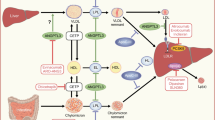
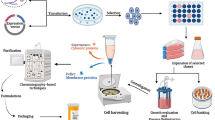
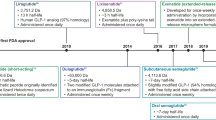
Abstract
Peptides mimicking the biological properties of apolipoproteins have shown beneficial properties against a variety of diseases and have emerged as a potential candidate for their treatments. In this review, we have discussed the emerging field of apolipoprotein-mimetic peptides for clinical use. We have briefly discussed the latest in the field of development of high-density lipoprotein mimetics and apolipoprotein-A and apolipoprotein-E mimetic peptides. We primarily focused on the therapeutic potential of apolipoprotein-mimetic peptides in terms of their broad spectrum applications reported in pre-clinical and clinical studies. We conclude with a discussion on the emergence of apolipoprotein-mimetic peptides as potential candidates for the treatment of a broad spectrum of disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as this is a review article and no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- Apo:
-
Apolipoprotein
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- CT:
-
Clinical trial
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
References
Amar MJ, D’Souza W, Turner S et al (2010) 5A apolipoprotein mimetic peptide promotes cholesterol efflux and reduces atherosclerosis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:634–641
Amar MJ, Sakurai T, Ikuta SA et al (2015) A novel apolipoprotein C-II mimetic peptide that activates lipoprotein lipase and decreases serum triglycerides in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 352:227–235
Bielicki JK, Zhang H et al (2010) A new HDL mimetic peptide that stimulates cellular cholesterol efflux with high efficiency greatly reduces atherosclerosis in mice. J Lipid Res 51:1496–1503
Birner-Gruenberger R, Schittmayer M, Holzer M, Marsche G (2014) Understanding high-density lipoprotein function in disease: recent advances in proteomics unravel the complexity of its composition and biology. Prog Lipid Res 56:36–46
Bloedon LT, Dunbar R, Duffy D et al (2008) Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients. J Lipid Res 49:1344–1352
Bocharov AV, Wu T, Baranova IN et al (2016) Synthetic amphipathic helical peptides targeting CD36 attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and acute lung injury. J Immunol 197:611–619
Bourdi M, Amar M, Remaley AT, Terse PS (2018) Intravenous toxicity and toxicokinetics of an HDL mimetic, Fx-5A peptide complex, in cynomolgus monkeys. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 100:59–67
Buga GM, Frank JS, Mottino GA et al (2006) D-4F decreases brain arteriole inflammation and improves cognitive performance in LDL receptor-null mice on a western diet. J Lipid Res 47:2148–2160
Buga GM, Frank JS, Mottino GA et al (2008) D-4F reduces EO6 immunoreactivity, SREBP-1c mRNA levels, and renal inflammation in LDL receptor-null mice fed a western diet. J Lipid Res 49:92–205
Cao J, Xu Y, Shang L et al (2015) Effect of the apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide EpK on atherosclerosis in apoE(-/-) Mice. Prog Biochem Biophys 42:833–842
Capodanno D, Mehran R, Gibson CM, Angiolillo DJ (2018) CSL112, a reconstituted, infusible, plasma-mimetic apolipoprotein A-I: safety and tolerability profiles and implications for management in patients with myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27:997–1005
Chattopadhyay A, Yang X, Mukherjee P et al (2018) Treating the intestine with oral ApoA-I mimetic Tg6F reduces tumor burden in mouse models of metastatic lung cancer. Sci Rep 8:9032
Cheng XX, Zheng YY, Bu P et al (2018) Apolipoprotein E as a novel therapeutic neuroprotection target after traumatic spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 299:97–108
Chernick D, Ortiz-Valle JA et al (2018) High-density lipoprotein mimetic peptide 4F mitigates amyloid-β-induced inhibition of apolipoprotein E secretion and lipidation in primary astrocytes and microglia. J Neurochem 147(5):647–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14554
Chiu LS, Anderton RS, Cross JL et al (2017) Assessment of neuroprotective peptides poly-arginine R18 COG1410 and APP96–110 experimental traumatic brain injury and in vitro neuronal excitotoxicity. Transl Neurosci 15:147–157
