Abstract
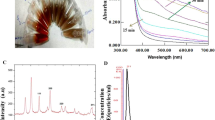
The aim of this investigation is to examine the anticancer activities of Balanites aegyptiaca fruit extract with its biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against colon and liver cancer cells. B. aegyptiaca aqueous extract was fractionated according to polarity and by biosynthesized AgNP. The cytotoxicity of the extract, semi-purified fractions, and the AgNPs was examined on noncancerous cell lines. The safer fraction was subjected to ultra-performance liquid chromatography-MS to identify the major active constituents. The anticancer activities of the nontoxic doses of all the used treatments were tested against HepG2 and CaCo2 cells. The nontoxic dose of the B. aegyptiaca (0.63 mg/ml) extract showed high anti-proliferative activities against HepG2 and CaCo2 with a percentage of 81 and 77%, respectively. The butanol fraction was safer than the other two fractions with 46.3 and 90.35% anti-proliferative activity against Caco2 and HepG2 cells, respectively. The nontoxic dose of AgNPs (0.63 mg/ml) inhibits both HepG2 and Caco2 cells with a percentage of 84.5 and 83.4%, respectively. In addition, AgNPs regulate the expression of certain genes with folding higher than that of crude extract. Saponin-coated AgNPs showed great abilities to select the most anticancer ingredient(s) from the B. aegyptiaca extract with a more safety pattern than the polarity gradient fractionation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall J.B & Walker D.H. (1991). Balanites aegyptiaca; A monograph. School of Agricultural and Forest Sciences Publication, University of Wales, No. 3.
Hall, J. B. (1992). Ecology of a key African multipurpose tree species, Balanites aegyptiaca (Balanitaceae): the state-of-knowledge. Journal of Forest Ecology and Management, 50(1–2), 1–30.
Chothani, D. L., & Vaghasiya, H. A. (2011). Review on Balanites aegyptiaca Del (desert date): phytochemical. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 5(9), 55–62.
Anani, K., Adjrah, Y., Ameyapoh, Y., Karou, S. D., Agbonon, A., de Souza, C., & Gbeassor, M. (2015). Effects of hydroethanolic extracts of Balanites aegyptiaca (L.) Delile (Balanitaceae) on some resistant pathogens bacteria isolated from wounds. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 164, 16–21.
Archibald, R. G. (1993). The use of the fruit of the tree Balanites aegyptiaca in the control of schistosomiasis in the Sudan. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene., 27, 207–210.
Beit-Yannai, E., Ben-Shabat, S., Goldschmidt, N., Chapagain, B. P., Liu, R. H., & Wiesman, Z. (2011). Antiproliferative activity of steroidal saponins from Balanites aegyptiaca—an in vitro study. Phytochemistry Letters., 4, 43–47.
Chapagain, B. P., Saharan, V., & Wiesman, Z. (2008). Larvicidal activity of saponins from Balanites aegyptiaca callus against Aedes aegypti mosquito. Bioresource Technology., 99, 1165–1168.
Jaiprakash, B., Karadi, R., Savadi, R., & Hukkeri, V. (2003). Hepatoprotective activity of bark of Balanites aegyptiaca Linn. Journal of Natural Remedies, 3, 205–207.
Koko, W., Abdalla, H., Galal, H., & Khalid, M. (2005). Evaluation of oral therapy on mansonial schistosomiasis using single dose of Balanites aegyptiaca fruits and praziquantel. Fitoterapia, 76, 30–34.
Motaal, A. A., Shaker, S., & Haddad, P. S. (2012). Antidiabetic activity of standardized extracts of Balanites aegyptiaca fruits using cell-based bioassays. Pharmacognosy Journal, 4, 20–24.
Speroni, E., Cervellati, R., Innocenti, G., Costa, S., Guerra, M., Dall’Acqua, S., & Govoni, P. (2005). Anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and antioxidant activities of Balanites aegyptiaca (L.) Delile. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 98, 117–125.
Kamel, M. A. (1998). Furostanol saponin from fruits of Balanites aegyptiaca. Phytochemistry, 48, 755–757.
Sarkar, J., Chattopadhyay, D., Patra, S., Deo, S. S., Sinha, S., Ghosh, M., Mukherjee, A., & Acharya, K. (2011). Alternaria alternata mediated synthesis of protein capped silver nanoparticles and their genotoxic activity. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures, 6, 563–573.
Maksoud, S. A., & El Hadidi, M. (1988). The flavonoids of Balanites aegyptiaca (Balanitaceae) from Egypt. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 160, 153–158.
Kamel, M., & Koskinen, A. (1995). Pregnane glycosides from fruits of Balanites aegyptiaca. Phytochemistry, 40, 1773–1775.
Ricci-Vitiani, L. I., Lombardi, D. G., Pilozzi, E., Biffoni, M., Todaro, M., Peschle, C., & De Maria, R. (2007). Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature, 445(7123), 111–115.
Lai, E. C., & Lau, W. Y. (2005). The continuing challenge of hepatic cancer in Asia. The Surgeon, 3, 210–215.
Patil, S. V., Salunke, B. K., Patil, C. D., Salunkhe, R. B., Gavit, P., & Maheshwari, V. L. (2010). Potential of extracts of the tropical plant Balanites aegyptiaca (L) Del. (Balanitaceae) to control the mealy bug, Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Crop Protection, 29, 1293–1296.
Zaahkouk, S. A. M., Aboul-Ela, E. I., Ramadan, M. A., Bakry, S., Ahmed, B. M., & Mhany, S. (2015). Anti carcinogenic activity of methanolic extract of Balanites aegyptiaca against breast, colon, and liver cancer cells. International Journal of Advanced Research, 3(6), 255–266.
