Abstract
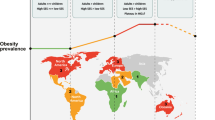
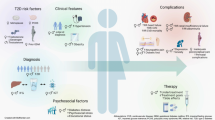
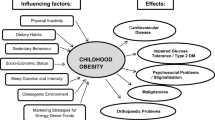
The incidence of overweight and obesity among children has increased dramatically in recent decades, with about one-third of children in the U.S. currently being either overweight or obese. Being overweight in early childhood increases risk for later obesity. There is evidence for the efficacy of family-based behavioral treatment to control weight and improve health outcomes. Obesity-related health risks have been documented, including metabolic syndrome. There is also increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) among youth in recent years, with obesity and family history of T2D generally present. Lower income and ethnic minority status are associated with both obesity and T2D in youth. Most youth with T2D do not achieve optimal glycemic control, and are at high risk for later health complications. Obesity and T2D represent significant public health issues with potentially great personal and societal cost. Research addressing the prevention of obesity and T2D among youth is urgently needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, et al. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. J Am Med Assn. 2014;311:806–814. This epidemiologic study reports rates of overweight and obesity in children in the United States by age, gender, and ethnic groups.
de Onis M, Blössner M, Borghi E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. Am J Clin Nutri. 2010;92:1257–64.
Kumanyika S, Grier S. Targeting interventions for ethnic minority and low-income populations. Future Child. 2006;16:187–207.
Cunningham SA, Kramer MR, Venkat Narayan KM. Incidence of childhood obesity in the United States. New Engl J Med. 2014;370:403–11. This prospective study demonstrates the importance of overweight in early childhood as a predictor of obesity later in childhood.
Pulgarón ER. Childhood obesity: a review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin Ther. 2013;35:A18–32.
Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Banyas B, Allen K, et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:802–10.
Weiss R, Dzuira J, Burgert TS, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Eng J Med. 2004;350:2362–74.
Huang J, Gottschalk M, Norman G, Calfas K, Sallis J, Patrick K. Compliance with behavioral guidelines for diet, physical activity and sedentary behaviors is related to insulin resistance among overweight and obese youth. BMC Res Notes. 2011;4:29.
Delamater AM, Pulgaron ER, Daigre A. Obesity in adolescence. In: O’Donohue W, Benuto L, Tolle L, editors. Adolescent health psychology. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 597–618. This chapter reviews the evidence for various approaches for treatment of obesity in adolescents.
Schwimmer JB, Burnwinkle TM, Varni JW. Health related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. J Am Med Assn. 2003;289:1813–9.
Goodman E, Whitaker RC. A prospective study of the role of depression in the development and persistence of adolescent obesity. Pediatrics. 2002;110:497–504.
Reilly JJ. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obesity. 2011;35:891–8.
Gortmaker SL, Must A, Perrin JM, et al. Social and economic consequences of overweight in adolescence and young adulthood. N Engl J Med. 1993;32:1008–12.
Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Maillot M, et al. Early adiposity rebound: causes and consequences for obesity in children and adults. Int J Obes. 2006;30:S11–7. Epidemiologic longitudinal study showing importance of early adiposity rebound as a predictor of higher body mass index later in childhood.
Williams SM, Goulding A. Patterns of growth associated with the timing of adiposity rebound. Obesity. 2009;17:335–41.
Pate RR, O’Neill JR, Liese AD, et al. Factors associated with development of excessive fatness in children and adolescents: a review of prospective studies. Obes Rev. 2013;14:645–58.
Thibault H, Contrand B, Saubusse E, et al. Risk factors for overweight and obesity in French adolescents: physical activity, sedentary behavior and parental characteristics. Nutrition. 2010;26:192–200.
Polley DC, Spicer MT, Knight AP, et al. Intrafamilial correlates of overweight and obesity in African-American and Native-American grandparents, parents, and children in rural Oklahoma. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105:262–5.
Kitsantas P, Gaffney KF. Risk profiles for overweight/obesity among preschoolers. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:563–8.
Francis LA, Ventura AK, Birch LL, et al. Parent overweight predicts daughters’ increase in BMI and disinhibited overeating from 5 to 13 years. Obesity. 2007;15:1544–53.
