Abstract
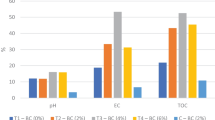
The aim of the present study was bioremediation of distillery sludge into a soil-enriching material. It was mixed with a complementary waste, cattle dung, and subjected to vermicomposting with (V) and without (T, control) Eisenia fetida in the ratio of 0:100 % (V1, T1), 10:90 (V2, T2), 25:75 (V3, T3), 50:50 (V4, T4), 75:25 (V5, T5) and 100:0 % (V6, T6), respectively. Survival rate, growth rate, onset of maturity, cocoon production and population build-up increased with increasing ratio of cattle dung. Maximum mortality of earthworm was observed in V6 mixture. On the basis of response surface design, the concentration of sludge giving highest number of worms, cocoons and hatchlings came out to be 21.11, 24.51 and 17.19 %, respectively. Nitrogen, phosphorus, sodium and pH increased during vermicomposting but decreased in the products without earthworm and there was increase in the contents of transition metals in the products of both the techniques. However, organic carbon, electrical conductivity and potassium showed an opposite trend.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramana, S., Biswas, A. K., Singh, A. B., & Yadava, R. B. R. (2001). Relative efficacy of different distillery effluents on growth, nitrogen fixation and yield of groundnut. Bioresource Technology, 81, 117–121.
Lung, A. J., Lin, C. M., Kim, J. M., Marshall, M. R., Nordstedt, R., Thompson, N. P., & Wei, C. I. (2001). Destruction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Enteritidis in cow manure composting. Journal of Food Protection, 64, 1309–1314.
Martin-Gil, J., Navas-Garcia, L. M., Gomez-Sobrino, E., Correa-Guimaraes, A., Hernandez-Navarro, S., Sanchez-Bascones, M., & Ramos-Sanchez, M. C. (2007). Composting and vermicomposting experiences in the treatments and bioconversion of asphaltens from the prestige oil spill. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1821–1829.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1996). In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Method of soil analysis (pp. 539–579). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, R. G. (1982). Nitrogen total. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis (pp. 575–624). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
John, M. K. (1970). Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and plant materials with ascorbic acid. Soil Science, 109, 214–220.
Suthar, S. (2008). Bioremediation of aerobically treated distillery sludge mixed with cow dung by using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. The Environmentalist, 28, 76–84.
Edwards, C. A., & Edward, C. A. (1998). The use of earthworms in the breakdown and management of organic wastes. In C. A. Edward (Ed.), Earthworm ecology (pp. 327–354). Boca Raton: Lewis.
Barne, A. Z., & Striganova, B. R. (2005). Evaluation of production parameters of earthworms Eiseniella tetraedera in laboratory culture. Biology Bulletin, 32, 323–326.
Lavelle, P. (1981). Strategies de reproduction chez les vers de terre. Acta Oecologica, 21, 17–133.
Jadia, C. D., & Fulekar, M. H. (2008). Vermicomposting of vegetable waste: a bio-physicochemical process based on hydro-operating bioreactor. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 3723–3730.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2002). The nature and properties of soils (13th ed.). New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India. 960 pp.
Beck-friis, B., Smars, S., Jonsson, H., & Kirchmann, H. (2001). SE-Structures and Environment: Gaseous emissions of carbon dioxide, ammonia and nitrous oxide from organic household waste in a compost reactor under different temperature regimes. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 78, 423–430.
Singh, J., Kaur, A., Vig, A. P., & Rup, P. J. (2010). Role of Eisenia fetida in rapid recycling of nutrients from biosludge of beverage industry. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 430–435.
Khawairakpam, M., & Bhargava, R. (2009). Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 948–954.
Kaur, A., Singh, J., Vig, A. P., Dhaliwal, S. S., & Rup, P. J. (2010). Cocomposting with and without Eisenia fetida for conversion of toxic paper mill sludge to a soil conditioner. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8192–8198.
Vig, A. P., Singh, J., Wani, S. H., & Dhaliwal, S. S. (2011). Vermicomposting of tannery sludge mixed with cattle dung into valuable manure using earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Bioresource Technology, 102, 7941–7945.
Guest, C. A., Johnston, C. T., King, J. J., Allenman, J. J., Tishmack, J. K., & Norton, L. D. (2001). Chemical characterisation of synthetic soil from composting coal combustion and pharmaceutical by- products. Journal of Environmental Quality, 80, 246–253.
Tognetti, C., Mazzarino, M. J., & Lao, F. (2007). Improving the quality of municipal organic waste compost. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1067–1076.
Cabrera, M. L., Kissel, D. E., & Vigil, M. F. (2005). Nitrogen mineralization from organic residues: Research opportunities. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 75–79.
Garg, V. K., & Kaushik, P. (2005). Effect of textile wastewater on different cultivar of wheat. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1189–1193.
Tripathi, G., & Bhardwaj, P. (2004). Comparative studies on biomass production, life cycles and composting efficiency of Eisenia foetida (Savigny) and Lampito mauritii (Kinberg). Bioresource Technology, 92, 275–278.
Alexander, M. (1983). Introduction to soil microbiology (2nd ed., p. 467). New Delhi: Wiley Eastern limited.
Krishnamoorthy, R. V. (1990). Mineralization of phosphorous by faecal phosphatase of some earthworms of Indian tropica. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, 99, 509–518.
Orozco, F. H., Cegarra, J., Trujillo, L. M., & Roig, A. (1996). Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia fetida: Effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 22, 162–166.
Delgado, M., Bigeriego, M., Walter, I., & Calbo, R. (1995). Use of California red worm in sewage sludge transformation. Turrialba, 45, 33–41.
Deolalikar, A. V., Mitra, A., Bhattacharyee, S., & Chakraborty, S. (2005). Effect of vermicomposting process on metal content of paper mill solid waste. Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, 47, 81–84.
Bhat, S. A., Singh, J., & Vig, A. P. (2013). Vermiremediation of dyeing sludge from textile mill with the help of exotic earthworm Eisenia fetida Savigny. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 5975–5982.
Suthar, S., & Singh, S. (2008). Feasibility of vermicomposting in biostabilization of sludge from a distillery industry. Sci Total Environment, 394, 237–243.
Selladurai, G., Anbusaravanan, N., Shyam, K. P., Kandhasamy, P., & Balamuthu, K. (2010). Recycling of distillery sludge from sugarcane industry using bioresource technology. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6, 218–223.
Romero, E., Plaza, C., Senesi, N., Nogales, R., & Polo, A. (2007). Humic acid-like fractions in raw and vermicomposted winery and distillery wastes. Geoderma, 139, 397–406.
Madan, S., & Yadav, A. (2012). Vermicomposting of Distillery sludge with different wastes by using Eisenia fetida. Advances in Applied Science Research, 3, 3844–3847.
Hemalatha, B. (2012). Recycling of industrial sludge along with municipal solid waste – vermicomposting method. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology, 3, 71–74.
Suthar, S. (2008). Metal remediations from partially composted distillery sludge using composting earthworm Eisenia foetida. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 10, 1099–1106.
Nogales, R., Cifuentes, C., & Benitez, E. (2005). Vermicomposting of winery wastes: A labo- ratory study. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B. Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 40, 659–673.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Department of Zoology, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, Punjab, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Kaur, A. & Vig, A.P. Bioremediation of Distillery Sludge into Soil-Enriching Material Through Vermicomposting with the Help of Eisenia fetida . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174, 1403–1419 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1116-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1116-7