Clinical Trials NCT02100839, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02100839. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT02315586, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02315586. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT04216342, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT04216342. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT00751608, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT00751608. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT02670824, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02670824. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT03802396, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT03802396. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Clinical Trials NCT03168581, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Clinical Trials. Gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT03168581. Accessed 29 Nov 2020
Dai C, Yao X, Keeran KJ et al (2012) Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates ovalbumin-induced neutrophilic airway inflammation via a granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47:186–195
Datta G, White CR, Dashti N, Chaddha M, Palgunachari MN, Gupta H, Handattu SP, Garber DW, Anantharamaiah GM (2010) Anti-inflammatory and recycling properties of an apolipoprotein mimetic peptide Ac-hE18A-NH(2). Atherosclerosis 208:134–141
Datta G, Gupta H, Zhang Z, Mayakonda P, Anantharamaiah GM, White CR (2011) HDL mimetic peptide administration improves left ventricular filling and cardiac output in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. J Clin Exp Cardiol 22:172
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Kanel GC, Atkinson RD, McCuskey RS (2008) Prevention of hepatic fibrosis in a murine model of metabolic syndrome with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Pathol 173:993–1001
Delk SC, Chattopadhyay A, Escola-Gil C, Fogelman AM, Reddy ST (2020) Apolipoprotein mimetics in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.11.002
Duffy D, Rader DJ (2009) Update on strategies to increase HDL quantity and function. Nat Rev Cardiol 6:455–463
Easton R, Gille A, D’Andrea D, Davis R, Wright SD, Shear C (2014) A multiple ascending dose study of CSL112, an infused formulation of ApoA-I. J Clin Pharmacol 54:301–310
Fazio S, Linton MF (2010) High-density lipoprotein therapeutics and cardiovascular prevention. J Clin Lipidol 4:411–419
Fox CA, Moschetti A, Ryan RO (2021) Reconstituted HDL as a therapeutic delivery device. Biochim Biophys Acta 1866:159025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.159025
Georgila K, Vyrla D, Drakos E (2019) Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cancers 11:1097
Getz GS, Wool D, Reardon CA (2010) HDL apolipoprotein-related peptides in the treatment of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory disorders. Curr Pharm Des 16:3173–3184
Ghosal K, Stathopoulos A, Thomas D, Phenis D, Vitek MP, Pimplikar SW (2013) The apolipoprotein-E-mimetic COG112 protects amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain-overexpressing animals from Alzheimer’s disease-like pathological features. Neurodegener Dis 12:51–58
Gibson CM, Korjian S et al (2016) Safety and tolerability of CSL112, a reconstituted, infusible, plasma-mimetic apolipoprotein A-I, after acute myocardial infarction: the AEGIS-I trial (ApoA-I event reducing in ischemic syndromes I). Circulation 134:1918–1930
Gibson CM, Kerneis M et al (2019) The CSL112-2001 trial: safety and tolerability of multiple doses of CSL112 (apolipoprotein A-I [human]), an intravenous formulation of plasma-mimetic apolipoprotein A-I, among subjects with moderate renal impairment after acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 208:81–90
Gille A, Wright S, Easton R, Shear C (2013) Infusion of CSL112, a novel formulation of human apolipoprotein A-I, in healthy subjects removes tissue cholesterol and directs its clearance. Eur Heart J 34:1947
Gille A, Easton R et al (2014) CSL112 enhances biomarkers of reverse cholesterol transport after single and multiple infusions in healthy subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34:2106–2114
Gille A, D’Andrea D et al (2018) CSL112 (apolipoprotein A-I [human]) enhances cholesterol efflux similarly in healthy individuals and stable atherosclerotic disease patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 38:953–963
Gkouskou KK, Ioannou M, Pavlopoulos GA et al (2016) Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesis. Oncogene 35:2496–2505
Gordon SM, Hofmann S, Askew DS, Davidson WS (2011) High density lipoprotein: it’s not just about lipid transport anymore. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22:9–15
Gou S, Wang L, Zhong C et al (2020) A novel apoA-I mimetic peptide suppresses atherosclerosis by promoting physiological HDL function in apoE−/− mice. Br J Pharmacol 177:4627–4644
Gupta H, Dai L, Datta G et al (2005) Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by an apolipoprotein AI mimetic peptide. Circ Res 97:236–243
