Abstract
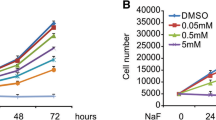
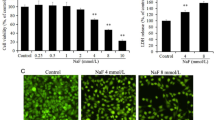
The present study investigated the effects of fluoride on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (ERS) and osteoblast apoptosis in vivo. Forty-eight Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (12/group) and exposed to 0, 50, 100, and 150 mg/L of fluoride in drinking water for 8 weeks, respectively. Peripheral blood samples and bilateral femurs were used to monitor the progression of fluorosis in the animals. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the bone tissues was used to determine the severity of osteofluorosis. The expression of ERS chaperones (glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), X-box binding protein l (XBP1), cysteine aspartate specific protease-12 (caspase-12), and growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153 (Gadd153/CHOP) was analyzed by immunohistochemistry staining, and osteoblast apoptosis was determined by TUNEL staining and flow cytometry. Accumulation of fluoride in bone was associated with the severity of osteofluorosis. The expression of GRP78, XBP1, caspase-12, and CHOP was increased in a dose-dependent manner. Fluoride-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts was also dose-dependent. High concentrations of fluoride induced ERS and osteoblast apoptosis in vivo. The increased expression of GRP78 and XBP1 increased the adaptation of osteoblasts to ERS to a certain extent. Caspase-12 and CHOP activation was associated with ERS and osteoblast apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliasgharpour M, Rahnamaye FM (2013) Trace elements in human nutrition: a review. Int J Med Invest 2(3):115–128
Buchancová J, Poláček H, Hudečková H, Murajda L, Osina O, Valachová J (2008) Skeletal fluorosis from the point of view of an occupational exposure to fluorides in former Czechoslovakia. Interdiscip Toxicol 1(2):193–197
Jha SK, Mishra VK, Sharma DK, Damodaran T (2011) Fluoride in the environment and its metabolism in humans. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 211:121–142
Harding MA, O'Mullane DM (2013) Water fluoridation and oral health. Acta Med Acad 42:131–139
Dhar V, Bhatnagar M (2009) Physiology and toxicity of fluoride. Indian J Dent Res 20:350–355
Everett ET (2011) Fluoride’s effects on the formation of teeth and bones, and the influence of genetics. J Dent Res 90:552–560
Debinski A, Nowicka G (2004) Effect of sodium fluoride on ectopic induction of bone tissue. Ann Acad Med Stetin 50:23–27
Nair M, Belak ZR, Ovsenek N (2011) Effects of fluoride on expression of bone-specific genes in developing Xenopus laevis larvae. Biochem Cell Biol 89:377–386
Krishnamachari KA (1986) Skeletal fluorosis in humans: a review of recent progress in the understanding of the disease. Prog Food Nutr Sci 10:279–314
Fujita T, Palmieri GMA (2000) Calcium paradox disease: calcium deficiency prompting secondary hyperparathyroidism and cellular calcium overload. Bone Miner Metab 18(3):109–125
Hua K, Zhao H, Huang M, Li GS (2003) Effects of fluoride on ionized calcium and calcium channel in osteoblast-like cell in vitro. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 19:179–181
Bary EL (2000) Expression of mRNA for the alpha 1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in human osteoblast like cell line and normal human osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int 66(2):145–150
Wang X, Eno CO, Altman BJ, Zhu Y, Zhao G, Olberding KE, Rathmell JC, Li C (2011) ER stress modulates cellular metabolism. Biochem J 435(1):285–296
Verkhratsky A, Toescu EC (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis and neuronal death. J Cell Mol Med 7(4):351–361
Smaili SS, Pereira GJ, Costa MM, Rocha KK, Rodrigues L, do Carmo LG, Hirata H, Hsu YT (2013) The role of calcium stores in apoptosis and autophagy. Curr Mol Med 13:252–265
Mahoney E, Byrd JC, Johnson AJ (2013) Autophagy and ER stress play an essential role in the mechanism of action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinaseinhibitor flavopiridol. Autophagy 9(3):434–435
Hetz C, Chevet E, Harding HP (2013) Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:703–719
Kaneko M (2012) Molecular pharmacological studies on the protection mechanism against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neurode-generative disease. Yakugaku Zasshi 132(12):1437–1442
Hamamura K, Yokota H (2007) Stress to endoplasmic reticulum of mouse osteoblasts induces apoptosis and transcriptional activation for bone remodeling. FEBS Lett 581(9):1769–1774
Higa A, Chevet E (2012) Redox signaling loops in the unfolded protein response. Cell Signal 24:1548–1555
Hammadi M, Oulidi A, Gackière F, Katsogiannou M, Slomianny C, Roudbaraki M, Dewailly E, Delcourt P, Lepage G, Lotteau S, Ducreux S, Prevarskaya N, Van Coppenolle F (2013) Modulation of ER stress and apoptosis by endoplasmic reticulum calcium leak via translocon during unfolded protein response: involvement of GRP78. FASEB J 27:1600–1609
