Abstract
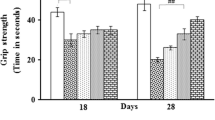
Fish oil (FO) supplementation could cause an increase in the concentration of plasmatic free fatty acids and, consequently, could compete with pro-inflammatory arachidonic acid (ARA) derived from brain biomembranes metabolism in the cerebrospinal fluid. Essential fatty acids (EFA) (n-3) have been reported by their antioxidant and neuroprotective properties, and therefore the influence of the FO supplementation on the reserpine-induced motor disorders was studied. Wistar rats were orally treated with FO solution for 5 days, and co-treated with reserpine (R; 1 mg/kg/mL) or its vehicle for 3 days (every other day). Reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and catalepsy (P < 0.05) were prevented by FO (P < 0.05). Biochemical evaluations showed that reserpine treatment increased the lipid peroxidation in the cortex and striatum (P < 0.05), while the FO supplementation prevented this oxidative effect in both brain regions (P < 0.05). Our results showed the protective role of FO in the brain lipid membranes, reinforcing the beneficial effect of n-3 fatty acids in the prevention of degenerative and motor disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALA:
-
α-Linolenic acid
- ARA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- DPA:
-
Docosapentaenoic acid
- EFA:
-
Essential fatty acid(s)
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- FO:
-
Fish oil
- FT:
-
Facial twitching
- LNA:
-
Linoleic acid
- MAO:
-
Monoamine oxidase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- SO:
-
Soybean oil
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- VCM:
-
Vacuous chewing movements
- VMAT:
-
Vesicular monoamine transporter
References
Sarsilmaz M, Songur A, Ozyurt H, Kus I, Ozen OA, Ozyurt B, Sogut S, Akyol O (2003) Potential role of dietary ω-3 essential fatty acids on some oxidant/antioxidant parameters in rats’ corpus striatum. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 69:253–259
Songur A, Sarsilmaz M, Sogut S, Ozyurt B, Ozyurt H, Zararsiz I, Turkoglu AO (2004) Hypothalamic superoxide dismutase, xanthine oxidase, nitric oxide, and malondialdehyde in rats fed with ω-3 fatty acids. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:693–698
Zararsiz I, Kus I, Akpolat N, Songur A, Ogeturk M, Sarsilmaz M (2006) Protective effects of omega-3 essential fatty acids against formaldehyde-induced neuronal damage in prefrontal cortex of rats. Cell Biochem Funct 24:237–244
Haag M (2003) Essential fatty acids and the brain. Can J Psychiatr 48:195–203
Jump DB (2002) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and regulation of gene transcription. Curr Opin Lipidol 13:155–164
Yehuda S, Rabinovitz S, Mostofski DI (2005) Essential fatty acids and stress. In: Yehuda S, Mostofsky DI (eds) Nutrition, stress and medical disorders. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 99–100
Chalon S, Delion-Vancassel S, Belzung C, Guilloteau D, Lequisquet AM, Besnard JC, Durand G (1998) Dietary fish oil induces affects in monoaminergic neurotransmission and behavior in rats. J Nutr 128:2512–2519
Wainwright PE (2002) Dietary essential fatty acids and brain function: a development perspective on mechanisms. Proc Nutr Soc 61:61–69
Wainwright PE, Xing HC, Mutsaers L, McCutcheon D, Kyle D (1997) Arachidonic acid offsets the effects on mouse brain and behavior of a diet with a low (n-6)/(n-3) ratio and very high levels of docosahexaenoic acid. J Nutr 127:184–193
Éthier I, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Rouillard C, Lévesque D (2004) Docosahexaenoic Acid Reduces Haloperidol-Induced Dyskinesias in Mice: Involvement of Nur77 and Retinoid Receptors. Biol Psychiatry 56:522–526
Yehuda S (1989) Behavioral effects of dietary fats. In: Chandra RK (ed) Health effects of fish and fish oils. ARTS St John’s, Canada, pp 327–335
Lee PH, Lee G, Paik MJ (2008) Polyunsaturated fatty acids levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 23:309–310
Fuentes P, Paris I, Nassif M, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2007) Inhibition of VMAT-2 and DT-diaphorase induce cell death in a substantia nigra-derived cell Line - an experimental cell model for dopamine toxicity studies. Chem Res Toxicol 20:776–783
Bilska A, Dubiel M, Sokolowska-Jez’ewicz M, Lorenc-Koci E, Wlodek L (2007) Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 146:1758–1771
Teixeira AM, Reckziegel P, Müller L, Pereira RP, Roos DH, Rocha JBT, Bürger ME (2009) Intense exercise potentiates oxidative stress in striatum of reserpine-treated animals. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:231–235
