Abstract
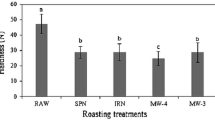
Roasting is a critical step in processing peanut snack foods. The conventional roasting using hot air ovens has drawbacks of low production rate, poor product quality, and high energy cost. This study investigated the feasibility of using hot air-assisted radio frequency (RF) to roast dried salted peanuts. Physicochemical properties, volatile compounds, and sensory quality of the roasted peanuts were determined. The quality changes and shelf-life of vacuum-packaged roast peanuts stored under an accelerated shelf-life testing (ASLT) trial conducted at 20 and 50 °C were also evaluated. After 45 min roasting, moisture content of the salted peanuts reduced from initial 7.7 to 3.1 % and acid and peroxide values were 0.26 ± 0.02 mg/g and 2.46 ± 0.10 meq/kg, respectively, all in the levels associating with good quality of roasted peanuts. Sensory evaluation further validated the good quality of the roasted peanuts. Totally, 69 volatile compounds were identified in the roasted peanuts, in which 3 new volatiles were produced after about 13 weeks of storage. During the storage, relative concentrations of the favorable volatile compounds (mainly pyrazines and furan compounds) decreased in a certain degree, while the relative concentrations of some undesirable flavor compounds increased. The roasted peanuts had 31 weeks of shelf-life based on the industrial standard on the peroxide value. This study demonstrated that hot air-assisted RF roasting can produce high-quality roasted peanuts with prolonged shelf-life, thus, a new technology for the peanut roasting industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOCS. (1998). AOCS official method Cd 8-53 peroxide value acetic acid-chloroform method. In D. Firestone (Ed.), Official methods and recommended practices of the AOCS (5th ed.). Champaign: American Oil Chemists’ Society.
Baker, G. L., Sims, C. A., Gorbet, D. A., Sanders, T. H., & O’Keefe, S. F. (2002). Storage water activity effect on oxidation and sensory properties of high-oleic peanuts. Journal of Food Science, 67(4), 1600–1603.
Baker, G. L., Cornell, J. A., Gorbet, D. W., O’Keefe, S. F., Sims, C. A., & Talcott, S. T. (2003). Determination of pyrazine and flavor variations in peanut genotypes during toasting. Journal of Food Science, 68(1), 394–400.
Chen, T., Kang, B., Chen, S., Chen, H., & Lin, H. (2010). Optimized parameters and quality analysis of salty and crisp peanut by far-infrared roasting. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 26(8), 320–325.
Farag, K. W., Lyng, J. G., Morgan, D. J., & Cronin, D. A. (2011). A comparison of conventional and radio frequency thawing of beef meats: effects on product temperature distribution. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4, 1128–1136.
Gao, M., Tang, J., Villa-Rojas, R., Wang, Y., & Wang, S. (2011). Pasteurization process development for controlling salmonella in in-shell almonds using radio frequency energy. Journal of Food Engineering, 104(2), 299–306.
Grosso, N. R., & Resurreccion, A. V. A. (2002). Predicting consumer acceptance ratings of cracker-coated and roasted peanuts from descriptive analysis and hexanal measurements. Journal of Food Science, 67(4), 1530–1537.
Ho, C. T., & Shahidi, F. (2005). Flavor components of fats and oil. In F. Shahidi (Ed.), Bailey’s industrial oil and fat products (pp. 387–411). New Jersey: Wiley.
Jiao, S., Tang, J., Johnson, J. A., & Wang, S. (2012). Industrial-scale radio frequency treatments for insect control in lentils. Journal of Stored Products Research, 48, 143–148.
Jiao, S., Deng, Y., Zhong, Y., Wang, D., & Zhao, Y. (2015). Investigation of radio frequency heating uniformity of wheat kernels by using the developed computer simulation model. Food Research International, 71, 41–49.
Jumah, R. (2005). Modelling and simulation of continuous and intermittent radio frequency-assisted fluidized bed drying of grains. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 83(C3), 203–210.
Kalua, C. M., Allen, M. S., Bedgood, D. R., Jr., Bishop, A. G., Prenzler, P. D., & Robards, K. (2007). Olive oil volatile compounds, flavor development and quality: a critical review. Food Chemistry, 100, 273–286.
Kim, S. Y., Sagong, H. G., Choi, S. H., Ryu, S., & Kang, D. H. (2012). Radio-frequency heating to inactivate Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 on black and red pepper spice. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 153, 171–175.