Silventoinen K, Rokholm B, Kaprio J, Sørensen TI. The genetic and environmental influences on childhood obesity: a systematic review of twin and adoption studies. Int J Obesity. 2010;34:29–40.
Huffman FG, Kanikireddy S, Patel M. Parenthood—a contributing factor to childhood obesity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2010;7:2800–10.
Hendrie GA, Coveney J, Cox DN. Defining the complexity of childhood obesity and related behaviours within the family environment using structural equation modelling. Public Health Nutr. 2011;15:48–57.
Elder JP, Arredondo EM, Campbell N, et al. Individual, family, and community environmental correlates of obesity in Latino elementary school children. J Sch Health. 2010;80:20–30.
Epstein LH, Raja S, Daniel TO, et al. The built environment moderates effects of family-based childhood obesity treatment over 2 years. Ann Behav Med. 2012;44:248–58.
Currie J, Della Vigna S, Moretti E, et al. The effect of fast food restaurants on obesity and weight gain. Am Economic J. 2010;2:32–63.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance—United States. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012;61:1–168. This study documents low rates of healthy eating and physical activity among high school students.
Dennison BA, Erb TA, Jenkins PL. Television viewing and television in bedroom associated with overweight risk among low-income preschool children. Pediatrics. 2002;109:1028–35.
Steffen LM, Shifan D, Fulton JE, et al. Overweight in children and adolescents associated with TV viewing and parental weight project heartbeat! Am J Prev Med. 2009;37:S50–5.
Trevino RP, Marshall RM, Hale DE, Rodriguez R, Baker G, Gomez J. Diabetes risk factors in low-income Mexican-American children. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:202–7.
Cruz ML, Weigensberg MJ, Huang TT, Ball G, Shaibi GQ, Goran MI. The metabolic syndrome in overweight Hispanic youth and the role of insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocr Metab. 2004;89:108–13.
Arslanian S, Suprasongsin C. Differences in the vivo insulin secretion and sensitivity of healthy Black vs White adolescents. J Pediatr. 1996;129:440–3.
Troiano RP. Physical inactivity among young people. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:706–7.
Gordon-Larsen P, McMurray RG, Popkin BM. Determinants of adolescent physical activity and inactivity patterns. Pediatrics. 2000;105:e83–90.
Black JL, Macinko J. Neighborhoods and obesity. Nutr Rev. 2008;66:2–20.
Sallis JF, Zakarian JM, Hovell MF, Hofstetter R. Ethnic, socioeconomic, and sex differences in physical activity among adolescents. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49:125–34.
Poortinga W. Perceptions of the environment, physical activity, and obesity. Soc Sci Med. 2006;63:2835–46.
Romero AJ. Low-income neighborhood barriers and resources for adolescents’ physical activity. J Adolesc Health. 2005;36:253–9.
Frank LD, Andresen MA, Schmid TL. Obesity relationships with community design, physical activity, and time spent in cars. Am J Prev Med. 2004;27:87–96.
Baker EA, Schootman M, Barnidge E, Kelly C. The role of race and poverty in access to foods that enable individuals to adhere to dietary guidelines. Prev Chron Dis. 2006;3:A76.
US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2010;125:361–7. This report provides recommendations for the evaluation and treatment of obesity in children and adolescents.
Nemet D, Barkan S, Epstein L, et al. Short and long term beneficial effects of a combined dietary-behavioral-physical activity intervention for the treatment of childhood obesity. Pediatrics. 2005;115:443–9.
Steele RG, Aylward B, Jensen CD, et al. Comparison of a family-based group intervention for youths with obesity to a brief individual family intervention: a practical clinical trial of Positively Fit. J Pediatr Psychol. 2011;37;1–11.
Saelens BE, Lozano P, Scholz K. A randomized clinical trial comparing delivery of behavioral pediatric obesity treatment using standard and enhanced motivational approaches. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38:954–64.
de Niet J, Timman R, Jongejan M, Passchier J, van den Akker E. Predictors of participant dropout at various stages of a pediatric lifestyle program. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e164–70.
Savoye M, Nowicka P, Shaw M, Yu S, Dziura J, Chavent G, et al. Long-term results of an obesity program in an ethnically diverse pediatric population. Pediatr. 2011;127:402–10.
