Abstract
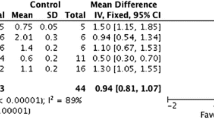
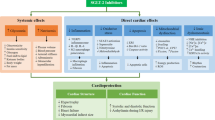
In patients with diabetes mellitus, the incidence of cardiovascular disease is increased, and the outcome following cardiovascular events is worse. The antihyperglycemic drug metformin appears to limit cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes. Indeed, preclinical studies have demonstrated that metformin limits (myocardial) ischemia and reperfusion injury, independent from its glucose-lowering effect. This cardioprotection is mediated by activation of the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK) pathway, activation of AMPK and by an increased formation of adenosine. In addition, metformin can modulate several cardiovascular risk factors and reduces the development of heart failure in murine models. Consequently, treatment with metformin might potentially improve cardiovascular outcome in patients at risk for myocardial ischemia, even if these patients do not have diabetes. In the current paper, we focus on the direct cardioprotective actions of metformin and the mechanisms that underlie these effects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Miki T, Itoh T, Sunaga D, Miura T. Effects of diabetes on myocardial infarct size and cardioprotection by preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11:67.
Nicholls SJ, Tuzcu EM, Kalidindi S, Wolski K, Moon KW, Sipahi I, et al. Effect of diabetes on progression of coronary atherosclerosis and arterial remodeling: a pooled analysis of 5 intravascular ultrasound trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:255–62.
Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–34.
Malmberg K, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Brown J, Zhao F, Hunt D, et al. Impact of diabetes on long-term prognosis in patients with unstable angina and non-q-wave myocardial infarction: Results of the oasis (organization to assess strategies for ischemic syndromes) registry. Circulation. 2000;102:1014–9.
Norhammar A, Lindback J, Ryden L, Wallentin L, Stenestrand U. Improved but still high short- and long-term mortality rates after myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus: A time-trend report from the swedish register of information and knowledge about swedish heart intensive care admission. Heart. 2007;93:1577–83.
Jonas M, Reicher-Reiss H, Boyko V, Behar S, Grossman E. Hospital and 1-year outcome after acute myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2003;17:665–70.
Mathew V, Gersh BJ, Williams BA, Laskey WK, Willerson JT, Tilbury RT, et al. Outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in the current era: a report from the prevention of restenosis with tranilast and its outcomes (presto) trial. Circulation. 2004;109:476–80.
Alserius T, Hammar N, Nordqvist T, Ivert T. Risk of death or acute myocardial infarction 10 years after coronary artery bypass surgery in relation to type of diabetes. Am Heart J. 2006;152:599–605.
Calafiore AM, Di Mauro M, Di Giammarco G, Contini M, Vitolla G, Iaco AL, et al. Effect of diabetes on early and late survival after isolated first coronary bypass surgery in multivessel disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;125:144–54.
Hayat SA, Patel B, Khattar RS, Malik RA. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Clin Sci (Lond). 2004;107:539–57.
Mehta JL, Rasouli N, Sinha AK, Molavi B. Oxidative stress in diabetes: a mechanistic overview of its effects on atherogenesis and myocardial dysfunction. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38:794–803.
Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115:3213–23.
• Aguilar D, Chan W, Bozkurt B, Ramasubbu K, Deswal A. Metformin use and mortality in ambulatory patients with diabetes and heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2011;4:53–8. In this cohort study in patients with diabetes and heart failure, metformin therapy was associated with a lower mortality rate.
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1121–35.
Ansley DM, Wang B. Oxidative stress and myocardial injury in the diabetic heart. J Pathol. 2012.
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–36.
Riksen NP, Smits P, Rongen GA. Ischaemic preconditioning: from molecular characterisation to clinical application—part i. Neth J Med. 2004;62:353–63.
Riksen NP, Smits P, Rongen GA. Ischaemic preconditioning: from molecular characterisation to clinical application–part ii. Neth J Med. 2004;62:409–23.
Qaseem A, Humphrey LL, Sweet DE, Starkey M, Shekelle P. Oral pharmacologic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical practice guideline from the american college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156:218–31.
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012;122:253–70.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, et al. Role of amp-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:1167–74.
El-Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Averet N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X. Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on the respiratory chain complex i. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:223–8.
Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP. Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J. 2000;348(Pt 3):607–14.