Labuza, T. P. (1984). Application of chemical kinetics to deterioration of foods. Journal of Chemical Education, 61(4), 348–358.
Liu, X., Jin, Q., Liu, Y., Huang, J., Wang, X., Mao, W., & Wang, S. (2011). Changes in volatile compounds of peanut oil during the roasting process for production of aromatic roasted peanut oil. Journal of Food Science, 76(3), C404–C412.
Nelson, S. O. (1996). Review and assessment of radio-frequency and microwave energy for stored-grain insect control. Transaction of ASAE, 39, 1475–1484.
Palazoğlu, T. K., Coşkun, Y., Kocadağlı, T., & Gӧkmen, V. (2012). Effect of radio frequency postdrying of partially baked cookies on acrylamide content, texture, and color of the final product. Journal of Food Science, 77(5), E113–E117.
Peryam, D. M. (1964). Consumer preference evaluation of the storage stability of foods. Food Technology, 18, 1460–1463.
Sanders, T. H. (2002). Groundnut (peanut) oil. In F. D. Gunstone (Ed.), Vegetable oils in food technology: composition, properties and uses (pp. 231–243). Florida: CRC Press LLC.
Schirack, A. V., Drake, M., Sanders, T. H., & Sandeep, K. P. (2006). Characterization of aroma-active compounds in microwave blanched peanuts. Journal of Food Science, 71(9), C513–C520.
Smith, A. L., & Barringer, S. A. (2014). Color and volatile analysis of peanuts roasted using oven and microwave technologies. Journal of Food Science, 79(10), C1895–C1906.
Smith, A. L., Perry, J. J., Marshall, J. A., Yousef, A. E., & Barringer, S. A. (2014). Oven, microwave, and combination roasting of peanuts: comparison of inactivation of Salmonella surrogate Enterococcus faecium, color, volatiles, flavor, and lipid oxidation. Journal of Food Science, 79(8), S1584–S1594.
Vranová, J., & Ciesarová, Z. (2009). Furan in food—a review. Czech Journal of Food Science, 27(1), 1–10.
Wambura, P., Wang, Y., Walker, L. T., Wang, Y., & Williams, L. (2008). Improvement of oxidative stability of roasted peanuts by edible coatings and ultrasonication. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 32, 469–485.
Wang, S., & Tang, J. (2001). Radio frequency and microwave alternative treatments for insect control in nuts: a review. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 10(3&4), 105–120.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Sun, T., Mitcham, E. J., Koral, T., & Birla, S. L. (2006). Considerations in design of commercial radio frequency treatments for postharvest pest control in in-shell walnuts. Journal of Food Engineering, 77, 304–312.
Wang, S., Tiwari, G., Jiao, S., Johnson, J. A., & Tang, J. (2010). Developing postharvest disinfestation treatments for legumes using radio frequency energy. Biosystems Engineering, 105, 341–349.
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, M., Tang, J., & Wang, S. (2014a). Pilot-scale radio frequency drying of macadamia nuts: heating and drying uniformity. Drying Technology, 32, 1052–1059.
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Johnson, J., Gao, M., Tang, J., Powers, J. R., & Wang, S. (2014b). Developing hot air-assisted radio frequency drying for in-shell macadamia nuts. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 278–288.
Warner, K. J. H., Dimick, P. S., Ziegler, G. R., Mumma, R. O., & Hollender, R. (1996). ‘Flavor-fade’ and off-flavors in ground roasted peanuts as related to selected pyrazines and aldehydes. Journal of Food Science, 61(2), 469–472.
Yang, M., Zhou, Q., Liu, C., Zheng, C., & Huang, F. (2011). Changes on quality and volatile flavour compositions of salty peanut by microwave baking during storage. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 33(6), 609–615.
Zhang, M., Tang, J., Mujumdar, A. S., & Wang, S. (2006). Trends in microwave-related drying of fruits and vegetables. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 17, 524–534.
Zhou, Q., Yang, M., Huang, F., & He, J. (2010). Dehydration characteristics of microwave-treated peanut and optimization of microwave dehydration for production of dried salted peanut. Food Science, 31(4), 63–67.
Zhou, Q. (2010). Study of microwave baking on salty peanuts and quality evaluation. Master’s Degree Dissertation. Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted in the Department of Food Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China. GC-MS was performed and analyzed in Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University. This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31401538) and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (20141685).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, S., Zhu, D., Deng, Y. et al. Effects of Hot Air-assisted Radio Frequency Heating on Quality and Shelf-life of Roasted Peanuts. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 308–319 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1624-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1624-7