Hafiane A, Bielicki JK, Johansson JO, Genest J (2015) Novel Apo E-mimetic ABCA1 agonist peptide (CS-6253) promotes reverse cholesterol transport and induces formation of prebeta-1 HDL in vitro. PLoS ONE 10:e0131997
Handattu SP, Garber DW et al (2009) Oral apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide improves cognitive function and reduces amyloid burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 34:525–534
Handattu SP, Nayyar G, Garber DW et al (2013) Two apolipoprotein E mimetic peptides with similar cholesterol reducing properties exhibit differential atheroprotective effects in LDL-R null mice. Atherosclerosis 227:58–64
Hara H, Yokoyama S (1991) Interaction of free apolipoproteins with macrophages: formation of high density lipoprotein-like lipoproteins and reduction of cellular cholesterol. J Biol Chem 266(5):3080–3086. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)49957-7
Hoane MR, Kaufman N, Vitek MP, McKenna SE (2009) COG1410 improves cognitive performance and reduces cortical neuronal loss in the traumatically injured brain. J Neurotrauma 26:121–129
Ibanez B, Giannarelli C, Cimmino G et al (2012) Recombinant HDL(Milano) exerts greater anti-inflammatory and plaque stabilizing properties than HDL(wild-type). Atherosclerosis 220:72–77
Jonas A, Phillips MC (2008) Lipoprotein structure. In: Vance DE, Vance JE (eds) Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins and membranes, 5th edn. Elsevier, pp 485–506
Kallend DG, Reijers JA et al (2016) A single infusion of MDCO-216 (ApoA-1 milano/POPC) increases ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux and pre-beta 1 HDL in healthy volunteers and patients with stable coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2:23–29
Karalis I, Jukema JW (2018) HDL mimetics infusion and regression of atherosclerosis: is it still considered a valid therapeutic option? Curr Cardiol Rep 20:66
Kempen HJ, Asztalos BF et al (2016) High-density lipoprotein subfractions and cholesterol E_ux capacities after infusion of MDCO-216 (Apolipoprotein A-IMilano/Palmitoyl-Oleoyl-Phosphatidylcholine) in healthy volunteers and stable coronary artery disease patients. Arter Thromb Vasc Biol 36:736–742
Kim TH, Lee YH, Kim KH et al (2010) Role of lung apolipoprotein A-I in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect on experimental lung injury and fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:633–642
Kontush A, Chapman MJ (2012) High-density lipoproteins: structure, metabolism, function, and therapeutics, 1st edn. Wiley, USA
Kootte RS, Smits LP, van der Valk FM et al (2015) Effect of open-label infusion of an apoA-I-containing particle (CER-001) on RCT and artery wall thickness in patients with FHA. J Lipid Res 56:703–712
Kruger AL, Peterson S, Turkseven S, Kaminski PM, Zhang FF, Quan S, Wolin MS, Abraham NG (2005) D-4F induces heme oxygenase-1 and extracellular superoxide dismutase, decreases endothelial cell sloughing, and improves vascular reactivity in rat model of diabetes. Circulation 111:3126–3134
Kwon WY, Suh GJ, Kim KS et al (2012) 4F, apolipoprotein AI mimetic peptide, attenuates acute lung injury and improves survival in endotoxemic rats. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72:1576–1583
Laskowitz DT, Lei B, Dawson HN et al (2012) The apoE-mimetic peptide COG1410 improves functional recovery in a murine model of intracerebral haemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 16:316–326
Laskowitz DT, Wang H et al (2017) Neuroprotective pentapeptide CN-105 is associated with reduced sterile inflammation and improved functional outcomes in a traumatic brain injury murine model. Sci Rep 7:46461
Lei B, James ML, Liu J et al (2016) Neuroprotective pentapeptide CN-105 improves functional and histological outcomes in a murine model of intracerebral haemorrhage. Sci Rep 6:34834
Leman LJ, Maryanoff BE, Ghadiri MR (2014) Molecules that mimic apolipoprotein A-I: potential agents for treating atherosclerosis. J Med Chem 57:2169–2196
Li X, Peng J, Pang J et al (2018) Apolipoprotein E-mimetic peptide COG1410 promotes autophagy by phosphorylating GSK-3beta in early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Neurosci 12:127
Lowenstein CJ, Cameron SJ (2010) High-density lipoprotein metabolism and endothelial function. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:166–170
Lund-Katz S, Phillips MC (2010) High density lipoprotein structure-function and role in reverse cholesterol transport. Subcell Biochem 51:183–227
Marinho AT, Lu H, Pereira SA et al (2019) Anti-tumorigenic and platinum-sensitizing effects of apolipoprotein A1 and apolipoprotein A1 mimetic peptides in ovarian cancer. Front Pharmacol 9:1524