Boyle JG, Salt IP, McKay GA. Metformin action on amp-activated protein kinase: a translational research approach to understanding a potential new therapeutic target. Diabet Med. 2010;27:1097–106.
Foretz M, Hebrard S, Leclerc J, Zarrinpashneh E, Soty M, Mithieux G, et al. Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the lkb1/ampk pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:2355–69.
• Roussel R, Travert F, Pasquet B, Wilson PW, Smith Jr SC, Goto S, et al. Metformin use and mortality among patients with diabetes and atherothrombosis. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:1892–9. In this large retrospective cohort study in patients with diabetes and established cardiovascular disease, the use of metformin was associated with a reduced mortality rate, also in patients with heart failure.
Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (ukpds 34). Uk prospective diabetes study (ukpds) group. Lancet. 1998;352:854–865
Schramm TK, Gislason GH, Vaag A, Rasmussen JN, Folke F, Hansen ML, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular risk associated with different insulin secretagogues compared with metformin in type 2 diabetes, with or without a previous myocardial infarction: a nationwide study. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1900–8.
Jorgensen CH, Gislason GH, Andersson C, Ahlehoff O, Charlot M, Schramm TK, et al. Effects of oral glucose-lowering drugs on long term outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus following myocardial infarction not treated with emergent percutaneous coronary intervention—a retrospective nationwide cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010;9:54.
Selvin E, Bolen S, Yeh HC, Wiley C, Wilson LM, Marinopoulos SS, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in trials of oral diabetes medications: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:2070–80.
Saenz A, Fernandez-Esteban I, Mataix A, Ausejo M, Roque M, Moher D. Metformin monotherapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005:CD002966.
Lamanna C, Monami M, Marchionni N, Mannucci E. Effect of metformin on cardiovascular events and mortality: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13:221–8.
Ginsberg HN. Review: efficacy and mechanisms of action of statins in the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:383–92.
Betteridge DJ. Long-term risk reduction: who needs treatment? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;68 Suppl 2:S15–22.
Karam JH. Type ii diabetes and syndrome x. Pathogenesis and glycemic management. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1992;21:329–50.
Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988;37:1595–607.
Bailey CJ, Turner RC. Metformin. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:574–9.
Giugliano D, De Rosa N, Di Maro G, Marfella R, Acampora R, Buoninconti R, et al. Metformin improves glucose, lipid metabolism, and reduces blood pressure in hypertensive, obese women. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:1387–90.
Hollenbeck CB, Johnston P, Varasteh BB, Chen YD, Reaven GM. Effects of metformin on glucose, insulin and lipid metabolism in patients with mild hypertriglyceridaemia and non-insulin dependent diabetes by glucose tolerance test criteria. Diabete Metab. 1991;17:483–9.
Jeppesen J, Zhou MY, Chen YD, Reaven GM. Effect of metformin on postprandial lipemia in patients with fairly to poorly controlled niddm. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:1093–9.
Reaven GM, Johnston P, Hollenbeck CB, Skowronski R, Zhang JC, Goldfine ID, et al. Combined metformin-sulfonylurea treatment of patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes in fair to poor glycemic control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992;74:1020–6.
Robinson AC, Burke J, Robinson S, Johnston DG, Elkeles RS. The effects of metformin on glycemic control and serum lipids in insulin-treated niddm patients with suboptimal metabolic control. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:701–5.
Tessier D, Maheux P, Khalil A, Fulop T. Effects of gliclazide versus metformin on the clinical profile and lipid peroxidation markers in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 1999;48:897–903.
Ghatak SB, Dhamecha PS, Bhadada SV, Panchal SJ. Investigation of the potential effects of metformin on atherothrombotic risk factors in hyperlipidemic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;659:213–23.
Kannel WB, Dawber TR, Kagan A, Revotskie N, Stokes 3rd J. Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease—six year follow-up experience. The framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1961;55:33–50.
Adler AI, Stratton IM, Neil HA, Yudkin JS, Matthews DR, Cull CA, et al. Association of systolic blood pressure with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (ukpds 36): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:412–9.
Petersen JS, DiBona GF. Acute sympathoinhibitory actions of metformin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1996;27:619–25.
Katakam PV, Ujhelyi MR, Hoenig M, Miller AW. Metformin improves vascular function in insulin-resistant rats. Hypertension. 2000;35:108–12.
