Abstract
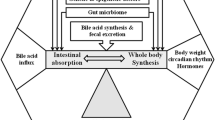
Cholesterol absorption and synthesis are inter-regulated, so if one changes then the other changes in the opposite direction. The regulation and detailed mechanism of cholesterol absorption have been intensely investigated. Inhibition of cholesterol absorption has become an additional factor for cholesterol lowering. Agents inhibiting cholesterol absorption, mainly plant stanols and sterols or ezetimibe, usually lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in monotherapy by less than 20%, indicating that these inhibitors can normalize cholesterol levels only in patients with a modest baseline hypercholesterolemia. Body weight, especially obesity with and without diabetes, and dietary plant sterols alter cholesterol absorption differently. This article briefly reviews some special questions of cholesterol absorption under these conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katan MB, Grundy SM, Jones P, et al.: Efficacy and safety of plant stanols and sterols in the management of blood cholesterol levels. Mayo Clin Proc 2003, 78:965–978.
Sudhop T, Lütjohann D, Kodal A, et al.: Inhibition of intestinal cholesterol absorption by ezetimibe in humans. Circulation 2002, 106:1943–1948.
Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH: Approaches to measuring cholesterol absorption in humans. Atherosclerosis 2004, 174:197–205.
Bosner MS, Lange LG, Stenson WF, Ostlund RE Jr: Percent cholesterol absorption in normal women and men quantified with dual stable isotopic tracers and negative ion mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res 1999, 40:302–308.
Miettinen TA, Kesäniemi YA: Cholesterol absorption: regulation of cholesterol synthesis and elimination and within-population variations of serum cholesterol levels. Am J Clin Nutr 1987, 49:629–635.
Miettinen TA, Tilvis RS, Kesäniemi YA: Serum plant sterols and cholesterol precursors reflect cholesterol absorption and synthesis in volunteers of a randomly selected male population. Am J Epidemiol 1990, 131:20–31.
Vuoristo M, Tilvis R, Miettinen TA: Serum plant sterols and lathosterol related to cholesterol absorption in coeliac disease. Clin Chim Acta 1988, 174:213–224.
Färkkilä MA, Tilvis RS, Miettinen TA: Regulation of plasma plant sterol levels in patients with gut resections. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1988, 48:715–722.
Gylling H, Miettinen TA: Serum noncholesterol sterols related to cholesterol metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia. Clin Chim Acta 1988, 178:41–50.
Tilvis RS, Miettinen TA: Serum plant sterols and their relation to cholesterol absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 1986, 43:92–97.
Vanhanen HT, Miettinen TA: Cholesterol absorption and synthesis during pravastatin, gemfibrozil and their combination. Atherosclerosis 1995, 115:135–146.
Gylling H, Miettinen TA: Serum cholesterol and cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism in hypercholesterolaemic NIDDM patients before and during sitostanol ester-margarine treatment. Diabetologia 1994, 37:773–780.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H: Cholesterol absorption efficiency and sterol metabolism in obesity. Atherosclerosis 2000, 153:241–248.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H, Strandberg T, Sarna S, for the Finnish 4S Investigators: Baseline serum cholestanol as predictor of recurrent coronary events in subgroup of Scandinavian simvastatin survival study. BMJ 1998, 316:1127–1130.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H: Cholesterol synthesis and absorption in coronary patients with lipid triad and isolated high LDL cholesterol in a 4S subgroup. Atherosclerosis 2003, 168:343–349.
Gylling H, Hallikainen M, Pihlajamäki J, et al.: Polymorphisms in the ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes associate with cholesterol absorption and insulin sensitivity. J Lipid Res 2004, 45:1660–1665.
Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, et al.: Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science 2000, 290:1771–1775.
Lee MH, Lu K, Hazard S, et al.: Identification of a gene, ABCG5, important in the regulation of dietary cholesterol absorption. Nat Genet 2001, 27:79–83.
Berge KE, von Bergmann K, Lütjohann D, et al.: Heritability of plasma noncholesterol sterols and relationship to DNA sequence polymorphism in ABCG5 and ABCG8. J Lipid Res 2002, 43:486–494.
Pihlajamäki J, Gylling H, Miettinen TA, Laakso M: Insulin resistance is associated with increased cholesterol synthesis and decreased cholesterol absorption in normoglycemic men. J Lipid Res 2004, 45:507–512.
Simonen PP, Gylling HK, Miettinen TA: Diabetes contributes to cholesterol metabolism regardless of obesity. Diabetes Care 2002, 25:1511–1515.
Simonen PP, Gylling H, Miettinen TA: Body weight modulates cholesterol metabolism in non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetes. Obes Res 2002, 10:328–335.
Simonen P, Gylling H, Howard AN, Miettinen TA: Introducing a new component of the metabolic syndrome: low cholesterol absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 2000, 72:82–88.
Gylling H, Miettinen TA: Inheritance of cholesterol metabolism of probands with high or low cholesterol absorption. J Lipid Res 2002, 43:1472–1476.
Repa JJ, Berge KE, Pomajzl C, et al.: Regulation of ATP-binding cassette sterol transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 by the liver X receptors a and b. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:18793–18800.
Yu L, York J, von Bergmann K, et al.: Stimulation of cholesterol excretion by the liver X receptor agonist requires ATP-binding cassette transporters G5 and G8. J Biol Chem 2003, 278:15565–15570.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H, Tuominen J, et al.: Low synthesis and high absorption of cholesterol characterize type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27:53–58.
Gylling H, Tuominen JA, Koivisto VA, Miettinen TA: Cholesterol metabolism in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53:2217–2222.
Björkhem I, Boberg KM, Leitersdorf E: Inborn errors in bile acid biosynthesis and storage of sterols other than cholesterol. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. Edited by Scriver CS, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001:2961–2988.
Bloks VW, Bakker-Van Waarde WM, Verkade HJ, et al.: Down-regulation of hepatic and intestinal Abcg5 and Abcg8 expression associated with altered sterol fluxes in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 2004, 47:104–112.
Miettinen TA, Strandberg TE, Gylling H, for the Finnish Investigators of the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study group: Noncholesterol sterols and cholesterol lowering by long-term simvastatin treatment in coronary patients: relation to basal serum cholestanol. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000, 20:1340–1346.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H: Effect of statins on noncholesterol sterol levels: Implications for use of plant stanols and sterols. Am J Cardiol 2005, 96(Suppl):40D-46D.
Miettinen TA, Railo M, Lepäntalo M, Gylling H: Plant sterols in serum and atherosclerotic plaques of patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005, 45:1794–1801.
Jones PJ, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Jenkins DJ, et al.: Effects of a diet high in plant sterols, vegetable proteins, and viscous fibres (dietary portfolio) on circulating sterol levels and red cell fragility in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Lipids 2005, 40:169–174.
Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Marchie A, et al.: Directs comparison of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods with a statin in hypercholesterolemic participants. Am J Clin Nutr 2005, 81:380–387.
Chen JT, Wesley R, Shamburek RD, et al.: Meta-analysis of natural therapies for hyperlipidemia: plant sterols and stanols versus policosanol. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25:171–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gylling, H., Miettinen, T.A. Cholesterol absorption: Influence of body weight and the role of plant sterols. Curr Atheroscler Rep 7, 466–471 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-005-0064-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-005-0064-7