Hu YF, Smyth GK, Zhang JG, White M, Lackovic K, Cengia LH, O’Reilly LA, Bouillet P, Cory S, Strasser A, Roberts AW (2011) Fas-mediated neutrophil apoptosis is accelerated by Bid, Bak, and Bax and inhibited by Bcl-2 and Mcl-1. PNAS 108(32):13135–13140. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110358108
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Samandas AC, Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos DS, Papaetropoulos T, Petsas T, Dougenis D (2007) Increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus of patients with myasthenia gravis. In vivo 21(1):123–132
Porter AG, Janicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6(2):99–104. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400476
Roboz GJ, Dias S, Lam G, Lane WJ, Soignet SL, Warrell RP, Rafii S (2000) Arsenic trioxide induces dose-and time-dependent apoptosis of endothelium and may exert an antileukemic effect via inhibition of angiogenesis. Blood 96(4):1525–1530
Zou WG, Yan MD, Xu WJ, Huo HR, Sun LY, Zheng ZC, Liu XY (2001) Cobalt chloride induces PC12 cells apoptosis through reactive oxygen species and accompanied by AP-1 activation. J Neurosci Res 64(6):646–653. doi:10.1002/jnr.1118
Al-Assaf AH, Alqahtani AM, Alshatwi AA, Syed NA, Shafi G, Hasan TN (2013) Mechanism of cadmium induced apoptosis inhuman peripheral blood lymphocytes: the role of p53, fas and caspase-3. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):1033–1039. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.09.006
Jung JY, Kim WJ (2004) Involvement of mitochondrial- and fas-mediated dual mechanism in CoCl2-induced apoptosis of rat PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 371(2–3):85–90. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.06.069
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures used in this experiment were approved by the Northeast Agricultural University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee under the approved protocol number SRM-06. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Hualong Feed Research Collaboration (No. 860035) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. C201420).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
All authors have read the manuscript and have agreed to submit it in its current form for consideration for publication in Biological Trace Element Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Zhu, Y., Wang, X. et al. Excess Manganese-Induced Apoptosis in Chicken Cerebrums and Embryonic Neurocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 180, 297–305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0992-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-0992-4