Marsche G (2015) It’s time to reassess the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) hypothesis: CSL112, a novel promising reconstituted HDL formulation. J Am Heart Assoc 4:e002371
McAdoo JD, Warner DS et al (2005) Intrathecal administration of a novel apoE-mimetic therapeutic peptide improves outcome following perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Neurosci Lett 381:305–308
McGrath K, Li X, Twigg SM, Heather AK (2020) Apolipoprotein-AI mimetic peptides D-4F and L-5F decrease hepatic inflammation and increase insulin sensitivity in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS One 15:e0226931
Mendez AJ (2010) The promise of apolipoprotein AI mimetics. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:171–176
Mendez-Fernandez Y, Major A (2010) Sizing up stability: combination therapy with Apo-AI peptide mimetics and statins in systemic lupus erythematosus-mediated atherosclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 12:139
Meriwether D, Sulaiman D, Volpe C et al (2019) Apolipoprotein A-I mimetics mitigate intestinal inflammation in COX2-dependent inflammatory bowel disease model. J Clin Invest 129:3670–3685
Meurs I, Van Eck M, Van Berkel TJ (2010) HDL: key molecule in cholesterol efflux and the prevention of atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des 16:1–23
Montoliu-Gaya L, Mulder SD, Herrebout MAC, Baayen JC, Villegas S, Veerhuis R (2018) Abeta-oligomer uptake and the resulting inflammatory response in adult human astrocytes are precluded by an anti-Abeta single chain variable fragment in combination with an apoE mimetic peptide. Mol Cell Neurosci 89:49–59
Moreira RS, Irigoyen M, Sanches TR et al (2014) Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide 4F attenuates kidney injury, heart injury, and endothelial dysfunction in sepsis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307:R514–R524
Nandedkar SD, Weihrauch D, Xu H et al (2011) D-4F, an apoA-1 mimetic, decreases airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and oxidative stress in a murine model of asthma. J Lipid Res 52:499–508
Nankar SA, Pande AH (2013) Physicochemical properties of bacterial pro-inflammatory lipids influence their interaction with apolipoprotein-derived peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:853–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.01.006
Nankar SA, Pande AH (2014) Properties of apolipoprotein E derived peptide modulate their lipid-binding capacity and influence their anti-inflammatory function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1841:620–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.01.006
Nankar SA, Bulani Y, Sharma SS, Pande AH (2020) ApoE-mimetic peptides attenuated diabetes-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Protein Pept Lett 27:193–200
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST et al (2004) Oral D-4F causes formation of pre-{beta} high-density lipoprotein and improves high-density lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport from macrophages in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Circulation 109:3215–3220
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST et al (2005) An oral apoJ peptide renders HDL antiinflammatory in mice and monkeys and dramatically reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1932–1937
Navab M, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Fogelman AM (2008) Apo A-1 mimetic peptides as atheroprotective agents in murine models. Curr Drug Targets 9:204–209
Navab M, Shechter I, Anantharamaiah GM, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Fogelman AM (2010) Structure and function of HDL mimetics. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:164–168
Nicholls SJ, Andrews J et al (2018a) Effect of serial infusions of CER-001, a pre-beta high-density lipoprotein mimetic, on coronary atherosclerosis in patients following acute coronary syndromes in the CER-001 atherosclerosis regression acute coronary syndrome trial: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol 3:815–822
Nicholls SJ, Puri R et al (2018b) Effect of infusion of high-density lipoprotein mimetic containing recombinant apolipoprotein A-I milano on coronary disease in patients with an acute coronary syndrome in the MILANO-PILOT trial: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol 3:806–814
Nissen SE, Tsunoda T et al (2003) Effect of recombinant ApoA-I Milano on coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 290:2292–2300
Nowacki TM, Remaley AT, Bettenworth D et al (2016) The 5A apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) mimetic peptide ameliorates experimental colitis by regulating monocyte infiltration. Br J Pharmacol 173:2780–2792
