Abstract
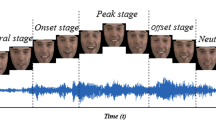
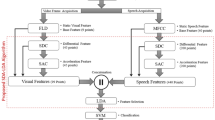
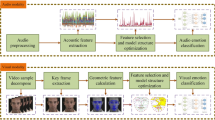
We present a fully automatic multimodal emotion recognition system based on three novel peak frame selection approaches using the video channel. Selection of peak frames (i.e., apex frames) is an important preprocessing step for facial expression recognition as they contain the most relevant information for classification. Two of the three proposed peak frame selection methods (i.e., MAXDIST and DEND-CLUSTER) do not employ any training or prior learning. The third method proposed for peak frame selection (i.e., EIFS) is based on measuring the “distance” of the expressive face from the subspace of neutral facial expression, which requires a prior learning step to model the subspace of neutral face shapes. The audio and video modalities are fused at the decision level. The subject-independent audio-visual emotion recognition system has shown promising results on two databases in two different languages (eNTERFACE and BAUM-1a).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atrey, P.K., Hossain, M.A., Saddik, A.E., Kankanhalli, M.S.: Multimodal fusion for multimedia analysis: a survey. Multimed. Syst. 16, 345–379 (2010)
Ayadi, M.E., Kamel, M.S., Karray, F.: Survey on speech emotion recognition: features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recognit. 44, 572–587 (2011)
Bozkurt, E., Erzin, E., Erdem, C.E., Erdem, A.T.: Formant position based weighted spectral features for emotion recognition. Speech Commun. 53, 1186–1197 (2011)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2, 27 (2011)
Datcu, D., Rothkrantz, L.J.: Emotion recognition using bimodal data fusion. In: Proceedings of the international conference on computer systems and technologies, pp 122–128 (2011)
Erdem, C.E., Bozkurt, E., Erzin, E., Erdem, A.T.: Ransac-based training data selection for emotion recognition from spontaneous speech. In: AFFINE (2010)
Erdem, C.E., Turan, C., Aydin, Z.: BAUM-2: a multilingual audio-visual affective face database. Multimed. Tools Appl. 74, 7429–7459 (2014)
Fasel, B., Luettin, J.: Automatic facial expression analysis: a survey. Pattern Recognit. 36, 259–275 (2003)
Gajsek, R., Struc, V., Mihelic, F.: Multi-modal emotion recognition using canonical correlations and acoustic features. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (2010)
Hermansky, H., Morgan, N.: RASTA processing of speech. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2, 578–589 (1994)
Jain, A.K., Dubes, R.C.: Algorithms for Clustering Data. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River (1988)
Kittler, J., Duin, M.H.R.P., Matas, J.: On combining classifiers. IEEE TPAMI 20(3), 226–239 (1998)
Kuan-Chieh, H., et al.: Learning collaborative decision-making parameters for multimodal emotion recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (2013)
Littlewort, G.C., et al.: Automatic coding of facial expressions displayed during posed and genuine pain. Image Vis. Comput. 27(12), 1797–1803 (2009)
Lucey, P., et al.: The extended cohn-kanade dataset (CK+): a complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In: IEEE CVPR Workshop (2010)
Mansoorizadeh, M., et al.: Multimodal information fusion application to human emotion recognition from face and speech. Multimed. Tools Appl. 49, 277–297 (2010)
Martin, O., Kotsia, I., Macq, B., Pitas, I.: The eNTERFACE05 audio-visual emotion database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Multimedia Database Management (2006)
Onder, O., Zhalehpour, S., Erdem, CE.: A Turkish audio-visual emotional database. In: IEEE signal processing and applications conference (SIU), pp. 1–4. http://www.baum1.bahcesehir.edu.tr (2013)
Paleari, M., Huet, B.: Toward emotion indexing of multimedia excerpts. In: Proceedings of the CBMI, pp. 425–432 (2008)
Ryan, A., et al.: Automated facial expression recognition system. In: IEEE ICCST, pp. 172–177 (2009)
Sariyanidi, E., Gunes, H., Cavallaro, A.: Automatic analysis of facial affect: a survey of registration, representation and recognition. IEEE TPAMI 37, 1113–1133 (2014)
Schuller, B., et .al.: Acoustic emotion recognition: A benchmark comparison of performances. In: IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, pp. 552–557 (2009)
Sharma, A., Anamika, D.: Facial expression recognition using virtual neutral image synthesis. In: Nat. Conf. Comp. Vi. Patt. Reco. Image Proc. and Graphics (2010)
Sloan, D.M., Kring, A.M.: Measuring changes in emotion during psychotherapy: conceptual and methodological issues. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 14, 307–322 (2007)
Turk, M., Pentland, A.: Eigenfaces for recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 3(1), 71–86 (1991)
Ulukaya, S., Erdem, C.E.: Gaussian mixture model based estimation of the neutral face shape for emotion recognition. Digit. Signal Process. 32, 11–23 (2014)
Wang, Y., et al.: Kernel cross-modal factor analysis for information fusion with application to bimodal emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 14(3), 597–607 (2012)
Yongjin, W., Ling, G.: Recognizing human emotional state from audiovisual signals. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 10, 936–946 (2008)
Zeng, Z.H., Pantic, M., Roisman, G.I., Huang, T.S.: A survey of affect recognition methods: audio, visual, and spontaneous expressions. IEEE TPAMI 31(1), 38–58 (2009)
Zhalehpour, S., Akhtar, Z., Erdem, C.: Multimodal emotion recognition with automatic peak frame selection. In: Proceedings of IEEE INISTA, pp. 116–121 (2014)
Zhu, X., Ramanan, D.: Face detection, pose estimation and landmark localization in the wild. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Turkish Scientific and Technical Research Council (TÜBİTAK) under project EEAG-110E056.
Sara Zhalehpour, Zahid Akhtar: The authors should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhalehpour, S., Akhtar, Z. & Eroglu Erdem, C. Multimodal emotion recognition based on peak frame selection from video. SIViP 10, 827–834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0822-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0822-0