Winett RA, Roodman AA, Winett SG, Bajzek W, Rovniak LS, Whiteley JA. The effects of Eat4Life internet-based health behavior program on the nutrition and activity practices of high school girls. J Gender Cult Health. 1999;4:239–54.
Davis AM, Sampilo M, Gallagher KS, Landrum Y, Malone B. Treating rural pediatric obesity through telemedicine: outcomes from a small randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38:932–43.
Lipana LS, Bindal D, Nettiksimmons J, et al. Telemedicine and face-to-face care for pediatric obesity. Telemed e-Health. 2013;19:806–8.
Delamater AM, Pulgaron ER, Rarback S, Hernandez J, Carrillo A, Christiansen S, et al. Web-based family intervention for overweight children: a pilot study. Childhood Obes. 2013;9:57–63.
Mulgrew KW, Shaikh U, Nettiksimmons J. Comparison of parent satisfaction with care for childhood obesity delivered face-to-face and by telemedicine. Telemed J E Health. 2011;17:383–7.
Kelly KP, Kirschenbaum DS. Immersion treatment of childhood and adolescent obesity: the first review of a promising intervention. Obes Rev. 2011;12:37–49.
Braet C, Tanghe A, Decaluwè V, et al. Inpatient treatment for children with obesity: weight loss, psychological well-being, and eating behavior. J Pediatr Pyschol. 2004;29:519–29.
Huelsing J, Kanafani N, Mao J, et al. Camp jump start: effects of a residential summer weight-loss camp for older children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e884–90.
Viner RM, Hsia Y, Tomsic T, et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-obesity drugs in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2010;11:593–602.
Kay JP, Alemzadeh R, Langley G, et al. Beneficial effects of metformin in normoglycemic morbidly obese adolescents. Metabolism. 2001;50:1457–61.
Srinivasan S, Ambler GR, Baur LA, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of metformin for obesity and insulin résistance in children and adolescents: Improvement in body composition and fasting insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2074–80.
Matson KL, Fallon RM. Treatment of obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2012;17:45–57.
Bondada S, Jen HC, Duegarte DA. Outcomes of bariatric surgery in adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2011;23:552–6. Review of studies of bariatric surgery outcomes for morbidly obese adolescents.
Messiah SE, Lopez-Mitnik G, Winegar D, et al. Changes in weight and co-morbidities among adolescents undergoing bariatric surgery: 1-year results from the Bariatric Outcomes Longitudinal Database. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9:503–13.
Inge TH, Xanthakos SA, Zeller MH. Bariatric surgery for pediatric obesity: now or later? Int J Obes. 2007;31:1–14.
Johnson SB, Pilkington LL, Lamp C, He J, Deeb LC. Parent reactions to a school‐based body mass index screening program. J School Health. 2009;79:216–23.
Grey M, Jaser SS, Holl MG, Jefferson V, Dziura J, Northrup V. A multifaceted school-based intervention to reduce risk for type 2 diabetes in at-risk youth. Prev Med. 2009;49:122–8.
The Healthy Study Group. A school-based intervention for diabetes risk reduction. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:443–53. Report of a national multi-site randomized controlled trial to prevent type 2 diabetes in youth.
Kaufman FR, Hirst K, Linder B, Baranowski T, Cooper DM, Foster GD, et al. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes in a sixth-grade multiracial cohort: the HEALTHY study. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:953–5.
Arslanian SA. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children: pathophysiology and risk factors. J Pediatr Endocr Met. 2000;13:1385–94.
Rosenbloom AL, Silverstein JH, Amemiya S, Zeitler P, Klingensmith G. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2007-2007. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in the child and adolescent. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009;9:512–26. Report of consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes in youth.
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus—present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8:228–36. Discussion of data on rising incidence of type 2 diabetes among youth throughout the world.
Cizza G, Brown RJ, Rothe KI. Rising incidence and challenges of childhood diabetes. A Mini-RevJ Endocrinol Invest. 2012;35:541–6.
Fagot-Campagna A, Pettitt DJ, Engelgau MM, Burrows NR, Geiss LS, Valdez R, et al. Type 2 diabetes among North American children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review and a public health perspective. J Pediatr. 2000;136:664–72.
