Abstract
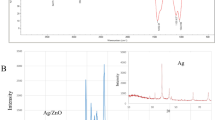
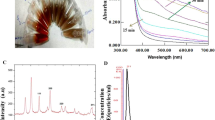
In the current study, biogenic silver nanoparticles (U-AgNPs) were synthesized using marine green macro-algal Ulva lactuca extract, and evaluated mechanism behind its anticancer activity against the Human colon cancer (HCT-116). The biogenic U-AgNPs were characterized using various physiochemical techniques. The TEM micrographs confirmed the spherical morphology of synthesized U-AgNPs, with a mean size of 8–14 nm. EDX spectrum as well as ICP-OES confirmed that AgNPs was nearly 90% purity for silver. FTIR Spectra analysis of U-AgNPs confirmed U. lactuca extract bioactive molecules presence over U-AgNPs surface as a stabilizing agent, thereby improving biocompatibility. The cytotoxicity study revealed the dose dependent cell death in colon cancer cells with no loss of viability in normal human colon epithelial cells. Furthermore, the fluorescence micrographs of nucleus staining assay revealed the DNA fragmentation and nucleus condensation of cancer cells treated with U-AgNPs, indicating an apoptosis-mediated cell death. The western bolt and RT-PCR analysis of U-AgNPs treated cancer cells showed the rise in proapoptotic markers (P53, Bax, and P21) and decline in anti-apoptotic markers (Bcl-2), thus confirming the p53-dependent apoptosis mediated cell death in HCT-116. Overall, our study concluded that novel biogenic U-AgNPs nanoparticles, synthesized using marine green macro-algal U. lactuca extract showed efficient anticancer activity against HCT-116 cell line and hence could work as potential therapeutic agent for targeted anti-cancer therapy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Gurunathan, M. Qasim, C. Park, H. Yoo, J.-H. Kim, K. Hong, Cytotoxic potential and molecular pathway analysis of silver nanoparticles in human colon cancer cells HCT116. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2269 (2018)
A. Fulfager, K.S. Yadav, Understanding the implications of co-delivering therapeutic agents in a nanocarrier to combat multidrug resistance (MDR) in breast cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 62, 102405 (2021)
A.-M. Florea, D. Büsselberg, Cisplatin as an anti-tumor drug: cellular mechanisms of activity, drug resistance and induced side effects. Cancers 3, 1351–1371 (2011)
P. Somu, S. Paul, Protein assisted one pot controlled synthesis of monodispersed and multifunctional colloidal silver–gold alloy nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 291, 111303 (2019)
J. Zhang, R. Misra, Nanomaterials in microfluidics for disease diagnosis and therapy development. Mater. Technol. 34, 92–116 (2019)
H. Bagur, C.C. Poojari, G. Melappa, R. Rangappa, N. Chandrasekhar, P. Somu, Biogenically synthesized silver nanoparticles using endophyte fungal extract of Ocimum tenuiflorum and evaluation of biomedical properties. J. Clust. Sci. 31, 1241–1255 (2019)
K.K. Yadav, M. Arakha, B. Das, B. Mallick, S. Jha, Preferential binding to zinc oxide nanoparticle interface inhibits lysozyme fibrillation and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 116, 955–965 (2018)
P. Somu, S. Paul, Surface conjugation of curcumin with self-assembled lysozyme nanoparticle enhanced its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy in multiple cancer cells. J. Mol. Liq. 338, 116623 (2021)
M. Abd Elkodous, G.S. El-Sayyad, I.Y. Abdelrahman, H.S. El-Bastawisy, F.M. Mosallam, H.A. Nasser et al., Therapeutic and diagnostic potential of nanomaterials for enhanced biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B 180, 411–428 (2019)
P. Chaudhary, F. Fatima, A. Kumar, Relevance of nanomaterials in food packaging and its advanced future prospects. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 30, 5180–5192 (2020)
P. Somu, S. Paul, A biomolecule-assisted one-pot synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its bioconjugate with curcumin for potential multifaceted therapeutic applications. New J. Chem. 43, 11934–11948 (2019)
D. Acharya, S. Satapathy, P. Somu, U.K. Parida, G. Mishra, Apoptotic effect and anticancer activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from marine algae chaetomorpha linum extract against human colon cancer cell HCT-116. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02304-7
F.-D. Cojocaru, D. Botezat, I. Gardikiotis, C.-M. Uritu, G. Dodi, L. Trandafir et al., Nanomaterials designed for antiviral drug delivery transport across biological barriers. Pharmaceutics 12, 171 (2020)
L. Carson, S. Bandara, M. Joseph, T. Green, T. Grady, G. Osuji et al., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties using Phyla dulcis plant extract. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2019.2714
C.A. Das, V.G. Kumar, T.S. Dhas, V. Karthick, K. Govindaraju, J.M. Joselin et al., Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthesis): a short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 27, 101593 (2020)
