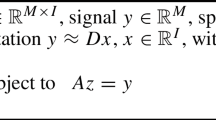Abstract
The multiple measurement vectors problem approximates a set of signals sharing a common sparsity pattern simultaneously, using different linear combinations of those signals obtained through a sensing matrix. In a situation where the signal matrix has full row-rank, MUltiple SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm guarantees to recover the jointly sparse signals, but for the rank-defective case, the MUSIC performance is voided. To address such a rank deficient case, our proposed method, line search low-rank jointly sparse signals (LS-LRJSS), provides a geometric analysis of the problem by characterizing the linear dependence of the measurements with the linear coefficients that permit the reconstruction of each point from its neighbors. Moreover, a subspace analysis has been done on a Grassmann manifold to obtain the subspace that the signal matrix belongs to. Several numerical experiments evidence that the proposed method is more accurate and less time-consuming compared to existing approaches especially wherever the sparsity level of the signals increases or the number of measurement vectors decreases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Natarajan, B.K.: Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. SIAM J. Comput. 24(2), 227–234 (1995)
Cotter, S.F., Rao, B.D., Engan, K., Kreutz-Delgado, K.: Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(7), 2477–2488 (2005)
Couvreur, C., Bresler, Y.: On the optimality of the backward greedy algorithm for the subset selection problem. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 21(3), 797–808 (2000)
Jung, H., Sung, K., Nayak, K.S., Kim, E.Y., Ye, J.C.: k-t FOCUSS: a general compressed sensing framework for high resolution dynamic MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 61(1), 103–116 (2009)
Gorodnitsky, I.F., George, J.S., Rao, B.D.: Neuromagnetic source imaging with FOCUSS: a recursive weighted minimum norm algorithm. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 95(4), 231–251 (1995)
Candès, E.J., Romberg, J., Tao, T.: Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
Foucart, S., Rauhut, H.: A mathematical introduction to compressive sensing (no. 3). Basel, Birkhäuser Basel (2013)
Donoho, D.L., Elad, M.: Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via l 1 minimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100(5), 2197–2202 (2003)
Tropp, J.A., Gilbert, A.C.: Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 53(12), 4655–4666 (2007)
Needell, D., Tropp, J.A.: CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl. Comput. Harmonic Anal. 26(3), 301–321 (2009)
Gorodnitsky, I.F., Rao, B.D.: Sparse signal reconstruction from limited data using FOCUSS: a re-weighted minimum norm algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(3), 600–616 (1997)
Ji, S., Xue, Y., Carin, L.: Bayesian compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(6), 2346–2356 (2008)
Lee, O., Kim, J.M., Bresler, Y., Ye, J.C.: Compressive diffuse optical tomography: noniterative exact reconstruction using joint sparsity. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(5), 1129–1142 (2011)
Bilik, I.: Spatial compressive sensing for direction-of-arrival estimation of multiple sources using dynamic sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 47(3), 1754–1769 (2011)
Chen, J., Huo, X.: Theoretical results on sparse representations of multiple-measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(12), 4634–4643 (2006)
Tropp, J.A., Gilbert, A.C., Strauss, M.J.: Algorithms for simultaneous sparse approximation. Part I: greedy pursuit. Signal Process. 86(3), 572–588 (2006)
Blanchard, J.D., Cermak, M., Hanle, D., Jing, Y.: Greedy algorithms for joint sparse recovery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(7), 1694–1704 (2014)
Tropp, J.A.: Algorithms for simultaneous sparse approximation. Part II: convex relaxation. Signal Process. 86(3), 589–602 (2006)
Kreutz-Delgado, K., Rao, B.D.: Measures and algorithms for best basis selection, In: Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, vol. 3, pp. 1881–1884, IEEE (1998)
Zhang, J.A., Chen, Z., Cheng, P., Huang, X.: Multiple-measurement vector based implementation for single-measurement vector sparse Bayesian learning with reduced complexity. Signal Process. 118, 153–158 (2016)
Makhzani, A., Valaee, S.: Reconstruction of jointly sparse signals using iterative hard thresholding. In: IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 3564–3568: IEEE (2012)
Foucart, S.: Recovering jointly sparse vectors via hard thresholding pursuit. In: Proceeding Sampling Theory and Applications (SampTA)] (2011)
Wipf, D., Nagarajan, S.: Iterative reweighted l 1 and l 2 methods for finding sparse solutions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 317–329 (2010)
Mishali, M., Eldar, Y.C.: Reduce and boost: Recovering arbitrary sets of jointly sparse vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(10), 4692–4702 (2008)
Gribonval, R., Rauhut, H., Schnass, K., Vandergheynst, P.: Atoms of all channels, unite! Average case analysis of multi-channel sparse recovery using greedy algorithms. J. Fourier Anal Appl. 14(5), 655–687 (2008)
Feng, P., Bresler, Y.: Spectrum-blind minimum-rate sampling and reconstruction of multiband signals. In: IEEE International Conference on Conference Proceedings on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP-96, vol. 3, pp. 1688–1691: IEEE (1996)
Lee, K., Bresler, Y., Junge, M.: Subspace methods for joint sparse recovery. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 58(6), 3613–3641 (2012)
Davies, M.E., Eldar, Y.C.: Rank awareness in joint sparse recovery. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 58(2), 1135–1146 (2012)
Kim, J.M., Lee, O.K., Ye, J.C.: Compressive MUSIC: revisiting the link between compressive sensing and array signal processing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 58(1), 278–301 (2012)
Absil, P.-A., Mahony, R., Sepulchre, R.: Optimization Algorithms on Matrix Manifolds. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2009)
Peng, J., Luo, T.: Sparse matrix transform-based linear discriminant analysis for hyperspectral image classification. SIViP 10(4), 761–768 (2016)
Wang, H., Celik, T.: Sparse representation-based hyperspectral image classification. SIViP 12(5), 1009–1017 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrkam, M., Tinati, M.A. & Yousefi Rezaii, T. Reconstruction of low-rank jointly sparse signals from multiple measurement vectors. SIViP 13, 683–691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1397-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1397-3