Abstract
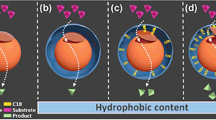
Chemically modified macromolecules were assembled with adsorptive trypsin in mesoporous silica foams (MCFs) to establish covalent linkage. Effects of catalytic properties and stability of immobilized trypsin were examined. The addition of chemically modified protein (BSA) and polysaccharide (ficoll) to the immobilized trypsin exhibited high coupled yield (above 90%) and relative activities (174.5% and 175.9%, respectively), showing no protein leaching after incubating for 10 h in buffers. They showed broader pH and temperature profiles, while the half life of thermal stability of BSA-modified preparation at 50 °C increased to 1.3 and 2.3 times of unmodified and free trypsin, respectively. The modified trypsin in aqueous-organic solvents exhibited 100% activity after 6 h at 50 °C. The kinetic parameters of trypsin preparations and suitable pore diameter of MCFs warranted compatibility of covalent modification for substrate transmission. The covalent crowding modification for immobilized trypsin in nanopores establishes suitable and accessible microenvironment and renders possibility of biological application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Brady and J. Jordan, Biotechnol. Lett., 31, 1639 (2009).
R. A. Sheldon, Adv. Synth. Catal., 349(8–9), 1289 (2007).
S.-K. Lee, S.-W. Park, Y.-I. Kim, K.-H. Chung, S.-I. Hong and S.-W. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19, 261 (2002).
Y. J. Wang and F. Caruso, Chem. Mater., 17, 953 (2005).
C. Mateo, J. M. Palomo, G. Fernandez-Lorente, J. M. Guisan, and R. Fernandez-Lafuente, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 40, 1451 (2007).
A. M. Wang, C. Zhou, Z. Q. Du, M. Q. Liu, S. M. Zhu and S. B. Shen, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 107, 219 (2009).
T. Liu, S. Wang and G. Chen, Talanta, 77, 1767 (2009).
M. Jiang and Z. H. Guo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 129, 730 (2007).
R. J. Ellis, Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol., 11, 114 (2001).
S. Zorrilla, G. Rivas, A. U. Acuna and M. P. Lillo, Protein Sci., 13, 2960 (2004).
B.C. Pessela, C. Mateo, M. Filho, A.V. Carrascosa, R. Fernandez-Lafuente and J. M. Guisan, Process Biochem., 43, 193 (2008).
C. Mateo, J. M. Palomo, G. Fernandez-Lorente, J. M. Guisan and R. Fernandez-Lafuente, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 40, 1451 (2007).
P. Schmid-winkel, W.W. Lukens, D. Y. Zhao, P. D. Yang, B. F. Chmelka and G. D. Stucky, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 121, 254 (1999).
M. M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem., 72, 248 (1987).
G.V. Lyubinskii, E. A. Kalinichenko and V. A. Tertykh, Theor. Exp. Chem., 28, 216 (1993).
F. Lopez-Gallego, L. Betancor, C. Mateo, A. Hidalgo, N. Alonso-Morales, G. Dellamora-Ortiz, J. M. Guisan and R. Fernandez-Lafuente, J. Biotechnol., 119, 70 (2005).
C. Mateo, J. M. Palomo, M. Fuentes, L. Betancor, V. Grazu, F. Lopez-Gallego, B. C. C. Pessela, A. Hidalgo, G. Fernandez-Lorente, R. Fernandez-Lafuente and J. M. Guisan, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 39, 274 (2006).
A. R. Kinjo and S. Takada, Phys. Rev., 66, 031911 (2002).
C. Zhou, A. M. Wang, Z. Q. Du, S. M. Zhu and S. B. Shen, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26, 1065 (2009).
R. J. Ellis, Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol., 11, 114 (2001).
C. M. Soares, H. F. De Castro, M. H. Santana and G.M. Zanin, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 91–93, 703 (2001).
M. S. Cheung and D. Thirumalai, J. Mol. Biol., 357, 632 (2006).
A. P. Minton, Curr. Opin. Struc. Biol., 10, 34 (2000).
Z. D. Zhang, Z. M. He and M. X. He, J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym., 14, 85 (2001).
B. B. Boonyaratanakornkit, C. B. Park and D. S. Clark, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1595, 235 (2002).
W.G. Wang, P. H. Li, S. B. Shen, H. J. Ying and P. K. Ouyang, Chinese J. Org. Chem., 26, 826 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Jiang, B., Sheng, Z. et al. Covalent crowding strategy for trypsin confined in accessible mesopores with enhanced catalytic property and stability. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28, 853–859 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0412-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0412-3