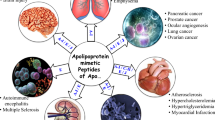
Abstract
Recent publications reveal the mechanism of action of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) mimetic peptides to be the remarkable binding affinity that oxidized lipids have for these peptides compared with apoA-I. There was no difference in the binding affinity of oxidized lipids or in peptide efficacy in reducing inflammation and atherosclerosis in rabbits injected with peptides synthesized from all D- or all L-amino acids. The apoA-I mimetic peptide 4F increased the formation of pre-β high-density lipoprotein, increased cholesterol efflux, and reduced lipoprotein oxidation in vitro; it increased antioxidants and vascular repair in type 1 diabetic rats; it improved vasodilation, oxidative stress, myocardial inflammation, and angiogenic potential in a mouse model of scleroderma; it reduced renal inflammation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-null mice fed a Western diet; it reduced arthritis in a rat model; it reduced adiposity, increased adiponectin levels, and improved insulin sensitivity in obese mice; and it improved high-density lipoprotein inflammatory properties in humans with coronary heart disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
deGoma EM, deGoma RL, Rader DJ: Beyond high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Evaluation high-density lipoprotein function as influenced by novel therapeutic approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008, 51:2199–2211.
Datta G, Chaddha M, Hama S, et al.: Effects of increasing hydrophobicity on the physical-chemical and biological properties of a class A amphipathic helical peptide. J Lipid Res 2001, 42:1096–1104.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST, et al.: Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005, 25:1325–1331.
Anantharamaiah GM, Mishra VK, Garber DW, et al.: Structural requirements for antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides. J Lipid Res 2007, 48:1915–1923.
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST, et al.: Oral D-4F causes formation of pre-beta high-density lipoprotein and improves high-density lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport from macrophages in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Circulation 2004, 109:r120–r125.
Bloedon LT, Dunbar RL, Duffy D, et al.: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:1344–1352.
Navab M, Hama SY, Anantharamaiah GM, et al.: Normal high density lipoprotein inhibits three steps in the formation of mildly oxidized low density lipoprotein: steps 2 and 3. J Lipid Res 2000, 41:1495–1508.
Van Lenten BJ, Wagner AC, Jung CL, et al.: Anti-inflammatory apoA-I mimetic peptides bind oxidized lipids with much higher affinity than human apoA-I. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:2302–2311.
Van Lenten BJ, Wagner AC, Navab M, et al.: Lipoprotein inflammatory properties and serum amyloid A levels but not cholesterol levels predict lesion area in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res 2007, 48:2344–2353.
Troutt JS, Alborn WE, Mosior MK, et al.: An apolipoprotein A-I mimetic dose-dependently increases the formation of Pre-beta1 HDL in human plasma. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:581–587.
Wool GD, Reardon CA, Getz GS: Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide helix number and helix linker influence potentially anti-atherogenic properties. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:1268–1283.
Peterson SJ, Husney D, Kruger AL, et al.: Long-term treatment with the apolipoprotein A1 mimetic peptide increases antioxidants and vascular repair in type I diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007, 322:514–520.
Weihrauch D, Xu H, Shi Y, et al.: Effects of D-4F on vasodilation, oxidative stress, angiostatin, myocardial inflammation, and angiogenic potential in tight-skin mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007, 293:H1432–H1441.
Buga GM, Frank JS, Mottino GA, et al.: D-4F reduces EO6 immunoreactivity, SREBP-1c mRNA levels, and renal inflammation in LDL receptor-null mice fed a Western diet. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:192–205.
Charles-Schoeman C, Banquerigo ML, Hama S, et al.: Treatment with an apolipoprotein A-1 mimetic peptide in combination with pravastatin inhibits collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Immunol 2008, 127:234–244.
Peterson SJ, Drummond G, Kim DH, et al.: L-4F treatment reduces adiposity, increases adiponectin levels, and improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. J Lipid Res 2008, 49:1658–1669.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Lenten, B.J., Wagner, A.C., Anantharamaiah, G.M. et al. Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides. Curr Atheroscler Rep 11, 52–57 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-009-0008-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-009-0008-8