Hallet PJ, Brotchie JM (2007) Striatal delta opioid receptor binding in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia. Mov Disord 22:28–40
Abilio VC, Silva RH, Carvalho RC, Grassl C, Calzavara MB, Registro S, D′Almeida V, Ribeiro R de R, Frussa-Filho R (2004) Important role of striatal catalase in aging- and reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 47:263–272
Bürger ME, Alves A, Callegari L, Athaide FR, Nogueira CCW, Zeni G, Rocha JBT (2003) Ebselen attenuates reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and oxidative stress in rat striatum. Progr Neuropharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:135–140
Bürger ME, Fachinetto R, Alves A, Callegari L, Rocha JBT (2005) Acute reserpine and subchronic haloperidol treatments change synaptosomal brain glutamate uptake and elicit orofacial dyskinesia in rats. Brain Res 1031:202–210
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2004) Reversal of reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and cognitive dysfunction by quercetin. Pharmacology 70:59–67
Hughes NR, McKnight AT, Woodruff GN, Hill MP, Crossman AR, Brotchie JM (1998) Kappa-opioid receptor agonists increase locomotor activity in the monoamine-depleted rat model of parkinsonism. Mov Disord 13:228–233
Hubbard A, Trugman JM (1993) Reversal of reserpine-induced catalepsy by selective D1 and D2 dopamine agonists. Mov Disord 8:473–478
Teixeira AM, Trevizol F, Colpo G, Garcia SC, Charo M, Pereira RP, Fachinetto R, JBT Rocha, Bürger ME (2008) Influence of chronic exercise on reserpine-induced oxidative stress in rats: Behavioral and antioxidant evaluations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:465–472
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Niculescu AB (2003) Oxidative mechanisms and tardive dyskinesia. CNS Drugs 17:47–62
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Bracha HS (1990) Increased indices of free radical activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tardive dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 28:535–539
Andreassen OA, Jorgensen HA (2000) Neurotoxicity associated with neuroleptic-induced oral dyskinesias in rats. Implications for tardive dyskinesia? Prog Neurobiol 61:525–541
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E, Offen D (2001) Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: the need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood barrier. Neuropharmacology 40:959–975
Halliwel B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Evans DR, Parikh VV, Khan MM, Coussons C, Buckley PF, Mahadik SP (2003) Red blood cell membrane essential fatty acid metabolism in early psychotic patients following antipsychotic drug treatment. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 69:393–399
Bazan N (2009) Cellular and molecular events mediated by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 signaling in photoreceptor cell survival and brain protection. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 81:205–211
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ozyurt B, Sarsilmaz M, Akpolat N, Ozyurt H, Akyol O, Herken H, Kus I (2007) The protective effects of omega-3 fatty acids against MK-801-induced neurotoxicity in prefrontal cortex of rat. Neurochem Int 50:196–202
Bazan NG (2006) The onset of brain injury and neurodegeneration triggers the synthesis of docosanoid neuroprotective signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:899–911
Bazan NG (2007) Omega-3 fatty acids, pro-inflammatory signaling and neuroprotection. Clin Nutr Metab Care 10:136–141
Fenton WS, Hibbeln J, Knable M (2000) Essential fatty acids, lipid membrane abnormalities, and the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 47:8–21
Sussman AN, Tran-Nguyen LTL, Neisewander JL (1997) Acute reserpine administration elicits long-term spontaneous oral dyskinesia. Eur J Pharmacol 337:157–160
Neiswander JL, Castañeda E, Davis DA (1994) Dose-dependent differences in the development of reserpine-induced oral-dyskinesia in rats: support for a model of tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 116:79–84
Raghavendra V, Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2001) Reversal of reserpine-induced vacuous chewing movements in rats by melatonin: involvement of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Brain Res 904:149–152
Colpo G, Trevisol F, Teixeira AM, Fachinetto R, Pereira RP, Athayde ML, Rocha JBT, Bürger ME (2007) Ilex paraguariensis has antioxidant and attenuates haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and memory dysfunction in rats. Neurotox Res 12:1–10
