Abstract
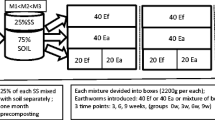
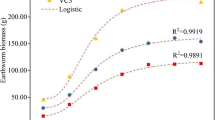
Heavy metal contamination of sewage sludge hampers its recycling. Contaminated sewage sludge was amended with different proportions of biochar and vermistabilized. Biochar produced from wheat straw was added at four proportions (0%, 2%, 4%, and 6%). Ten earthworms Eisenia fetida were added, and the sludge was vermistabilized for 60 days. Heavy metal and nutrient concentrations and the accumulation of metals to E. fetida were measured. The treatment with 4% biochar was the most efficient in reducing the concentrations of heavy metals. The concentration of Cd decreased 55%, Cr 28%, Cu 30%, and Pb 21%. The concentrations of plant nutrients increased: total N 43%, total P 92%, and total K 60%. E. fetida accumulated all heavy metals in their internal tissues. The survival and reproductive rate of E. fetida improved during the vermistabilization process. We interpret that the biochar alone did not improve the decomposition process, but the main actors were the earthworms E. fetida. The most efficient proportion of biochar was 4%, not the highest tested (6%). We recommend 4% biochar to be used in the vermistabilization of heavy metal–contaminated municipal sewage sludge. The study benefits both the management of heavy metal–contaminated sewage sludge and agriculture where the final vermistabilization product can be used to improve crop production.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data related to this manuscript is incorporated in the manuscript only.
References
Ahadi, N., Sharifi, Z., Hossaini, S. M. T., Rostami, A., & Renella, G. (2020). Remediation of heavy metals and enhancement of fertilizing potential of a sewage sludge by the synergistic interaction of woodlice and earthworms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, 121573.
Alahdal, H. M., AlYahya, S., Ameen, F., Sonbol, H., & Alomary, M. N. (2021). A review on Saudi Arabian wastewater treatment facilities and available disinfection methods: Implications to SARS-CoV-2 control. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 101574.
Alkhudhiri, A., Darwish, N. B., & Hilal, N. (2019). Analytical and forecasting study for wastewater treatment and water resources in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 32, 100915.
Alshehrei, F., Al-Enazi, N. M., & Ameen, F. (2021). Vermicomposting amended with microalgal biomass and biochar produce phytopathogen-resistant seedbeds for vegetables. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–8.
Ameen, F., & Al-Homaidan, A. A. (2021). Compost inoculated with fungi from a mangrove habitat improved the growth and disease defense of vegetable plants. Sustainability, 13(1), 124.
Ameen, F., & Al-Homaidan, A. A. (2022). Improving the efficiency of vermicomposting of polluted organic food wastes by adding biochar and mangrove fungi. Chemosphere, 286, 131945.
Bhat, S. A., Singh, S., Singh, J., Kumar, S., Vig, A. P., et al. (2018). Bioremediation and detoxification of industrial wastes by earthworms: Vermicompost as powerful crop nutrient in sustainable agriculture. Bioresource Technology, 252, 172–179.
Biruntha, M., Karmegam, N., Archana, J., Selvi, B. K., Paul, J. A. J., Balamuralikrishnan, B., et al. (2020). Vermiconversion of biowastes with low-to-high C/N ratio into value added vermicompost. Bioresource Technology, 297, 122398.
Coelho, C., Foret, C., Bazin, C., Leduc, L., Hammada, M., Inácio, M., & Bedell, J. P. (2018). Bioavailability and bioaccumulation of heavy metals of several soils and sediments (from industrialized urban areas) for Eisenia fetida. Science of the Total Environment, 635, 1317–1330.
Dominguez, J., Aira, M., Kolbe, A. R., Gómez-Brandón, M., & Pérez-Losada, M. (2019). Changes in the composition and function of bacterial communities during vermicomposting may explain beneficial properties of vermicompost. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–11.
Drewes, J. E., Patricio Roa Garduño, C., & Amy, G. L. (2012). Water reuse in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia-Status, prospects and research needs. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 12(6), 926–936.
Fu, X., Huang, K., Cui, G., Chen, X., Li, F., Zhang, X., & Li, F. (2015). Dynamics of bacterial and eukaryotic community associated with stability during vermicomposting of pelletized dewatered sludge. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 104, 452–459.