H. Bagur, R.S. Medidi, P. Somu, P.J. Choudhury, C.S. Karua, P.K. Guttula et al., Endophyte fungal isolate mediated biogenic synthesis and evaluation of biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles. Mater. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2020.1819089
K.S. Siddiqi, A. Husen, R.A. Rao, A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16, 14 (2018)
A. Chaitanyakumar, K.K. Yadav, L.A. Gomez, P. Somu, S. Senthoor, P.J. Choudhury et al., Biogenically engineered silver nanoparticles using bael leaf extract and evaluation of its therapeutic potential. Mater. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2021.1965701
S. Deshmukh, S. Patil, S. Mullani, S. Delekar, Silver nanoparticles as an effective disinfectant: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 97, 954–965 (2019)
D. Acharya, S. Satapathy, J.J. Thathapudi, P. Somu, G. Mishra, Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine algae Cladophora glomerata and evaluation of apoptotic effects in human colon cancer cells. Mater. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2020.1863597
L. Wang, T. Zhang, P. Li, W. Huang, J. Tang, P. Wang et al., Use of synchrotron radiation-analytical techniques to reveal chemical origin of silver-nanoparticle cytotoxicity. ACS Nano 9, 6532–6547 (2015)
C. Marambio-Jones, E.M. Hoek, A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 12, 1531–1551 (2010)
S. Mahanta, S. Prathap, D.K. Ban, S. Paul, Protein functionalization of ZnO nanostructure exhibits selective and enhanced toxicity to breast cancer cells through oxidative stress-based cell death mechanism. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 173, 376–388 (2017)
J.H. Ahire, M. Behray, C.A. Webster, Q. Wang, V. Sherwood, N. Saengkrit et al., Synthesis of carbohydrate capped silicon nanoparticles and their reduced cytotoxicity, in vivo toxicity, and cellular uptake. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 4, 1877–1886 (2015)
E. Panzarini, S. Mariano, C. Vergallo, E. Carata, G.M. Fimia, F. Mura et al., Glucose capped silver nanoparticles induce cell cycle arrest in HeLa cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 41, 64–74 (2017)
R. Kalaiarasi, N. Jayallakshmi, P. Venkatachalam, Phytosynthesis of nanoparticles and its applications. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 11, 1–16 (2010)
O.V. Kharissova, H.R. Dias, B.I. Kharisov, B.O. Pérez, V.M.J. Pérez, The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 240–248 (2013)
M. Ghanbari, F. Davar, A.E. Shalan, Effect of rosemary extract on the microstructure, phase evolution, and magnetic behavior of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and its application on anti-cancer drug delivery. Ceram. Int. 47, 9409–9417 (2021)
M. Loghman-Estarki, E.M. Sharifi, H. Sheikh, A. Alhaji, M. Naderi, Development of biocompatibility in the orthodontic brackets based on MgAl2O4/Si3N4 nanocomposites. Compos. B Eng. 173, 106989 (2019)
S. Trivedi, M.A. Alshehri, C. Panneerselvam, H.A. Al-Aoh, F. Maggi, S. Sut et al., Insecticidal, antibacterial and dye adsorbent properties of Sargassum muticum decorated nano-silver particles. S. Afr. J. Bot. 139, 432–441 (2021)
N. Khatoon, J.A. Mazumder, M. Sardar, Biotechnological applications of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Curr. Res. 2, 107 (2017)
A.J. Adur, N. Nandini, K.S. Mayachar, R. Ramya, N. Srinatha, Bio-synthesis and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles using anaerobically digested parthenium slurry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 183, 30–34 (2018)
M. Fernandez, R. Munoz-Olivas, J. Luque-Garcia, SILAC-based quantitative proteomics identifies size-dependent molecular mechanisms involved in silver nanoparticles-induced toxicity. Nanotoxicology 13, 812–826 (2019)
P. Gopinath, S.K. Gogoi, P. Sanpui, A. Paul, A. Chattopadhyay, S.S. Ghosh, Signaling gene cascade in silver nanoparticle induced apoptosis. Colloids Surf. B 77, 240–245 (2010)
D. Shahbazzadeh, H. Ahari, A. Motalebi, A. Anvar, S. Moaddab, T. Asadi et al., In vitro effect of nanosilver toxicity on fibroblast and mesenchymal stem cell lines. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 10, 487–496 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Director of NRME Research Laboratory, Newredmars Education Pvt Ltd for allowing to carry out the research work. The authors sincerely thank Saveetha Institute of Medical And Technical Sciences (Deemed-to-be University) for their support, encouragement, and extending all the necessary facilities in the university.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acharya, D., Satapathy, S., Yadav, K.K. et al. Systemic Evaluation of Mechanism of Cytotoxicity in Human Colon Cancer HCT-116 Cells of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Marine Algae Ulva lactuca Extract. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 596–605 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02133-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02133-8