Nappez, C., Liagre, B., & Beneytout, J. L. (1995). Changes in lipoxygenase activities in human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells during diosgenin induced differentiation. Cancer Letters, 96, 133–140.
Ali, B. H., Bashir, A. K., & Rasheed, R. A. (2001). Effect of the traditional medicinal plants Rhazya stricta, Balanites aegyptiaca and Haplophylum tuberculatum on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Phytotherapy Research, 15(7), 598–603.
Borenfreund, E., & Puerner, J. A. (1985). Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicology Letters, 24, 1s19–1124.
El-Deeb, N. M., El-Sherbiny, I. M., El-Aassara, M. R., & Hafez, E. E. (2015). Novel trend in colon cancer therapy using silver nanoparticles synthesized by honey bee. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 6, 2.
Lebrin, F. I., Goumans, M. J., Jonker, L., Carvalho, R. L., Valdimarsdottir, G., Thorikay, M., Mummery, C., Arthur, H. M., & ten Dijke, P. (2004). Endoglin promotes endothelial cell proliferation and TGF-beta/ALK1 signal transduction. The EMBO Journal, 23(20), 4018–4028.
Sawada, G., Raub, J., Decker, D., & Buxser, S. (1998). Analytical and numerical techniques for the evaluation of free radical damage in cultured cells using scanning laser microscopy. Cytometry, 25(3), 254–262.
Sagna, M. B., Diallo, A., Sarr, P. S., Ndiaye, O., Goffner, D., & Guisse, A. (2015). Biochemical composition and nutritional value of Balanites aegyptiaca (L.) Del fruit pulps from northern Ferlo in Senegal. African Journal of Biotechnology, 13(2), 336–342.
Ya’u, J., Abdulmalik, U., Yaro, A., Chindo, B., Anuka, J., & Hussaini, I. (2011). Behavioral properties of Balanites aegyptiaca in rodents. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 135, 725–729.
Garbi, M., Kabbashi, A., Awatif, A., & Hamed, Y. S. (2015). Antigiardial, antiamoebic and cytotoxic activity of the leaves extracts of Vitex trifolia. Advancement in Medicinal Plant Research, 3(1), 1–7.
Sarker, S., Bartholomew, B., & Nash, R. (2000). Alkaloids from Balanites aegyptiaca. Fitoterapia, 71, 328–330.
Neychev, V., Nikolova, E., Zhelev, N., & Mitev, V. (2007). Saponins from Tribulus terrestris L. are less toxic for normal human fibroblasts than for many cancer lines: influence on apoptosis and proliferation. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 232, 126–133.
An, C., Xin-Ming, Q., Li-Kun, G., Lin-Lin, L., Fang-Ping, C., Ying, X., Xiong-Fei, W., Xiang-Hong, L., & Jin, R. (2006). Tetrandrine-induced apoptosis in rat primary hepatocytes is initiated from mitochondria: caspases and endonuclease G (Endo G) pathway. Toxicology, 218, 1–12.
Li, X., Fang, P., Mai, J., Choi, E. T., Wang, H., & Yang, X. (2013). Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 6, 19.
Sayin, V. I., Ibrahim, M. X., Larsson, E., Nilsson, J. A., Lindahl, P., & Bergo, M. O. (2014). Antioxidants accelerate lung cancer progression in mice. Science Translational Medicine, 6(221), 221ra15.
Gorrini, C., Harris, I. S., & Mak, T. W. (2013). Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 12, 931–947.
Yassin, A., Elnouby, M., El-Deeb, N., & Hafez, E. (2016). Tungsten oxide nanoplates; the novelty in targeting metalloproteinase-7 gene in both cervix and colon cancer cells. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(4), 623–637.
Onodera, A., Nishiumi, F., Kakiguchi, K., Tanaka, A., Tanabe, N., Honma, A., Yayama, K., Yoshioka, Y., Nakahira, K., & Yonemura, S. (2015). Short-term changes in intracellular ROS localisation after the silver nanoparticles exposure depending on particle size. Toxicology Reports, 2, 574–579.
Pickering, B., De Mel, S., Lee, M., Howell, M., Habens, F., Dallman, C., Neville, L., Potter, K., Mann, J., & Mann, D. (2007). Pharmacological inhibitors of NF-κB accelerate apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Oncogene, 26, 1166–1177.
Brunelle, J. K., & Letai, A. (2009). Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. Journal of Cell Science, 122, 437–441.
Puthalakath, H., Huang, D. C., O’Reilly, L. A., King, S. M., & Strasser, A. (1999). The proapoptotic activity of the Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by interaction with the dynein motor complex. Molecular Cell, 3, 287–296.
Murillo, M. M., del Castillo, G., Sánchez, A., Fernández, M., & Fabregat, I. (2005). Involvement of EGF receptor and c-Src in the survival signals induced by TGF-β1 in hepatocytes. Oncogene, 24, 4580–4587.
Pham, L. V., Tamayo, A. T., Yoshimura, L. C., Lo, P., & Ford, R. J. (2003). Inhibition of constitutive NF-κB activation in mantle cell lymphoma B cells leads to induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The Journal of Immunology, 171, 88–95.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Research Institute (MAPRI), Khartoum, Sudan, for kindly providing the plant material and plant identification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding Sources
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yassin, A.M., El-Deeb, N.M., Metwaly, A.M. et al. Induction of Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells Through Extrinsic and Intrinsic Pathways by Balanites aegyptiaca Furostanol Saponins and Saponin-Coated SilverNanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 182, 1675–1693 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2426-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2426-3