Bhalla RC, Toth KF, Tan E, Bhatty RA, Mathias E, Sharma RV. Vascular effects of metformin. Possible mechanisms for its antihypertensive action in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am J Hypertens. 1996;9:570–6.
Verma S, Yao L, Dumont AS, McNeill JH. Metformin treatment corrects vascular insulin resistance in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2000;18:1445–50.
Landin K, Tengborn L, Smith U. Treating insulin resistance in hypertension with metformin reduces both blood pressure and metabolic risk factors. J Intern Med. 1991;229:181–7.
Landin-Wilhelmsen K. Metformin and blood pressure. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1992;17:75–9.
Nagi DK, Yudkin JS. Effects of metformin on insulin resistance, risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and plasminogen activator inhibitor in niddm subjects. A study of two ethnic groups. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:621–9.
He H, Zhao Z, Chen J, Ni Y, Zhong J, Yan Z, et al. Metformin-based treatment for obesity-related hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1430–9.
Tremoli E, Ghiselli G, Maderna P, Colli S, Sirtori CR. Metformin reduces platelet hypersensitivity in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1982;41:53–60.
Gin H, Freyburger G, Boisseau M, Aubertin J. Study of the effect of metformin on platelet aggregation in insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1989;6:61–7.
Kakafika AI, Liberopoulos EN, Mikhailidis DP. Fibrinogen: a predictor of vascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13:1647–59.
Anfosso F, Chomiki N, Alessi MC, Vague P, Juhan-Vague I. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 synthesis in the human hepatoma cell line hep g2. Metformin inhibits the stimulating effect of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1993;91:2185–93.
Vague P, Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Badier C, Valadier J. Metformin decreases the high plasminogen activator inhibition capacity, plasma insulin and triglyceride levels in non-diabetic obese subjects. Thromb Haemost. 1987;57:326–8.
Krysiak R, Okopien B. Haemostatic effects of metformin in simvastatin-treated volunteers with impaired fasting glucose. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012.
McCoy RG, Irving BA, Soop M, Srinivasan M, Tatpati L, Chow L, et al. Effect of insulin sensitizer therapy on atherothrombotic and inflammatory profiles associated with insulin resistance. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:561–70.
Agarwal N, Rice SP, Bolusani H, Luzio SD, Dunseath G, Ludgate M, et al. Metformin reduces arterial stiffness and improves endothelial function in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:722–30.
El Messaoudi S, Rongen GA, de Boer RA, Riksen NP. The cardioprotective effects of metformin. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011;22:445–53.
Solskov L, Lofgren B, Kristiansen SB, Jessen N, Pold R, Nielsen TT, et al. Metformin induces cardioprotection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury in the rat heart 24 hours after administration. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;103:82–7.
Bhamra GS, Hausenloy DJ, Davidson SM, Carr RD, Paiva M, Wynne AM, et al. Metformin protects the ischemic heart by the akt-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103:274–84.
Paiva M, Riksen NP, Davidson SM, Hausenloy DJ, Monteiro P, Goncalves L, et al. Metformin prevents myocardial reperfusion injury by activating the adenosine receptor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009;53:373–8.
Paiva MA, Goncalves LM, Providencia LA, Davidson SM, Yellon DM, Mocanu MM. Transitory activation of ampk at reperfusion protects the ischaemic-reperfused rat myocardium against infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2010;24:25–32.
Calvert JW, Gundewar S, Jha S, Greer JJ, Bestermann WH, Tian R, et al. Acute metformin therapy confers cardioprotection against myocardial infarction via ampk-enos-mediated signaling. Diabetes. 2008;57:696–705.
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore: Its fundamental role in mediating cell death during ischaemia and reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:339–41.
Hausenloy DJ, Maddock HL, Baxter GF, Yellon DM. Inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening: a new paradigm for myocardial preconditioning? Cardiovasc Res. 2002;55:534–43.
Zhang L, He H, Balschi JA. Metformin and phenformin activate amp-activated protein kinase in the heart by increasing cytosolic amp concentration. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293:H457–66.
Mubagwa K, Flameng W. Adenosine, adenosine receptors and myocardial protection: an updated overview. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;52:25–39.
Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N. Cardiac remodeling—concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an international forum on cardiac remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:569–82.
Kirpichnikov D, McFarlane SI, Sowers JR. Metformin: an update. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:25–33.
Xie Z, Lau K, Eby B, Lozano P, He C, Pennington B, et al. Improvement of cardiac functions by chronic metformin treatment is associated with enhanced cardiac autophagy in diabetic ove26 mice. Diabetes. 2011;60:1770–8.
• Gundewar S, Calvert JW, Jha S, Toedt-Pingel I, Ji SY, Nunez D, et al. Activation of amp-activated protein kinase by metformin improves left ventricular function and survival in heart failure. Circ Res. 2009;104:403–11. In a mouse model of coronary artery occlusion, long term administration of metformin reduced infarct size and prevented adverse cardiac remodeling, via activation of AMPK.
Yin M, van der Horst IC, van Melle JP, Qian C, van Gilst WH, Sillje HH, et al. Metformin improves cardiac function in a nondiabetic rat model of post-mi heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301:H459–68.
Sasaki H, Asanuma H, Fujita M, Takahama H, Wakeno M, Ito S, et al. Metformin prevents progression of heart failure in dogs: role of amp-activated protein kinase. Circulation. 2009;119:2568–77.
Xiao H, Ma X, Feng W, Fu Y, Lu Z, Xu M, et al. Metformin attenuates cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting the tgfbeta1-smad3 signalling pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87:504–13.
Benes J, Kazdova L, Drahota Z, Houstek J, Medrikova D, Kopecky J, et al. Effect of metformin therapy on cardiac function and survival in a volume-overload model of heart failure in rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;121:29–41.
Shimizu I, Minamino T, Toko H, Okada S, Ikeda H, Yasuda N, et al. Excessive cardiac insulin signaling exacerbates systolic dysfunction induced by pressure overload in rodents. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:1506–14.
Meier JJ, Gallwitz B, Schmidt WE, Mugge A, Nauck MA. Is impairment of ischaemic preconditioning by sulfonylurea drugs clinically important? Heart. 2004;90:9–12.
Gross GJ, Auchampach JA. Blockade of atp-sensitive potassium channels prevents myocardial preconditioning in dogs. Circ Res. 1992;70:223–33.
Tavackoli S, Ashitkov T, Hu ZY, Motamedi M, Uretsky BF, Birnbaum Y. Simvastatin-induced myocardial protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury is mediated by activation of atp-sensitive k+ channels. Coron Artery Dis. 2004;15:53–8.
Bolen S, Feldman L, Vassy J, Wilson L, Yeh HC, Marinopoulos S, et al. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and safety of oral medications for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:386–99.
Bennett WL, Maruthur NM, Singh S, Segal JB, Wilson LM, Chatterjee R, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of medications for type 2 diabetes: an update including new drugs and 2-drug combinations. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154:602–13.
Yu Q, Gao F, Ma XL. Insulin says no to cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;89:516–24.
Lonborg J, Vejlstrup N, Kelbaek H, Botker HE, Kim WY, Mathiasen AB, et al. Exenatide reduces reperfusion injury in patients with st-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1491–9.
Matheeussen V, Jungraithmayr W, De Meester I. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 as a therapeutic target in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Ther. 2012;136:267–82.
Ye Y, Perez-Polo JR, Aguilar D, Birnbaum Y. The potential effects of anti-diabetic medications on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106:925–52.
Riksen NP, Hausenloy D. Limitation of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in clinical practice: new hopes and dissapointments. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012;23:588–90
Lexis CP, van der Horst IC, Lipsic E, van der Harst P, van der Horst-Schrivers AN, Wolffenbuttel BH, et al. Metformin in non-diabetic patients presenting with st elevation myocardial infarction: rationale and design of the glycometabolic intervention as adjunct to primary percutaneous intervention in st elevation myocardial infarction (gips)-iii trial. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2012;26:417–26.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by a grant of the Dutch Heart Foundation (to NPR and GA) and the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMW; Clinical Fellowship to NPR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Coronary Heart Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Messaoudi, S., Rongen, G.A. & Riksen, N.P. Metformin Therapy in Diabetes: The Role of Cardioprotection. Curr Atheroscler Rep 15, 314 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-013-0314-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-013-0314-z