Abstract
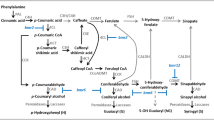
In this study, we cloned a full-length cDNA and the genomic DNA sequence of SmCCoAOMT (GenBank ID JQ007585) from Salvia miltiorrhiza. The 744-bp open-reading frame encodes a protein of 247 amino acids that shares 95 % similarity with one in Vitis vinifera. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed that SmCCoAOMT is most highly expressed in the stems and can be induced by methyl jasmonate (MeJA) and XC-1 treatment. To evaluate its function in vivo, we generated RNA interference transgenic plants through Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer. Compared with untransformed control plants, the transgenics had significantly less lignin and the expression of lignin-biosynthetic genes SmCCR and SmCOMT was depressed. In 90-day-old roots from plants of transgenic line M5, accumulations of rosmarinic acid and salvianolic acid B (Sal B) were greatly reduced by 0.89- and 0.69-fold, respectively. This low-Sal B phenotype was stable in the roots, with the level of accumulation being approximately 43.58 mg g−1 dry weight, which was 52 % of the amount measured in the untransformed control. Our results suggest that SmCCoAOMT is involved in lignin biosynthesis and affects the accumulation of phenolic acids. This study also provides potential guidance for using lignin-related genes to genetically engineer Salvia miltiorrhiza.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi, C., Chen, F., Jackson, L., Gill, B. S., & Li, W. (2010). Expression of lignin biosynthetic genes in wheat during development and upon infection by fungal pathogens. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 29, 149–161.
Bo, W., Wei, S., Li, Q., Ying, L., Luo, H., Song, J., Chao, S., Qian, J., Zhu, Y., & Hayward, A. (2014). Genome-wide identification of phenolic acid biosynthetic genes in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Planta, 241, 711–725.
Chen, Y., Zein, I., Brenner, E. A., Andersen, J. R., Landbeck, M., Ouzunova, M., & Lübberstedt, T. (2010). Polymorphisms in monolignol biosynthetic genes are associated with biomass yield and agronomic traits in European maize (Zea mays L. BMC Plant Biology, 10, 12.
Christin, F., Maike, V. O., Vinzenz, H., & Thomas, V. (2012). The role of CCoAOMT1 and COMT1 in Arabidopsis anthers. Planta, 236, 51–61.
Doyle, J., & Doyle, J. (1986). A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochemistry, 19, 11–15.
Ehlting, J., Mattheus, N., Aeschliman, D. S., Li, E., Hamberger, B., Cullis, I. F., Zhuang, J., Kaneda, M., Mansfield, S. D., & Samuels, L. (2005). Global transcript profiling of primary stems from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies candidate genes for missing links in lignin biosynthesis and transcriptional regulators of fiber differentiation. Plant Journal, 42, 618–640.
Fossdal, C. G., Nagy, N. E., Hietala, A. M., Kvaalen, H., Slimestad, R., Woodward, S., & Solheim, H. (2012). Indications of heightened constitutive or primed host response affecting the lignin pathway transcripts and phenolics in mature Norway spruce clones. Tree Physiology, 32, 1137–1147.
Gleave, A. P. (1993). A versatile binary vector system with a T-DNA organizational-structure conducive to efficient integration of cloned DNA into the plant genome. Plant Molecular Biology, 20, 1203–1207.
Grabber, J. H., Ralph, J., Hatfield, R. D., & Quideau, S. (1997). P-hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl, and syringyl lignins have similar inhibitory effects on wall degradability. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 45, 2530–2532.
Guindon, S., & Gascuel, O. (2003). PhyML—a simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 52, 696–704.
Holsters, M., Waele, D. D., Depicker, A., Messens, E., Montagu, M. V., & Schell, J. (1978). Transfection and transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Molecular & General Genetics, 163, 181–187.
Hua, W., Zhang, Y., Song, J., Zhao, L., & Wang, Z. (2011). De novo transcriptome sequencing in Salvia miltiorrhiza to identify genes involved in the biosynthesis of active ingredients. Genomics, 98, 272–279.
Lei, X., & Chiou, G. C. Y. (2012). Studies on cardiovascular actions of Salvia miltiorrhiza. American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 14, 26–32.
Li, L., Zhou, Y., Cheng, X., Sun, J., Marita, J. M., Ralph, J., & Chiang, V. L. (2003). Combinatorial modification of multiple lignin traits in trees through multigene cotransformation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 4939–4944.
Li, X., Chen, W., Zhao, Y., Xiang, Y., Jiang, H., Zhu, S., & Cheng, B. (2013). Downregulation of caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) by RNA interference leads to reduced lignin production in maize straw. Genetics & Molecular Biology, 36, 540–546.
Martz, F., Maury, S., Pinçon, G., & Legrand, M. (1998). cDNA cloning, substrate specificity and expression study of tobacco caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase, a lignin biosynthetic enzyme. Plant Molecular Biology, 36, 427–437.
Meyermans, H., Morreel, K., Lapierre, C., Pollet, B., Bruyn, A., De Busson, R., Herdewijn, P., Devreese, B., Beeumen, J., Van Marita, J. M., John, R., Cuiying, C., Bart, B., Marc, V. M., Eric, M., & Wout, B. (2000). Modifications in lignin and accumulation of phenolic glucosides in poplar xylem upon down-regulation of caffeoyl-coenzyme A O-methyltransferase, an enzyme involved in lignin biosynthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 36899–36909.
Miguens, F. C. (1993). Identification of compatible and incompatible interactions between Arabidopsis thaliana and Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and characterization of the hypersensitive response. Journal of Crystal Growth, 310, 4451–4455.