Liese AD, D'Agostino RB, Hamman RF, Kilgo PD, Lawrence JM, Liu LL, et al. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1510–8.
Dabelea D, Bell RA, D'Agostino RB, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, et al. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. J Am Med Assoc. 2007;297:2716–24.
American Diabetes Association. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:381–9.
Kaufman F. Type 2 diabetes in youth: rates, antecedents, treatment, problems and prevention. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8:4–6.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Daniels SR, Standiford D, Khoury PR, Zeitler P. Increased incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among adolescents. J Pediatr. 1996;128:608–15.
Neufeld ND, Raffel LJ, Landon C, Chen YDI, Vadheim CM. Early presentation of type 2 diabetes in Mexican-American youth. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:80–6.
Haines L, Wan KC, Lynn R, Barrett TG, Shield J. Rising incidence of type 2 diabetes in children in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1097–101.
Mohan V, Jaydip R, Deepa R. Type 2 diabetes in Asian Indian youth. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8 Suppl 9:28–34.
Tang M, Chen Y, Krewski D. Gender-related differences in the association between socioeconomic status and self-reported diabetes. Int J Epidemiol. 2003;32:381–5.
Delva J, O’Malley PM, Johnston LD. Racial/ethnic and socioeconomic status differences in overweight and health-related behaviors among American students: national trends 1986-2003. J Adolescent Health. 2006;39:536–45.
Shaw J. Epidemiology of childhood type 2 diabetes and obesity. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8 Suppl 9:7–15.
Scott CR, Smith JM, Michaeleen C, Pihoker C. Characteristics of youth-onset noninsulin-diabetes mellitus and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus at diagnosis. Pediatrics. 1997;100:84–91.
Dean HJ, Sellers EA. Comorbidities and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8 Suppl 9:35–41.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Acute and chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Lancet. 2007;369:1823–31.
Copeland KC, Zeitler P, Geffner M, Guandalini C, Higgins J, Hirst K, et al. The TODAY Study Group. Characteristics of adolescents and youth with recent-onset type 2 diabetes: the TODAY cohort at baseline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:159–67.
Levitt Katz LE, Magge SN, Hernandez ML, Murphy KM, McKnight HM, Lipman T. Glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes declines as early as two years after diagnosis. J Pediatr. 2011;158:100–5.
Rhodes ET, Prosser LA, Hoerger TJ, Lieu T, Ludwig DS, Laffel LM. Estimated morbidity and mortality in adolescents and young adults diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2012;29:453–63. This report estimates the high morbidity and early mortality expected among youth with type 2 diabetes.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Standiford D, Hamiel D, Dolan LM, Cohen R, Zeitler S. The type 2 family: a setting for development and treatment of adolescent type 2 diabetes. Arch Pediat Adol Med. 1999;153:1063–7.
Rothman RL, Mulvaney S, Elasy TA, VanderWoude A, Gebretsadik T, Shintani A, et al. Self-management behaviors, racial disparities, and glycemic control among adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Pediatrics. 2008;121:e912–9.
Shaibi GQ, Faulknere MS, Wegensberg MJ, Fritschi C, Goran MI. Cardiorespiratory fitness and physical activity in youth with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9:460–3.
Kriska A, Delahanty L, Edelstein S, Amodei N, Chadwick J, Copeland K, et al. Sedentary behavior and physical activity in youth with recent onset of type 2 diabetes. Pediatrics. 2013;131:e850–6.
Jones KL, Arslanian S, Peterokova VA, Park J, Tomlinson MJ. Effect of metformin in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:89–94.
George MM, Copeland KC. Current treatment options for type 2 diabetes mellitus in youth: today’s realities and lessons from the TODAY study. Curr Diab Rep. 2013;13:72–80. This article discusses implications of the TODAY trial including a review of various pharmacologic treatment approaches.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Clinical presentation and treatment of type 2 diabetes in children. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(9):16–27 (b).
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Barriers to the treatment of adolescent type 2 diabetes—a survey of provider perceptions. Pediatr Diabetes. 2003;4:24–8.