Zimmer L, Durand G, Guilloteau D, Chalon S (1999) n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency and dopamine metabolism in the rat frontal cortex. Lipids 34:S251
Zimmer L, Delpal S, Guilloteau D, Aïoun J, Durand G, Chalon S (2000) Chronic n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency alters dopamine vesicle density in the rat frontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 284:25–28
Zimmer L, Vancassel S, Cantagrel S, Breton P, Delamanche S, Guiloteau D, Durand G, Chalon S (2002) The dopamine mesocorticolimbic pathway is affected by deficiency in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am J Clin Nutr 75:662–667
Delion S, Chalon S, Herault J, Guilloteau D, Besnard JC, Durand G (1994) Chronic dietary alpha-linolenic acid deficiency alters dopaminergic and serotoninergic neurotransmission in rats. J Nutr 124:2466–2476
Delion S, Chalon S, Guilloteau D, Besnard JC, Durand G (1996) Alpha-linolenic acid dietary deficiency alters age-related changes of dopaminergic and serotoninergic transmission in the rat frontal cortex. J Neurochem 66:1582–1591
Calder PC (2001) Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation and immunity. World Rev Nutr Diet 88:109–116
Farooqui AA, Horrocks LA (2006) Phospholipase A2-generated lipid mediators in the brain: the good, the bad and the ugly. Neuroscientist 12:245–260
De Caterina R, Massaro M (2005) Omega-3 fatty acids and the regulation of expression of endothelial pro-atherogenic and pro-inflammatory genes. J Membr Biol 206:103–116
Farooqui AA, Horrocks LA, Farooqui T (2000) Glycerophospholipids in brain: their metabolism, incorporation into membranes and involvement in neurological disorders. Chem Phys Lipids 106:1–29
Burgess JR, Stevens L, Zhang W, Peck L (2000) Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Clin Nutr 71:327S–330S
Sorgi PJ, Hallowell EM, Hutchins HL, Sears B (2007) Effects of an open-label pilot study with high-dose EPA/DHA concentrates on plasma phospholipids and behavior in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nutr J 6:16
Chen CT, Liu Z, Bazinet RP (in press) Rapid de-esterification and loss of eicosapentaenoic acid from rat brain phospholipids: an intracerebroventricular study. J Neurochem. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07116.x
Samadi P, Gregoire C, Rouillard C, Bedard PJ, Di Paolo T, Levesque D (2006) Docosahexaenoic acid reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine monkeys. Ann Neurol 59:282–288
Naidu P, Kulkarni SK (2001) Possible involvement of prostaglandins in haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 430:295–298
Ono N, Abiru T, Sugiyama K, Kamiya H (1992) Influence of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on the cataleptic behaviour induced by haloperidol in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 46:59–63
Barcelos RCS, Benvegnú DM, Boufleur N, Reckziegel P, Müller LG, Pase CS, Bürger ME (2010) Effects of n-3 essential fatty acids (n-3 EFA) on motor disorders and memory dysfunction typical neuroleptic-induced: behavioral and biochemical parameter. Neurotox Res 17:228–237
Mills SC, Windsor AC, Knight SC (2005) The potential interactions between polyunsaturated fatty and colonic inflammatory processes. Clin Exp Immunol 142:216–228
Wu A, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilha F (2004) Dietary omega-3 fatty acids normalize BDNF levels, reduce oxidative damage, and counteract learning disability after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 21:1457–1467
Nemets B, Stahl Z, Belmaker RH (2002) Addition of omega-3 fatty acid to maintenance medication treatment for recurrent unipolar depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry 159(3):477–479
Robinson PJ, Noronha J, DeGeorge JJ, Freed LM, Nariai T, Rapoport SI (1992) A quantitative method for measuring regional in vivo fatty-acid incorporation into and turnover within brain phospholipids: review and critical analysis. Brain Res 17:187–214
DeMar JC Jr, Ma K, Bell JM, Rapoport SI (2004) Half-lives of docosahexahenoic acid in rat brain phospholipids are prolonged by 15 weeks of nutritional deprivation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Neurochem 91:1125–1137
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Barcelos, R.C.S., Benvegnú, D.M., Boufleur, N. et al. Short Term Dietary Fish Oil Supplementation Improves Motor Deficiencies Related to Reserpine-Induced Parkinsonism in Rats. Lipids 46, 143–149 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-010-3514-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-010-3514-0