Abstract
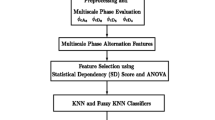
Early and accurate detection of myocardial infarction is imperative for reducing the mortality rate due to heart attack. Present work proposes a novel technique aiming toward accurate and timely detection of inferior myocardial infarction (IMI). Stationary wavelet transform has been used to decompose the segmented multilead electrocardiogram (ECG) signal into different sub-bands. Sample entropy, normalized sub-band energy, log energy entropy, and median slope calculated over selected bands of multilead ECG are used as features. Support vector machine (SVM) and K-nearest neighbor (KNN) have been used to classify between subjects admitted for health control (HC) and patients suffering from IMI, using attributes selected on the basis of gain ratio. The full length ECG of lead II, III, and aVF of all the subjects having IMI or admitted for HC from Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Database (PTB-DB) has been used in the present work. The proposed technique has been scrutinized under both “class-oriented,” and more practical, “subject-oriented” approach. Under the class-oriented approach, data have been divided into training and test data irrespective of the patients, whereas in subject-oriented approach, data from one patient have been used for test and training has been done on the rest of the subjects. Under the class-oriented approach, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (Roc), sensitivity (Se%), specificity (Sp%), positive predictivity (+P%), and accuracy (Ac%) is Roc \(=\) 0.9945, Se% \(=\) 98.67, Sp% \(=\) 98.72, +P% \(=\) 98.79, Ac% \(=\) 98.69 using KNN and Roc \(=\) 0.9994, Se% \(=\) 99.35, Sp% \(=\) 98.29, +P% \(=\) 98.41, Ac% \(=\) 98.84 using SVM. For the subject-oriented approach, an average Ac% \(=\) 81.71, Se% \(=\) 79.01, Sp% \(=\) 79.26, and +P% \(=\) 80.25 has been achieved. This shows the potential of the proposed technique to work for an unknown subject, on which it has not been trained.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mozaffarian, D., et al.: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 131(24), E29–E322 (2015)
Reddy, K.S., Yusuf, S.: Emerging epidemic of cardiovascular disease in developing countries. Circulation 97(6), 596–601 (1998)
W.H.O.: World health statistics 2015: part ii: global health indicators. Technical report, World Health Organisation (2015)
IANS: Heart attack kills one person every 33 seconds in India. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/health-fitness/health-news/Heart-attack-kills-one-person-every-33-seconds-in-India/articleshow/52339891.cms. Times of India, 19 May 2016
Thygesen, K., Alpert, J.S., Jaffe, A.S., Simoons, M.L., Chaitman, B.R., White, H.D.: Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation 126(16), 2020–2035 (2012)
Antman, E.M., et al.: ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarctionexecutive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines (writing committee to revise the 1999 guidelines for the management of patients with acute myocardial infarction). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 44(3), 671–719 (2004)
Nair, T.: Cardiology in india: state of the art or straight off the heart? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 57(3), 377–379 (2011)
Acharya, U.R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V.K., Oh, S.L., Adam, M., Koh, J.E., Tan, J.H., Ghista, D.N., Martis, R.J., Chua, C.K., et al.: Automated detection and localization of myocardial infarction using electrocardiogram: a comparative study of different leads. Knowl. Based Syst. 99, 146–156 (2016)
Jayachandran, E.S., et al.: Analysis of myocardial infarction using discrete wavelet transform. J. Med. Syst. 34(6), 985–992 (2010)
Banerjee, S., Mitra, M.: Application of cross wavelet transform for ECG pattern analysis and classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 63(2), 326–333 (2014)
Papaloukas, C., Fotiadis, D.I., Likas, A., Michalis, L.K.: An ischemia detection method based on artificial neural networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 24(2), 167–178 (2002)
Safdarian, N., Dabanloo, N.J., Attarodi, G.: A new pattern recognition method for detection and localization of myocardial infarction using t-wave integral and total integral as extracted features from one cycle of ECG signal. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 7(10), 818–824 (2014)
Lahiri, T., Kumar, U., Mishra, H., Sarkar, S., Roy, A.D.: Analysis of ecg signal by chaos principle to help automatic diagnosis of myocardial infarction. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 68, 866–870 (2009)
Lu, H., Ong, K., Chia, P.: An automated ECG classification system based on a neuro-fuzzy system. In: Computers in Cardiology, pp. 387–390. IEEE, Cambridge, MA, USA (2000)
Arif, M., Malagore, I.A., Afsar, F.A.: Detection and localization of myocardial infarction using k-nearest neighbor classifier. J. Med. Syst. 36(1), 279–289 (2012)
Mitra, S., Mitra, M., Chaudhuri, B.B.: A rough-set-based inference engine for ECG classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 55(6), 2198–2206 (2006)
Sun, L., Lu, Y., Yang, K., Li, S.: Ecg analysis using multiple instance learning for myocardial infarction detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(12), 3348–3356 (2012)
Al-Kindi, S.G., Tafreshi, R.: Real-time detection of myocardial infarction by evaluation of ST-segment in digital ECG. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 1(3), 225–230 (2011)
