Abstract
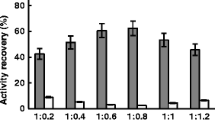
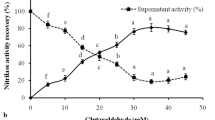
Cross-linked enzyme aggregates of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL-CLEAs) from Rhodotorula glutinis were prepared. The effects of the type of aggregating agent, its concentration, and that of cross-linking agent were studied. PAL-CLEAs production was most effective using ammonium sulfate (40 % saturation), followed by cross-linking for 1 h with 0.2 % (v/v) glutaraldehyde. Moreover, the storage and operational stability of the resulting PAL-CLEAs were also investigated. Compared to the free enzyme, the PAL-CLEAs exhibited the expected increased stability of the enzyme against various deactivating conditions such as pH, temperature, denaturants, and organic solvents and showed higher storage stability than its soluble counterpart. Additionally, the reusability of PAL-CLEAs with respect to the biotransformation of l-phenylalanine was evaluated. PAL-CLEAs could be recycled at least for 12 consecutive batch reactions without dramatic activity loss, which should dramatically increase the commercial potential of PAL for synthesis of l-phenylalanine. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of immobilization of PAL as cross-linked enzyme aggregates.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aytar, B. S., & Bakir, U. (2008). Process Biochemistry, 43, 125–131.
Mateo, C., Palomo, J. M., Langen, L. M., van-Rantwijk, F., & Sheldon, R. A. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 15, 273–276.
Sheldon, R. A. (2007). Biochemical Society Transactions, 35, 1583–1587.
Cabana, H., Jones, J. P., & Agathos, S. N. (2007). Journal of Biotechnology, 132, 23–31.
Gupta, P., Dutt, K., Misra, S., Raghuwanshi, S., & Saxena, R. K. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 4074–4076.
Kaul, P., Stolz, A., & Banerjee, U. C. (2007). Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis, 349, 2167–2176.
Fiske, M. J., & Kane, J. F. (1984). Journal of Bacteriology, 160, 676–681.
D’ Cunha, G. B. (2005). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 36, 498–502.
Rosler, J., Krekel, F., & Amrhein, N. (1997). Plant Physiology, 113, 175–179.
Yue, H. Y., Yuan, Q. P., & Wang, W. Ch. (2007). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 37, 231–237.
Leng, Y., Zheng, P., & Sun, Zh. H. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 1669–1672.
Serpil, T., Bulent, A., & Tuncer, H. O. (1995). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 17, 445–542.
D’ Cunha, G. B., Satyanarayan, V., & Nair, P. M. (1996). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 19, 421–427.
Batal, A. I. E. (2002). Acta Microbiologica Polonica, 51, 139–152.
Zhang, B. Zh., & Cui, J. D. (2010). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 2795–2800.
Nakamichi, K., Yamada, N. S., & Chibata, I. (1983). European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 158–162.
Cui, J. D., Jia, S. R., & Sun, A. Y. (2008). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 46, 631–635.
Orndorff, S. A., Costantino, N., & Stewart, D. (1988). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 996–1002.
Shah, S., Sharma, A., & Gupta, M. N. (2006). Analytical Biochemistry, 351, 207–213.
Xu, D. Y., Yang, Y., & Yang, Zh. (2011). Journal of Biotechnology, 152, 30–36.
Hormigo, D., Garcia-Hidalgo, J., Acebal, C., De La Mata, I., & Arroyo, M. (2011). Bioresource Technology, doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.035.
Rees, D. G., & Jones, D. H. (1996). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 19, 282–288.
Acknowledgments
The project was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Project No. 21072041), Open Funding Project of the National Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering (no. KF2010-12) and the Foundation (no. GYWSW02) of Tianjin Key Laboratory of Industrial Microbiology (Tianjin University of Science and Technology), People’s Republic of China, Natural Science Foundation of Hebei University of Science and Technology (NO. XL201149), and Foundation of Hebei University of Science and Technology for Distinguished Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, JD., Zhang, S. & Sun, LM. Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase: Novel Biocatalysts for Synthesis of L-Phenylalanine. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 835–844 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9738-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9738-0