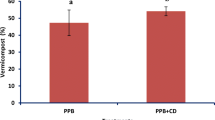
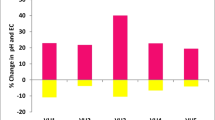
Abstract
In Colombia, more than 1 million tons of coffee pulp are produced every year. Its transformation into compost by means of turned piles has led to a final product with poor physical and chemical characteristics and vermicomposting has been suggested as an alternative method of transforming these wastes into a useful organic fertilizer. The ability of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to transform coffee pulp into a valuable compost was evaluated. The influence of bed depth and time on different C fractions, N content and availability of nutrients was studied. The results showed that the C and N contents were not affected by the depth of the bed, whereas time affected both. An increase in the fractionation ratio, determined by calculating the C in the fraction smaller than 100 μm as a percentage of C in the samples as a whole, and low values of humic-like substances were recorded during vermicomposting. After ingestion of the pulp by the earthworms, an increase in available P, Ca, and Mg but a decrease in K were detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham FT (1982) Boron. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis, pp 431–448
Bruckert S (1982) Analysis of the organo-mineral complexes of soils. In: Bonneau M, Souchier B (eds) Constituents and properties of soils. Academic Press, London, pp 214–237
Cegarra J, Frutos C, Tercero A, Roig A, De Godos A (1989) Study of soluble humic substances from newly prepared organic fertilizers. Sci Total Environ 81/82:579–588
Cortez J, Hameed R, Bouché MB (1989) C and N transfer in soil with or without earthworms fed with 14C-and 15N-labelled wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 21:491–497
Edwards CA (1988) Breakdown of animal, vegetable and industrial organic wastes by earthworms. In: Edwards CA, Neuhauser EF (eds) Earthworms in waste and environmental management. SPB Academic, The Hague, pp 21–31
Edwards CA, Burrows I (1988) The potential of earthworm composts as plant growth media. In: Edwards CA, Neuhauser EF (eds) Earthworms in waste and environmental management. SPB Academic, The Hague, pp 211–219
Edwards CA, Lofty JR (1977) Biology of earthworms. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Haimi J, Huhta V (1986) Capacity of various organic residues to support adequate earthworm biomass for vermicomposting. Biol Fertil Soils 2:23–27
Hartenstein F, Hartenstein E, Hartenstein R (1981) Gut load and transit time in the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Pedobiologia 22:5–20
Hervas L, Mazuelos C, Senesi N, Saiz-Jimenez C (1989) Chemical and physicochemical characterization of vermicomposts and their humic acid fractions. Sci Total Environ 81/82:543–550
Kaplan DL, Hartenstein R, Neuhauser EF, Malecki MR (1980) Physicochemical requirements in the environment of the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Soil Biol Biochem 12:347–352
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Mansell GP, Syers JK, Gregg PEH (1981) Plant availability of phosphorus in dead herbage ingested by surface-casting earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 13:163–167
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified simple solution method for the deremination of phosphate in natural water. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Navarro AF, Cegarra J, Roig A, Bernal MP (1991) An automatic microanalysis method for the determination of organic carbon in wastes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 22:2137–2144
Reinecke AJ, Venter JM (1987) Moisture preferences, growth and reproduction of the compost worm Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta). Biol Fertil Soils 3:135–141
Satchell JE, Martin K (1984) Phosphatase activity in earthworms faeces. Soil Biol Biochem 16:191–194
Thomas GW (1982) Exchangeable cations. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis, pp 159–165
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orozco, F.H., Cegarra, J., Trujillo, L.M. et al. Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia fetida: Effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biol Fert Soils 22, 162–166 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384449
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384449