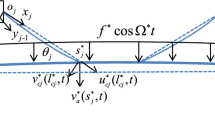
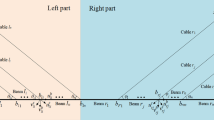
Abstract
In this paper, a novel structural modification approach has been adopted to eliminate the early coupling between the bending and torsional mode shapes of vibrations for a cable stayed bridge model generated using ABAQUS software. Two lateral steel beams are added to the middle span of the structure. Frequency analysis is dedicated to obtain the natural frequencies of the first eight mode shapes of vibrations before and after the structural modification approach. Numerical simulations of wind excitations are conducted for the 3D model of the cable stayed bridge with duration of 30 s supporting on real data of a strong wind from the literature. Both vertical and torsional displacements are calculated at the mid span of the deck to analyze both the bending and the torsional stiffness of the system before and after the structural modification. The results of the frequency analysis after applying lateral steel beams declared a safer structure against vertical and torsional vibrations and rarely expected flutter wind speed. Furthermore, the coupling between the vertical and torsional mode shapes has been removed to larger natural frequencies magnitudes with a high factor of safety. The novel structural approach manifested great efficiency in increasing vertical and torsional stiffness of the structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Areias P, Rabczuk T, Msekh M. Phase-field analysis of finite-strain plates and shells including element subdivision. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016 (in press)
Areias P, Reinoso J, Camanho P, Rabczuk T. A constitutive-based element-by-element crack propagation algorithm with local remeshing. Computational Mechanics, 2015, 56(2): 291–315
Areias P, Msekh M A, Rabczuk T. Damage and fracture algorithm using the screened Poisson equation and local remeshing. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2016, 158: 116–143
Nguyen-Thanh N, Valizadeh N, Nguyen M N, Nguyen-Xuan H, Zhuang X, Areias P, Zi G, Bazilevs Y, De Lorenzis L, Rabczuk T. An extended isogeometric thin shell analysis based on Kirchhoff-Love theory. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 284: 265–291
Areias PMA, Rabczuk T, Camanho P P. Finite strain fracture of 2D problems with injected anisotropic softening elements. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 72: 50–63
Areias P, Rabczuk T, Dias-da-Costa D. Element-wise fracture algorithm based on rotation of edges. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 110: 113–137
Areias P, Rabczuk T, Camanho P P. Initially rigid cohesive laws and fracture based on edge rotations. Computational Mechanics, 2013, 52(4): 931–947
Vu-Bac N, Lahmer T, Zhuang X, Nguyen-Thoi T, Rabczuk T. A software framework for probabilistic sensitivity analysis for computationally expensive models. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 100: 19–31
Ren H, Zhuang X, Cai Y, Rabczuk T. Dual-horizon peridynamics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2016, 108(12): 1451–1476
Vu-Bac N, Rafiee R, Zhuang X, Lahmer T, Rabczuk T. Uncertainty quantification for multiscale modeling of polymer nanocomposites with correlated parameters. Composites. Part B, Engineering, 2014, 68: 446–464
Ghasemi H, Brighenti R, Zhuang X, Muthu J, Rabczuk T. Optimum fiber content and distribution in fiber-reinforced solids using a reliability and NURBS based sequential optimization approach. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2015, 51(1): 99–112
Valizadeh N, Bazilevs Y, Chen J S, Rabczuk T. A coupled IGAmeshfree discretization of arbitrary order of accuracy and without global geometry parameterization. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 293: 20–37
Nguyen B H, Tran H D, Anitescu C, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T. An isogeometric symmetric galerkin boundary element method for elastostatic analysis. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 306: 252–275
Nguyen V P, Anitescu C, Bordas S P A, Rabczuk T. Isogeometric analysis: An overview and computer implementation aspects. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2015, 117(4190): 89–116
Anitescu C, Jia Y, Zhang Y, Rabczuk T. An isogeometric collocation method using super convergent points. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 284: 1073–1097
Amiri F, Anitescu C, Arroyo M, Bordas S, Rabczuk T. XLME interpolants, a seamless bridge between XFEM and enriched meshless methods. Computational Mechanics, 2014, 53(1): 45–57
Nanthakumar S, Lahmer T, Zhuang X, Zi G, Rabczuk T. Detection of material interfaces using a regularized level set method in piezoelectric structures. Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering, 2016, 24(1): 153–176
Talebi H, Silani M, Rabczuk T. Concurrent multiscale modelling of three dimensional crack and dislocation propagation. Advances in Engineering Software, 2015, 80: 82–92
Talebi H, Silani M, Bordas S, Kerfriden P, Rabczuk T. A computational library for multiscale modelling of material failure. Computational Mechanics, 2014, 53(5): 1047–1071