Jwa M, Chang P (2012) PARP16 is a tail-anchored endoplasmic reticulum protein required for the PERK- and IRE1α-mediated unfolded protein response. Nat Cell Biol 14(11):1223–1230
Pfaffenbach KT, Amy S (2011) The critical role of GRP78 in physiologic and pathologic stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23(2):150–156
Dhahbi JM, Mote PL, Tillman JB, Walford RL, Spindler SR (1997) Dietary energy tissue-specifically regulates endoplasmic reticulum chaperone gene expression in the liver of mice. J Nutr 127(9):1758–1764
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ (2011) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol 54:795–809
Jurczak MJ, Lee AH, Jornayvaz FR, Lee HY, Birkenfeld AL, Guigni BA, Kahn M, Samuel VT, Glimcher LH, Shulman GI (2012) Dissociation of inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1α)-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation from hepatic insulin resistance in conditional X-box-blinding protein-1 (XBP1) knock-out mice. J Biol Chem 287(4):2558–2567
Liu D, Zhang M, Yin H (2013) Signaling pathways involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. Int J Neurosci 123(3):155–162
Yan X, Feng C, Chen Q, Li W, Wang H, Lv L, Smith GW, Wang J (2009) Effects of sodium fluoride treatment in vitro on cell proliferation, apoptosis and caspase-3 and caspase-9 mRNA expression by neonatal rat osteoblasts. Arch Toxicol 83:451–458
Moriya S, Miyazawa K, Kawaguchi T, Che XF, Tomoda A (2011) Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CHOP (GADD153) induction in the cytotoxicity of 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one in cancer cells. Int J Oncol 39(4):981–988
Komatsu S, Miyazawa K, Moriya S, Takase A, Naito M, Inazu M, Kohno N, Itoh M, Tomoda A (2012) Clarithromycin enhances bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity via endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CHOP (GADD153) induction and autophagy in breast cancercells. Int J Oncol 40(4):1029–1039
Bromati CR, Lellis-Santos C, Yamanaka TS, Nogueira TC, Leonelli M, Caperuto LC, Gorjão R, Leite AR, Anhê GF, Bordin S (2011) UPR induces transient burst of apoptosis in islets of early lactating rats through reduced AKT phosphorylation via ATF4/CHOP stimulation of TRB3 expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300(1):92–100
Wei W, Gao Y, Wang C, Zhao L, Sun D (2013) Excessive fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and interferes enamel proteinases secretion. Environ Toxicol 28(6):332–341
Zhou YL, Shi HY, Li XN, Lv P, Li GS, Liu QY, Xu H (2013) Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in aberrant activation of fluoride-treated osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res 154(3):448–456
Zhang Y, Liang YJ, Guo XY, Li X (2005) The effect of high dose fluoride on the rat offspring osteoblasts which ingested by female rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 34(1):29–32
Zhang Y, Sun X, Sun GF, Liu S, Wang L (2006) DNA damage induced by fluoride in rat osteoblasts. Fluoride 39(3):191–194
Zhang Y, Sun G, Jin Y, Wang Y (2003) Effects of fluoride on cell cycle and apoptosis in cultured osteoblasts of rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 32(5):432–433
Zhang Y, Sun GF, Jin YP, Wang Y (2003) Effects of fluoride on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast. Chin J Public Health 19(4):411–413
Zhou R, Zaki AE, Eisenmann DR (1996) Morphometry and autoradiography of altered rat enamel rat enamel protein processing due to chronic exposure to fluoride. Arch Oral Biol 41(8–9):739–747
Shore RC, Robinson C, Kirkham J, Herold RC (1993) An immunohistochemical study of the effects of fluoride on enamel development in the rat incisor. Arch Oral Biol 38(7):607–610
Lubkowska A, Chlubek D, Machoy-Mokrzyniska A (2006) The effect of alternating administration of aluminum chloride and sodium fluoride in drinking water on the concentration of fluoride in serum and its content in bones of rats. Ann Acad Med Stetin 52(Suppl 1):67–71
Tu J, Liu K, Song Y, Zhang Y, Cui C, Lu C (2011) Interactive effect of fluoride burden with calcitonin receptor gene polymorphisms on the risk of F bone injury. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 84(5):533–538
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptpsis and cytotoxicity by amyloidbeta. Nature 403(6765):98–103
Ren G, Ferreri M, Wang Z, Su Y, Han B, Su J (2011) Sodium fluoride affects proliferation and apoptosis through insulin-like growth factor I receptor in primary cultured mouse osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:914–923
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072245) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 20102278).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Gu, H. et al. Fluorosis Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Osteoblasts In Vivo. Biol Trace Elem Res 164, 64–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0192-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0192-4