Govarthanan, M., Mythili, R., Selvankumar, T., Kamala-Kannan, S., & Kim, H. (2018). Myco-phytoremediation of arsenic-and lead-contaminated soils by Helianthus annuus and wood rot fungi, Trichoderma sp. isolated from decayed wood. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 151, 279–284.
Govarthanan, M., Mythili, R., Selvankumar, T., Kamala-Kannan, S., Rajasekar, A., & Chang, Y.-C. (2016). Bioremediation of heavy metals using an endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus sp. RM isolated from the roots of Tridax procumbens. 3 Biotech, 6(2), 1–7.
Govarthanan, M., Lee, G. -W., Park, J. -H., Kim, J. S., Lim, S. -S., Seo, S. -K., et al. (2014). Bioleaching characteristics, influencing factors of Cu solubilization and survival of Herbaspirillum sp. GW103 in Cu contaminated mine soil. Chemosphere, 109, 42–48.
Govarthanan, M., Lee, K. -J., Cho, M., Kim, J. S., Kamala-Kannan, S., & Oh, B. -T. (2013). Significance of autochthonous Bacillus sp. KK1 on biomineralization of lead in mine tailings. Chemosphere, 90(8), 2267–2272.
Guan, T. X., He, H. B., Zhang, X. D., & Bai, Z. (2011). Cu fractions, mobility and bioavailability in soil-wheat system after Cu-enriched livestock manure applications. Chemosphere, 82(2), 215–222.
Hait, S., & Tare, V. (2012). Transformation and availability of nutrients and heavy metals during integrated composting–Vermicomposting of sewage sludges. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 79, 214–224.
He, X., Zhang, Y., Shen, M., Zeng, G., Zhou, M., & Li, M. (2016). Effect of vermicomposting on concentration and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge with additive materials. Bioresource Technology, 218, 867–873.
Karmegam, N., Jayakumar, M., Govarthanan, M., Kumar, P., Ravindran, B., & Biruntha, M. (2021). Precomposting and green manure amendment for effective vermitransformation of hazardous coir industrial waste into enriched vermicompost. Bioresource Technology, 319, 124136.
Karmegam, N., Karthikeyan, V., & Ambika, D. (2012). Vermicomposting of sugarcane trash and leaf litter in combination with pressmud using the earthworm, Perionyx Ceylanensis. Dynamic Soil, Dynamic Plant, 6(1), 57–64.
Khan, M. B., Cui, X., Jilani, G., Tang, L., Lu, M., Cao, X., et al. (2020). New insight into the impact of biochar during vermi-stabilization of divergent biowastes: Literature synthesis and research pursuits. Chemosphere, 238, 124679.
Lee, L. H., Wu, T. Y., Shak, K. P. Y., Lim, S. L., Ng, K. Y., Nguyen, M. N., & Teoh, W. H. (2018). Sustainable approach to biotransform industrial sludge into organic fertilizer via vermicomposting: A mini-review. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 93(4), 925–935.
Malińska, K., & Zabochnicka-Świkatek, M. (2013). Selection of bulking agents for composting of sewage sludge. Environment Protection Engineering, 39(2).
Malińska, K., Golańska, M., Caceres, R., Rorat, A., Weisser, P., & Ślęzak, E. (2017). Biochar amendment for integrated composting and vermicomposting of sewage sludge–The effect of biochar on the activity of Eisenia fetida and the obtained vermicompost. Bioresource Technology, 225, 206–214.
Ndegwa, P. M., & Thompson, S. A. (2000). Effects of C-to-N ratio on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresource Technology, 75(1), 7–12.
Nelson, D. W., & Bremner, J. M. (1972). Preservation of soil samples for inorganic nitrogen analyses 1. Agronomy Journal, 64(2), 196–199.
Ouda, O. K. M. (2014). Impacts of agricultural policy on irrigation water demand: A case study of Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Water Resources Development, 30(2), 282–292.
Ouda, O. K. M., Raza, S. A., Nizami, A. S., Rehan, M., Al-Waked, R., & Korres, N. E. (2016). Waste to energy potential: A case study of Saudi Arabia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 61, 328–340.
Pathak, A., Dastidar, M. G., & Sreekrishnan, T. R. (2009). Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8), 2343–2353.
Qasem, N. A. A., Mohammed, R. H., & Lawal, D. U. (2021). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water, 4(1), 1–15.