Talebi H, Silani M, Bordas S P A, Kerfriden P, Rabczuk T. Molecular dynamics/XFEM coupling by a three-dimensional extended bridging domain with applications to dynamic brittle fracture. International Journal for Multiscale Computational Engineering, 2013, 11(6): 527–541
Ghorashi S, Valizadeh N, Mohammadi S, Rabczuk T. T-spline based XIGA for fracture analysis of orthotropic media. Computers & Structures, 2015, 147: 138–146
Zi G, Rabczuk T, Wall W A. Extended meshfree methods without branch enrichment for cohesive cracks. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 40(2): 367–382
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T. Application of particle methods to static fracture of reinforced concrete structures. International Journal of Fracture, 2006, 137(1-4): 19–49
Rabczuk T, Bordas S, Zi G. A three-dimensional meshfree method for continuous multiple crack initiation, nucleation and propagation in statics and dynamics. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 40(3): 473–495
Bordas S, Rabczuk T, Zi G. Three-dimensional crack initiation, propagation, branching and junction in non-linear materials by extrinsic discontinuous enrichment of meshfree methods without asymptotic enrichment. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75 (5): 943–960
Rabczuk T, Zi G, Bordas S, Nguyen-Xuan H. A geometrically nonlinear three dimensional cohesive crack method for reinforced concrete structures. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75(16): 4740–4758
Rabczuk T, Bordas S, Zi G. On three-dimensional modelling of crack growth using partition of unity methods. Computers & Structures, 2010, 88(23-24): 1391–1411
Rabczuk T, Zi G. A meshfree method based on the local partition of unity for cohesive cracks. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 39(6): 743–760
Rabczuk T, Zi G, Bordas S, Nguyen-Xuan H. A simple and robust three-dimensional cracking-particle method without enrichment. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199(37-40): 37–40, 2437–2455
Rabczuk T, Areias P M A, Belytschko T. A meshfree thin shell method for nonlinear dynamic fracture. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 72(5): 524–548
Amiri F, Milan D, Shen Y, Rabczuk T, Arroyo M. Phase-field modeling of fracture in linear thin shells. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 69: 102–109
Areias P, Rabczuk T. Finite strain fracture of plates and shells with configurational forces and edge rotation. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2013, 94(12): 1099–1122
Chau-Dinh T, Zi G, Lee P S, Song J H, Rabczuk T. Phantom-node method for shell models with arbitrary cracks. Computers & Structures, 2012, 92–93: 242–256
Nguyen-Thanh N, Kiendl J, Nguyen-Xuan H, Wuchner R, Bletzinger K U, Bazilevs Y, Rabczuk T. Rotation free isogeometric thin shell analysis using PHT-splines. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 200(47-48): 3410–3424
Nguyen-Thanh N, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas S. A smoothed finite element method for shell analysis. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 198(2): 165–177
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T. A three dimensional large deformation meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 196(29-30): 2777–2799
Rabczuk T, Eibl J, Stempniewski L. Simulation of high velocity concrete fragmentation using SPH/MLSPH. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2003, 56(10): 1421–1444
Rabczuk T, Eibl J, Stempniewski L. Numerical analysis of high speed concrete fragmentation using a meshfree Lagrangian method. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2004, 71(4-6): 547–556
Rabczuk T, Eibl J. Modeling dynamic failure of concrete with meshfree particle methods. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32(11): 1878–1897
Rabczuk T, Samaniego E, Belytschko T. Simplied model for predicting impulsive loads on submerged structures to account for fluid-structure interaction. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(2): 163–177
Rabczuk T, Areias P M A, Belytschko T. A simplied meshfree method for shear bands with cohesive surfaces. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 69(5): 993–1021
Rabczuk T, Samaniego E. Discontinuous modelling of shear bands using adaptive meshfree methods. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 197(6-8): 641–658
Rabczuk T, Gracie R, Song J H, Belytschko T. Immersed particle method for fluid-structure interaction. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 81(1): 48–71
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T. Cracking particles: A simplified meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2004, 61(13): 2316–2343
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T, Xiao S P. Stable particle methods based on Lagrangian kernels. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 193(12-14): 1035–1063
Rabczuk T, Akkermann J, Eibl J. A numerical model for reinforced concrete structures. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42(5-6): 1327–1354
Rabczuk T, Eibl J. Numerical analysis of prestressed concrete beams using a coupled element free Galerkin/nite element method. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2004, 41(3-4): 1061–1080