Schou, A., Grove, U.S., Worbech, T.H., Andersen, M.P., Terkelsen, C.J., Kaltoft, A.K., Struijk, J.J., et al.: ECG based estimation of area at risk in acute myocardial infarction. In: Computing in Cardiology, pp. 413–416. IEEE, Hangzhou, China (2011)
Liu, B., Liu, J., Wang, G., Huang, K., Li, F., Zheng, Y., Luo, Y., Zhou, F.: A novel electrocardiogram parameterization algorithm and its application in myocardial infarction detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 61, 178–184 (2015)
Sharma, L., Tripathy, R., Dandapat, S.: Multiscale energy and eigenspace approach to detection and localization of myocardial infarction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 62(7), 1827–1837 (2015)
Zheng, H., Wang, H., Nugent, C., Finlay, D.: Supervised classification models to detect the presence of old myocardial infarction in body surface potential maps. In: Computers in Cardiology, pp. 265–268. IEEE, Valencia, Spain (2006)
Chang, P.-C., Lin, J.-J., Hsieh, J.-C., Weng, J.: Myocardial infarction classification with multi-lead ECG using hidden Markov models and gaussian mixture models. Appl. Soft Comput. 12(10), 3165–3175 (2012)
Tripathy, R., Dandapat, S.: Detection of myocardial infarction from vectorcardiogram using relevance vector machine. SIVip. 1–8 (2017). doi:10.1007/s11760-017-1068-9
Yang, H., Kan, C., Liu, G., Chen, Y.: Spatiotemporal differentiation of myocardial infarctions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 10(4), 938–947 (2013)
Le, T.Q., Bukkapatnam, S.T., Benjamin, B.A., Wilkins, B.A., Komanduri, R.: Topology and random-walk network representation of cardiac dynamics for localization of myocardial infarction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(8), 2325–2331 (2013)
Rangayyan, R.M.: Biomedical Signal Analysis, vol. 33. Wiley, New York (2015)
Bousseljot, R., Kreiseler, D., Schnabel, A.: Nutzung der ekg-signaldatenbank cardiodat der ptb uber das internet. Biomed. Eng. 40(s1), 317–318 (1995)
Goldberger, A., Amaral, L., Glass, L., Hausdorff, J., Ivanov, P., Mark, R., Mietus, J., Moody, G., Peng, C.-K., Stanley, H.: PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23), e215–e220 (2000)
Sharma, L.D., Sunkaria, R.K.: A robust QRS detection using novel pre-processing techniques and kurtosis based enhanced efficiency. Measurement 87, 194–204 (2016)
Asgari, S., Mehrnia, A., Moussavi, M.: Automatic detection of atrial fibrillation using stationary wavelet transform and support vector machine. Comput. Biol. Med. 60, 132–142 (2015)
Garcia, M., Rodenas, J., Alcaraz, R., Rieta, J.J.: Application of the relative wavelet energy to heart rate independent detection of atrial fibrillation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 131, 157–168 (2016)
Addison, P.S.: Wavelet transforms and the ECG: a review. Physiol. Meas. 26(5), R155 (2005)
Molina-Pico, A., Cuesta-Frau, D., Aboy, M., Crespo, C., Miro-Martinez, P., Oltra-Crespo, S.: Comparative study of approximate entropy and sample entropy robustness to spikes. Artif. Intell. Med. 53(2), 97–106 (2011)
Marwaha, P., Sunkaria, R.K.: Complexity quantification of cardiac variability time series using improved sample entropy (i-sampen). Aust. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 39(3), 1–9 (2016)
Neurauter, A., Eftestol, T., Kramer-Johansen, J., Abella, B.S., Sunde, K., Wenzel, V., Lindner, K.H., Eilevstjonn, J., Myklebust, H., Steen, P.A., et al.: Prediction of countershock success using single features from multiple ventricular fibrillation frequency bands and feature combinations using neural networks. Resuscitation 73(2), 253–263 (2007)
Saeys, Y., Inza, I., Larranaga, P.: A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 23(19), 2507–2517 (2007)
Oliveira, R.B., Papa, J.P., Pereira, A.S., Tavares, J.M.R.: Computational methods for pigmented skin lesion classification in images: review and future trends. Neural Comput. Appl. 1–24 (2016). doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2482-6
Han, J., Pei, J., Kamber, M.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Elsevier, New York (2011)
Mitchell, T.M: Machine Learning. McGraw-Hill (1997)
Papa, J.P., FalcaO, A.X., De Albuquerque, V.H.C., Tavares, J.M.R.: Efficient supervised optimum-path forest classification for large datasets. Pattern Recogn. 45(1), 512–520 (2012)
de Albuquerque, V.H.C., Nunes, T.M., Pereira, D.R., Luz, E.J.D.S., Menotti, D., Papa, J.P., Tavares, J.M.R.: Robust automated cardiac arrhythmia detection in ECG beat signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 1–15 (2016). doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2472-8
Iwashita, A.S., Papa, J.P., Souza, A., Falcao, A.X., Lotufo, R., Oliveira, V., De Albuquerque, V.H.C., Tavares, J.M.R.: A path-and label-cost propagation approach to speedup the training of the optimum-path forest classifier. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 40, 121–127 (2014)
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India for providing the financial assistance. This work has been done at Medical Imaging and Computational Modeling of Physiological System Research Laboratory at Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, L.D., Sunkaria, R.K. Inferior myocardial infarction detection using stationary wavelet transform and machine learning approach. SIViP 12, 199–206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1146-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1146-z