Qiu, B., Tao, X., Wang, H., Li, W., Ding, X., & Chu, H. (2021). Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 105081.
Rathika, R., Khalifa, A. Y. Z., Srinivasan, P., Praburaman, L., Kamala-Kannan, S., Selvankumar, T., et al. (2020). Effect of citric acid and vermi-wash on growth and metal accumulation of Sorghum bicolor cultivated in lead and nickel contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 243, 125327.
Sanchez-Hernandez, J. C., Ro, K. S., & Diaz, F. J. (2019). Biochar and earthworms working in tandem: Research opportunities for soil bioremediation. Science of the Total Environment, 688, 574–583.
Shrimal, S., & Khwairakpam, M. (2010). Effect of C/N ratio on vermicomposting of vegetable waste. Dynamic Soil, Dynamic Plant, 4, 123–126.
Singh, J., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2013). Reduction of bioavailability and leachability of heavy metals during vermicomposting of water hyacinth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(12), 8974–8985.
Soobhany, N., Mohee, R., & Garg, V. K. (2017). Inactivation of bacterial pathogenic load in compost against vermicompost of organic solid waste aiming to achieve sanitation goals: A review. Waste Management, 64, 51–62.
Suthar, S., & Singh, S. (2008). Feasibility of vermicomposting in biostabilization of sludge from a distillery industry. Science of the Total Environment, 394(2–3), 237–243.
Suthar, S., Pandey, B., Gusain, R., Gaur, R. Z., et al. (2017). Nutrient changes and biodynamics of Eisenia fetida during vermicomposting of water lettuce (Pistia sp.) biomass: A noxious weed of aquatic system. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 199–207.
Suthar, S., Sajwan, P., & Kumar, K. (2014). Vermiremediation of heavy metals in wastewater sludge from paper and pulp industry using earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 109, 177–184.
Swati, A., & Hait, S. (2018). A comprehensive review of the fate of pathogens during vermicomposting of organic wastes. Journal of Environmental Quality, 47(1), 16–29.
Tandon, H. L. S., et al. (2005). Methods of analysis of soils, plants, waters, fertilisers & organic manures. Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37(1), 29–38.
Wang, L., Wang, Y., Ma, F., Tankpa, V., Bai, S., Guo, X., & Wang, X. (2019). Mechanisms and reutilization of modified biochar used for removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 1298–1309.
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Lian, J., Chao, J., Gao, Y., Yang, F., & Zhang, L. (2013). Impact of fly ash and phosphatic rock on metal stabilization and bioavailability during sewage sludge vermicomposting. Bioresource Technology, 136, 281–287.
Wu, Y., Chen, C., Wang, G., Xiong, B., Zhou, W., Xue, F., et al. (2020). Mechanism underlying earthworm on the remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil. Science of the Total Environment, 728, 138904.
Xiang, W., Zhang, X., Chen, J., Zou, W., He, F., Hu, X., et al. (2020). Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere, 252, 126539.
Yatoo, A. M., Ali, M. N., Baba, Z. A., & Hassan, B. (2021). Sustainable management of diseases and pests in crops by vermicompost and vermicompost tea. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 41(1), 1–26.
Yesil, H., & Tugtas, A. E. (2019). Removal of heavy metals from leaching effluents of sewage sludge via supported liquid membranes. Science of the Total Environment, 693, 133608.
Yuvaraj, A., Thangaraj, R., & Maheswaran, R. (2019). Decomposition of poultry litter through vermicomposting using earthworm Drawida sulcata and its effect on plant growth. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(11), 7241–7254.
Yuvaraj, A., Thangaraj, R., Karmegam, N., Ravindran, B., Chang, S. W., Awasthi, M. K., & Kannan, S. (2021). Activation of biochar through exoenzymes prompted by earthworms for vermibiochar production: A viable resource recovery option for heavy metal contaminated soils and water. Chemosphere, 130458.
Zhang, J., Mueller, C., & Cai, Z. (2015). Heterotrophic nitrification of organic N and its contribution to nitrous oxide emissions in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 84, 199–209.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the National Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH), King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (Award Number 2-17-01-001-0051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors have participated and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ameen, F., Al-Homaidan, A.A. Treatment of heavy metal–polluted sewage sludge using biochar amendments and vermistabilization. Environ Monit Assess 194, 861 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10559-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10559-x