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T. Adaptivity for structured meshfree particle methods in 2D and 3D. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 63(11): 1559–1582
Budarapu P R, Sudhir Sastry Y B, Natarajan R. Design concepts of an aircraft wing: Composite and morphing airfoil with auxetic structures. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2016, (in press)
Sudhir Sastry Y B, Budarapu P R, Madhavi N, Krishna Y N. Buckling analysis of thin wall stiffened composite panels. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96(B): 459–471
Sudhir Sastry Y B, Budarapu P R, Krishna Y, Devaraj S. Studies on ballistic impact of the composite panels. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 72: 2–12
Thai H C, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas S, Nguyen-Thanh N, Rabczuk T. Isogeometric analysis of laminated composite plates using the higher-order shear deformation theory. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2015, 22(6): 451–469
Thai C H, Ferreira A J M, Bordas S, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H. Isogeometric analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates using a new inverse trigonometric shear deformation theory. European Journal of Mechanics. A, Solids, 2014, 43: 89–108
Phan-Dao H, Nguyen-Xuan H, Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thoi T, Rabczuk T. An edge-based smoothed finite element method for analysis of laminated composite plates. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2013, 10(1): 1340005
Thai C H, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thanh N, Le T H, Nguyen-Thoi T, Rabczuk T. Static, free vibration and buckling analysis of laminated composite Reissner-Mindlin plates using NURBS-based isogeometric approach. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2012, 91(6): 571–603
Nguyen-Xuan H, Rabczuk T, Bordas S, Debongnie J F. A smoothed finite element method for plate analysis. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 197(13-16): 13–16, 1184–1203
Budarapu P R, Javvaji B, Sutrakar V K, Roy Mahapatra D, Zi G, Rabczuk T. Crack propagation in Graphene. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118(6): 064307
Yang S W, Budarapu P R, Mahapatra D R, Bordas S P A, Zi G, Rabczuk T. A meshless adaptive multiscale method for fracture. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96B: 382–395
Budarapu P R, Sudhir Sastry Y B, Javvaji B, Mahapatra D R. Vibration analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in elastic medium. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2014, 8(2): 151–159
Budarapu P R, Narayana T S S, Rammohan B, Rabczuk T. Directionality of sound radiation from rectangular panels. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 89: 128–140
Budarapu P R, Gracie R, Yang S W, Zhaung X, Rabczuk T. Efficient coarse graining in multiscale modeling of fracture. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 69: 126–143
Budarapu P R, Gracie R, Bordas S P A, Rabczuk T. An adaptive multiscale method for quasi-static crack growth. Computational Mechanics, 2014, 53(6): 1129–1148
Valizadeh N, Natarajan S, Gonzalez-Estrada O A, Rabczuk T, Bui T Q, Bordas S P A. NURBS-based finite element analysis of functionally graded plates: Static bending, vibration, buckling and flutter. Composite Structures, 2013, 99: 309–326
Shin Y B, Sin S H, Kim Y M, Hwang J S. Performance evaluation of linear active mass damper for bridges through wind tunnel test. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Structural Dynamics. EURODYN 2014, Porto, Portugal, 30 June–2 July, 2014
Vairo G. A Simple analytical approach to the aeroelastic stability problem of long span cable stayed bridges. International Journal for Computational Methods in Engineering Science and Mechanics, 2010, 11(1): 1–19
Man S K. Lateral and torsional vibration control of long span bridge deck using novel tuned liquid column dampers. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Kowloon: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, 2004
Ge Y J, Xiang H F. Bluff Body Aerodynamics Application I challenging bridge span Length. BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics and Applications, Milano, Italy, 20–24 July, 2008
Ding Q, Lee P K K. Computer simulation of buffeting actions of suspension bridges under turbulent wind. Computers & Structures, 2000, 76(6): 787–797
Zhang W. Fatigue performance of exciting bridges under dynamic loads from winds and vehicles. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Louisiana: Louisiana State University, 2012
He X, Babak M, Conte J P, Ahmed E. Modal identification study of Vincent Thomas Bridge using simulated wind-induced ambient vibration data. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2008, 23: 373–388
Winther S J, Sorensen N, Nielsen S R K. Aeroelastic stability of suspension bridges using CFD. In: Proceedings of International Symposium of the International Association for Shell and Spatial Structures (IASS). Structural Architecture towards the future looking to the past. Venice, Italy, 3–6 December 2007
Preumont A, Voltan M, Sangiovanni A, Bastaits R, Mokrani B, Alaluf D. An investigation of the active damping of Suspension Bridges. Mathematics and Mechanics of Complex Systems, 2015, 3 (4): 385–406