Oehler B, Kloka J, Mohammadi M, Ben-Kraiem A, Rittner HL (2020) D-4F, an ApoA-I mimetic peptide ameliorating TRPA1-mediated nocifensive behaviour in a model of neurogenic inflammation. Mol Pain 16:1744806920903848
Ou J, Ou Z, Jones DW et al (2003) L-4F, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic, dramatically improves vasodilation in hypercholesterolemia and sickle cell disease. Circulation 107:2337–2341
Pane K, Sgambati V, Zanfardino A et al (2016) A new cryptic cationic antimicrobial peptide from human apolipoprotein E with antibacterial activity and immunomodulatory effects on human cells. FEBS 283(11):2115–2131. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13725
Pang J, Chen Y, Kuai L et al (2017) Inhibition of blood-brain barrier disruption by an apolipoprotein E-mimetic peptide ameliorates early brain injury in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res 8:257–272
Park SW, Lee EH, Lee EJ et al (2013) Apolipoprotein A1 potentiates lipoxin A4 synthesis and recovery of allergen-induced disrupted tight junctions in the airway epithelium. Clin Exp Allergy 43:914–927
Peng M, Zhang Q, Liu Y et al (2020) Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide L-4F suppresses granulocytic-myeloid-mimetic suppressor cells in mouse pancreatic cancer. Front Pharmacol 11:576
Peterson SJ, Kim DH, Li M et al (2009) The L-4F mimetic peptide prevents insulin resistance through increased levels of HO-1, pAMPK, and pAKT in obese mice. J Lipid Res 50:1293–1304
Reijers JAA, Kallend DG et al (2017) MDCO-216 does not induce adverse immunostimulation, in contrast to its predecessor ETC-216. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 31:381–389
Ribaric S (2018) Peptides as potential therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 23:283
Rivas-Urbina A, Rull A, Aldana-Ramos J et al (2020) Subcutaneous administration of apolipoprotein J-mimetic mimetic peptide d-[113-122]apoJ improves LDL and HDL function and prevents atherosclerosis in LDLR-KO mice. Biomolecules 10:829
Shah PK (2007) Emerging HDL-based therapies for atherothrombotic vascular disease. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 9(1):60–70
Shah PK (2011) Atherosclerosis: targeting endogenous apo A-I–a new approach for raising HDL. Nat Rev Cardiol 8:187–188
Sharifov OF, Nayyar G, Garber DW et al (2011) Apolipoprotein E mimetics and cholesterol-lowering properties. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 11:371–381
Sharma S, Umar S, Potus F et al (2014) Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide 4F rescues pulmonary hypertension by inducing microRNA-193-3p. Circulation 130:776–785
Sherman CB, Peterson SJ, Frishman WH (2010) Apolipoprotein AI mimetic peptides: a potential new therapy for the prevention of atherosclerosis. Cardiol Rev 18:141–147
Singh K, Chaturvedi R, Barry DP et al (2011) The apolipoprotein E-mimetic peptide COG112 inhibits NF-kappaB signaling proinflammatory cytokine expression and disease activity in murine models of colitis. J Biol Chem 286:3839–3850
Skaggs BJ, Hahn BH, Sahakian L, Grossman J, McMahon M (2010) Dysfunctional, pro-inflammatory HDL directly upregulates monocyte PDGFR beta, chemotaxis and TNF alpha production. Clin Immunol 137:147–156
Spillmann F, Schultheiss HP, Tschope C, Van Linthout S (2010) High-density lipoprotein-raising strategies: update. Curr Pharm Des 16:1517–1530
Su F, Kozak KR, Imaizumi S et al (2010) Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and apoA-I mimetic peptides inhibit tumor development in a mouse model of ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19997–20002
Su F, Anantharamaiah GM, Palgunachari MN et al (2020) Bovine HDL and dual domain HDL-mimetic peptides inhibit tumor development in mice. J Cancer Res Ther Oncol 8:101
Suematsu Y, Kawachi E, Idemoto Y et al (2019) Anti-atherosclerotic effects of an improved apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide. Int J Cardiol 297:111–117
Tabet F, Remaley AT, Segaliny AI et al (2010) The 5A apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide displays antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties in vivo and in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:246–252
Tanaka S, Couret D, Tran-Dinh A et al (2020) High-density lipoproteins during sepsis: from bench to bedside. Crit Care 24:134
Tardif JC, Gregoire J et al (2007) Effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein infusions on coronary atherosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 297:1675–1682
Tardif JC, Ballantyne CM et al (2014) Effects of the high-density lipoprotein mimetic agent CER-001 on coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized trial. Eur Heart J 35:3277–3286