The TODAY Study Group. A clinical trial to maintain glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2247–56. Reports the results of a large national multi-site randomized controlled trial to improve glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes.
Delamater AM, Jacquez F, Patino-Fernandez, AM. Type 2 diabetes in youth. In O’Donohue W, Tolle L, editors. Behavioral Approaches to Chronic Disease in Adolescence. New York: Springer; 2009.
Willi SM, Martin K, Datko FM, Brant BP. Treatment of type 2 diabetes in childhood using a very-low-calorie diet. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:348–53.
Inge TH, Miyano G, Bean J, Helmrath M, Courcoulas A, Harmon CM, et al. Reversal of type 2 diabetes mellitus and improvements in cardiovascular risk factors after surgical weight loss in adolescents. Pediatrics. 2009;123:214–22.
Mulvaney SA, Schlundt DG, Mudasiru E, Fleming M, Vander Woude AM, Russell WE, et al. Parent perceptions of caring for adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:993–7.
Jones KL. Non-insulin dependent diabetes in children and adolescents: the therapeutic challenge. Clin Pediatr. 1998;37:103–10.
Anderson BJ, Cullen K, McKay S. Quality of life, family behavior, and health outcomes in children with type 2 diabetes. Pediatr Ann. 2005;34:722–9.
Kawahara R, Amemiya T, Yoshino M, et al. Dropout of young non-insulin-dependent diabetics from diabetic care. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 1994;24:181–5.
Owada M, Nitadori Y, Kitagawa T. Treatment of NIDDM in youth. Clin Pediatr. 1998;37:117–21.
Pihoker C, Scott CR, Lensing SY, Cradock MM, Smith J. Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in African-American youths of Arkansas. Clin Pediatr. 1998;37:97–102.
Reinehr T, Schober E, Roth CL, Wiegand S, Holl R. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in a 2 year follow-up: insufficient adherence to diabetes centers. Horm Res Pediatr. 2008;69:107–13.
Grinstein G, Muzumdar R, Aponte L, Vuguin P, Saenger P, DiMartino-Nardi J. Presentation and 5-year follow-up of type 2 diabetes mellitus in African-American and Caribbean-Hispanic adolescents. Horm Res Pediatr. 2003;60:121–6.
Radius SM, Dillman TE, Becker MH, Rosenstock IM, Horvath WJ. Adolescent perspectives on health and illness. Adolescence. 1980;15:375–84.
Skinner AC, Weinberger M, Mulvaney S, Schlundt D, Rothman RL. Accuracy of perceptions of overweight and relation to self-care behaviors among adolescents with type 2 diabetes and their parents. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:227–9.
Auslander WF, Sterzing PR, Zayas LE, White NH. Psychosocial resources and barriers to self-management in African American adolescents with type 2 diabetes: a qualitative analysis. Diabetes Educ. 2010;36:613–22.
Mulvaney SA, Mudasiru E, Schlundt DG, Baughman CL, Fleming M, VanderWoude A, et al. Self-management in type 2 diabetes: the adolescent perspective. Diabetes Educator. 2008;34:674–82.
Levitt Katz LE, Swami S, Abraham M, et al. Neuropsychiatric disorders at the presentation of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children. Pediatr Diabetes. 2005;6:84–9.
Lawrence JM, Standiford DA, Loots B, Klingensmith GJ, Williams DE, Ruggiero A, et al. Prevalence and correlates of depressed mood among youth with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1348–58.
Anderson BJ, Edelstein S, Abramson NW, Levitt Katz LE, et al. Depressive symptoms and quality of life in adolescents with type 2 diabetes: baseline data from the TODAY study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2205–7.
The TODAY Study Group. Binge eating, mood, and quality of life in youth with type 2 diabetes: baseline data from the TODAY study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:858–60.
Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Jacobs RJ, Gotthalk M, Kaufman F, Jones K. The PedsQL in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:631–7.
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful for the assistance provided by Maria Toro in the preparation of this manuscript.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Elizabeth R. Pulgaron and Alan M. Delamater declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Obesity
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulgaron, E.R., Delamater, A.M. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes in Children: Epidemiology and Treatment. Curr Diab Rep 14, 508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-014-0508-y
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-014-0508-y