Pacheco B, Fujino Y, Sulekh A. Estimation curve for modal damping in stay cables with viscous damper. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1993, 119(6): 1961–1979
Wang H, Li A, Zong Z, Tong T, Zhou R. Damper Optimization for Long-Span Suspension Bridges: Formulations and Applications. IGI global, Pennsylvania, 2013, DOI: 10.4018/978-1-4666-2029-2. ch005
Fujino Y, Siringoringo D M, Nagayama T, Su D. Control, simulation and monitoring of bridge vibration — Japan’s recent development and practice. IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-II, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 8–10 August, 2010
Naimul Haque Md. Shaping effects on aerodynamics of long-span cable-supported bridge deck by unsteady RANS. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Louisiana: Yokohama National University, 2015
Krzystof W. Passive Aerodynamic Control of Wind Induced Instabilitues in Long Span Bridges. Wydawnictwo Politechniki Gdanskiej, Gdansk, 2002
Nicholas P. Jones, Cheryl A. Spartz. structural damping estimation for long-span bridges. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1990, 116 (11): 2414–2433
Xiong L, Liao H L, Li M S. The flutter performance study for a suspension bridge based on numerical analysis and wind-tunnel test. The 2014 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental and Materials Research (ACEM14), Busan, Korea, 24–28 August, 2014
Bakis K N, Massaro M, Williams MS, Limebeer D J N. Aeroela stic control of long-span suspension bridges with controllable winglets. Journal of Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2016, DOI: 10.1002/stc.1839
Kusano I, Baldomir A, Jurado J A, Hernandez S. Reliability based design optimization of long span bridges considering flutter. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 135: 149–162
Su C, Han D J, Yan Q S, Au F T K, Tham L G, Lee P K K, Lam K M, Wong K Y. Wind-induced vibration analysis of the Hong Kong Ting Kau Bridge. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, Structures and Buildings, 2003, 156(3): 263–272
Phan D H, Nguyen N T. Flutter and buffeting control of long-span suspension bridge by passive flaps: Experiment and Numerical Simulation. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Science, 2013, 14(1): 46–57
Kusano I. Reliability based design optimization of long span bridges under flutter constraint. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. La Coruna: Universidade Da Coruna, 2015
Cheng S. Structural and aerodynamic stability analysis of long span cable stayed bridges. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Ottawa: Carleton University, 1999
Petersen C. Schwingungsdämpfer im Ingenieurbau. Munich: Maurer Söhne GmbH and Co KG, 2001
Ziegler F, Kazemi Amiri A. Bridge vibrations effectively damped by means of tuned liquid column gas dampers. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2013, 14(1): 1–16
Caruso G. Othman Ben Mekki, Frederic Bourquin. Modeling and experimental validation of a new electromechanical damping device. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2009, 11(4): 1–9
Chen X Z, Kareem A, Matsumoto M. Multimode coupled flutter and buffeting analysis of long span bridges. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2001, 89: 649–664
Sato H, Hirahara N, Fumoto K, Hirano S, Kusuhara S. Full aeroelastic model test of a super long-span bridge with slotted box girder. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(12-15): 2023–2032
Dyrbye C, Hansen S O. Wind loads on structures. UK: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 1997
Johansson J, Andersen M S, Øvre M S. Non-flutter design principle for long span bridges. In: Proceedings of the Eighth Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering. 2013
Andersen M S, Sahin E, Laustsen B, Lenius M, Læso J R. Implementation of the non-flutter design principle. In: XIII Conference of the Italian Association for Wind Engineering INVENTO 2014. Genova, Italy, 22–25 June, 2014
Bartoli G, D’Asdia P, Febo S, Mannini C, Noè S, Procino L. Innovative configurations for long-span suspension bridges. EACWE 5 Florence, Italy, 19–23 July, 2009
Simiu E, Scanlan R H. Wind Effects on Structures: An Introduction to Wind Engineering. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1986
Wang H, TAO Tian-you, CHENG Huai-yu, LI Ai-qun. A simulation study on the optimal control of buffeting displacement for the Sutong Bridge with multiple tuned mass dampers. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 2014, 15(10): 798–812
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank and express his gratitude to Prof. Dr.-Ing. Timon Rabczuk, the chair of computational mechanics at Bauhaus Universität-Weimar, Germany, for his continuous support and invaluable assistance in providing guidance and consultancy relating to this research paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nariman, N.A. A novel structural modification to eliminate the early coupling between bending and torsional mode shapes in a cable stayed bridge. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 11, 131–142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-016-0376-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-016-0376-4