Negi, S., Tak, H., & Ganapathi, T. R. (2015). In vitro xylem vessel elements formation from banana embryogenic cells and expression analysis of vessel development-related genes. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 9, 47–54.
Oksman-Caldentey, K. M., & Inze, D. (2004). Plant cell factories in the post-genomic era: new ways to produce designer secondary metabolites. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 433–440.
Pang, S. L., Ong, S. S., Lee, H. H., Zamri, Z., Kandasamy, K. I., Choong, C. Y., & Wickneswari, R. (2014). Isolation and characterization of CCoAOMT in interspecific hybrid of Acacia auriculiformis x Acacia mangium—a key gene in lignin biosynthesis. Genetics and Molecular Research, 13, 7217–7238.
Rahantamalala, A., Rech, P., Martinez, Y., Chaubet-Gigot, N., Grima-Pettenati, J., & Pacquit, V. (2010). Coordinated transcriptional regulation of two key genes in the lignin branch pathway—CAD and CCR—is mediated through MYB-binding sites. BMC Plant Biology, 10, 107–113.
Rest, B. V. D., Danoun, S., Boudet, A. M., & Rochange, S. F. (2006). Down-regulation of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) induces dramatic changes in soluble phenolic pools. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 1399–1411.
Schmittgen, T. D., & Livak, K. J. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nature Protocols, 3, 1101–1108.
Senthil-Kumar, M., Hema, R., Suryachandra, T. R., Ramegowda, H. V., Gopalakrishna, R., Rama, N., Udayakumar, M., & Mysore, K. S. (2010). Functional characterization of three water deficit stress-induced genes in tobacco and Arabidopsis: an approach based on gene down regulation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48, 35–44.
Seok, B., Kim, B. G., Na, R. J., Lee, Y., Lim, Y., Chong, Y., & Ahn, J. H. (2009). Structural modeling and biochemical characterization of flavonoid O-methyltransferase from rice. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 30, 2803–2805.
Sewalt, V., Ni, W., Blount, J. W., Jung, H. G., Masoud, S. A., Howles, P. A., Lamb, C., & Dixon, R. A. (1997). Reduced lignin content and altered lignin composition in transgenic tobacco down-regulated in expression of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase or cinnamate 4-hydroxylase. Plant Physiology, 115, 41–50.
Shaipulah, N. F. M., Muhlemann, J. K., Woodworth, B. D., Moerkercke, A. V., Verdonk, J. C., Ramirez, A. M., Haring, M. A., Dudareva, N., & Schuurink, R. (2015). CCoAOMT downregulation activates anthocyanin biosynthesis in petunia. Plant Physiology, 170.
Song, J., & Wang, Z. (2011). RNAi-mediated suppression of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene in Salvia miltiorrhiza causes abnormal phenotypes and a reduction in rosmarinic acid biosynthesis. Journal of Plant Research, 124, 183–192.
Thévenin, J., Pollet, B., Letarnec, B., Saulnier, L., Gissot, L., Maia-Grondard, A., Lapierre, C., & Jouanina, L. (2011). The simultaneous repression of CCR and CAD, two enzymes of the lignin biosynthetic pathway, results in sterility and dwarfism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Plant, 4, 70–82.
Tschaplinski, T. J., Standaert, R. F., Engle, N. L., Martin, M. Z., Sangha, A. K., Parks, J. M., Smith, J. C., Samuel, R., Nan, J., & Pu, Y. (2012). Down-regulation of the caffeic acid O-methyltransferase gene in switchgrass reveals a novel monolignol analog. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 5, 1–15.
Wagner, A., Tobimatsu, Y., Phillips, L., Flint, H., Torr, K., Donaldson, L., Pears, L., & Ralph, J. (2011). CCoAOMT suppression modifies lignin composition in Pinus radiata. The Plant Journal, 67, 119–129.
Wang, D., Yao, W., Song, Y., Liu, W., & Wang, Z. (2012). Molecular characterization and expression of three galactinol synthase genes that confer stress tolerance in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Journal of Plant Physiology, 169, 1838–1848.
Wang, Z., Cui, L., Chen, C., Liu, X., Yan, Y., & Wang, Z. (2012). Downregulation of cinnamoyl CoA reductase affects lignin and phenolic acids biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 30, 1229–1236.
Wilson, S. A., & Roberts, S. C. (2014). Metabolic engineering approaches for production of biochemicals in food and medicinal plants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 26, 174–182.
Yan, Q., Shi, M., Ng, J., & Wu, J. Y. (2006). Elicitor-induced rosmarinic acid accumulation and secondary metabolism enzyme activities in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Plant Science, 170, 853–858.
Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Niu, X., Qi, J., Tao, A., Zhang, L., Fang, P., Lin, L. H., & Su, J. (2014). The CCoAOMT1 gene from jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) is involved in lignin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene, 546, 398–402.
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., & Wang, Z. (2010). The Arabidopsis PAP1 transcription factor plays an important role in the enrichment of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 58, 565–574.
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Wu, Y., Hua, W., Chen, C., Ge, Q., & Wang, Z. (2013). Pathway engineering for phenolic acid accumulations in Salvia miltiorrhiza by combinational genetic manipulation. Metabolic Engineering, 21, 71–80.
Zhou, Y., & Fu, R. (2015). Continuing treatment with Salvia miltiorrhiza injection attenuates myocardial fibrosis in chronic iron-overloaded mice. PloS One, 10, 659–663.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, China (2012JQ4013) and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31300256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ge, Q., Chen, C. et al. Function Analysis of Caffeoyl-CoA O-Methyltransferase for Biosynthesis of Lignin and Phenolic Acid in Salvia miltiorrhiza . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181, 562–572 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2231-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2231-4