Tsujita M, Wolska A, Gutmann DAP, Remaley AT (2018) Reconstituted discoidal high-density lipoproteins: bioinspired nanodiscs with many unexpected applications. Curr Atherosclerosis Rep 20(12):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-018-0759-1
Tu TM, Kolls BJ et al (2017) Apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide, CN-105, improves outcomes in ischemic stroke. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 4:246–265
Van Lenten BJ, Wagner AC, Anantharamaiah GM et al (2002) Influenza infection promotes macrophage traffic into arteries of mice that is prevented by D-4F, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide. Circulation 106:1127–1132
Van Lenten BJ, Wagner AC, Navab M et al (2004) D-4F, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, inhibits the inflammatory response induced by influenza A infection of human type II pneumocytes. Circulation 110:3252–3258
Van Linthout S, Spillmann F, Schultheiss HP, Tschope C (2010) High-density lipoprotein at the interface of type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disorders. Curr Pharm Des 16:1504–1516
Vucic E, Rosenson RS (2011) Recombinant high-density lipoprotein formulations. Curr Atheroscler Rep 13:81–87
Wang H, Durham L, Dawson H et al (2007) An apolipoprotein E-based therapeutic improves outcome and reduces Alzheimer’s disease pathology following closed head injury: evidence of pharmacogenomic interaction. Neuroscience 144:1324–1333
Wang C, Yang C, Yang Y et al (2013) An apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide with activities against multidrug-resistant bacteria and immunomodulatory effects. J Pept Sci 19(12):745–750. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.2570
Watson CE, Weissbach N, Kjems L et al (2011) Treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease with L-4F, an apo-A1 mimetic, did not improve select biomarkers of HDL function. J Lipid Res 52:361–373
Wei J, Zheng M, Liang P, Wei Y, Yin X, Tang Y, Xue Y (2013) Apolipoprotein E and its mimetic peptide suppress Th1 and Th17 responses in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurobiol Dis 56:59–65
Wolska A, Lo L, Sviridov DO et al (2020) A dual apolipoprotein C-II mimetic-apolipoprotein C-III antagonist peptide lowers plasma triglycerides. Sci Transl Med 12:eaaw7905
Wolska A, Reimund M, Sviridov DO, Amar MJ, Remaley AT (2021) Apolipoprotein mimetic peptides: potential new therapies for cardiovascular diseases. Cells 10(3):597–615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030597
Xu Y, Liu H, Liu M, Li F, Liu L, Du F, Fan D, Yu H (2016) A human apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide reduces atherosclerosis in aged apolipoprotein E null mice. Am J Transl Res 8:3482–3492
Yang N, Tian H, Zhan E et al (2019) Reverse-D-4F improves endothelial progenitor cell function and attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury. Respir Res 20:131
Yao X, Dai C, Fredriksson K et al (2011) 5A, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, attenuates the induction of house dust mite-induced asthma. J Immunol 186:576–583
Ying R, Yuan Y, Qin YF et al (2013) The combination of L-4F and simvastatin stimulate cholesterol efflux and related proteins expressions to reduce atherosclerotic lesions in apoE knockout mice. Lipids Health Dis 12:180
Zanfardino A, Bosso A, Gallo G et al (2018) Human apolipoprotein E as a reservoir of cryptic bioactive peptides: the case of ApoE 133–167. J Pept Sci 24(7):e3095. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.3095
Zhang Z, Datta G, Zhang Y et al (2009) Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide treatment inhibits inflammatory responses and improves survival in septic rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H866–H873
Zhao W, Du F, Zhang M, Sun S, Yu H, Fan D (2011) A new recombinant human apolipoprotein E mimetic peptide with high-density lipoprotein binding and function enhancing activity. Exp Biol Med 236:1468–1476
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks the Department of Biotechnology (New Delhi, Government of India; Grant # BT/PR23283/MED/30/1953/2018 and CRG/2020/000865) and National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, S.A.S. Nagar (NPLC-AHP), for providing support through a research grants. The authors also thank Dr. Ipsita Roy, Department of Biotechnology, NIPER-SAS Nagar for her valuable assistance in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nankar, S.A., Kawathe, P.S. & Pande, A.H. HDL, ApoA-I and ApoE-Mimetic Peptides: Potential Broad Spectrum Agent for Clinical Use?. Int J Pept Res Ther 28, 52 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-021-10352-3
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-021-10352-3