Abstract
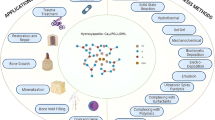
A solvothermal method has been successfully used to prepare nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA) hollow spheres with average diameters of about 500 nm and shell thicknesses of about 100 nm in a glycerin/water mixed solvent. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images show that the shells of the HA hollow spheres are actually composed of nanosheets with thicknesses of about 10 nm. By tuning the glycerin/water volume ratio, two other kinds of HA solid spheres with average diameters of about 6 or 20 μm were assembled from nanoflakes. The properties of the different kinds of spheres as drug delivery carriers were evaluated. Ibuprofen (IBU) was chosen as the model drug to load into the HA samples. The nanostructured HA samples showed a slow and sustained release of IBU. The HA hollow spheres exhibited a higher drug loading capacity and more favorable release properties than the HA solid spheres and thus are very promising for controlled drug release applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma M Y, Zhu Y J, Li L, Cao S W. Nanostructured porous hollow ellipsoidal capsules of hydroxyapatite and calcium silicate: preparation and application in drug delivery. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008, 18(23): 2722–2727
Uskoković V, Uskoković D P. Nanosized hydroxyapatite and other calcium phosphates: chemistry of formation and application as drug and gene delivery agents. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2011, 96(1): 152–191
Zhang H G, Zhu Q S, Wang Y. Morphologically controlled synthesis of hydroxyapatite with partial substitution of fluorine. Chemistry of Materials, 2005, 17(23): 5824–5830
Tseng Y H, Mou C Y, Chan J C. Solid-state NMR study of the transformation of octacalcium phosphate to hydroxyapatite: a mechanistic model for central dark line formation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(21): 6909–6918
Cao X Y, Wen F, Bian W, Cao Y, Pang S J, Zhang WK. Preparation and comparison study of hydroxyapatite and Eu-hydroxyapatite. Frontiers of Materials Science in China, 2009, 3(3): 255–258
Jagadeesan D, Deepak C, Siva K, Inamdar M S, Eswaramoorthy M. Carbon Spheres Assisted Synthesis of Porous Bioactive Glass Containing Hydroxycarbonate Apatite Nanocrystals: a Material with High in Vitro Bioactivity. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(19): 7379–7384
Zhu D M, Wang F, Gao C L, Xu Z. Construction of PS/PNIPAM core-shell particles and hollow spheres by using hydrophobic interaction and thermosensitive phase separation. Frontiers of Chemical Engineering in China, 2008, 2(3): 253–256
Lächelt U, Wagner E. Invading target cells: multifunctional polymer conjugates as therapeutic nucleic acid carriers. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2011, 5(3): 275–286
Almirall A, Larrecq G, Delgado J A, Martínez S, Planell J A, Ginebra M P. Fabrication of low temperature macroporous hydroxyapatite scaffolds by foaming and hydrolysis of an α-TCP paste. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(17): 3671–3680
Ma M G, Zhu J F. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of hierarchically nanostructured hydroxyapatite hollow spheres. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 36: 5522–5526
Sun R X, Lu Y P, Chen K Z. Preparation and characterization of hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres by spray drying method. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2009, 29(4): 1088–1092
Shum H C, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S, Weitz D A. Double emulsion droplets as microreactors for synthesis of mesoporous. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(22): 5548–5555
Sun R X, Chen K Z, Lu Y P. Fabrication and dissolution behavior of hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres intended for controlled drug release. Materials Research Bulletin, 2009, 44(10): 1939–1942
Cheng X K, He Q J, Li J Q, Huang Z L, Chi R A. Control of pore size of the bubble-template porous carbonated hydroxyapatite microsphere by adjustable pressure. Crystal Growth & Design, 2009, 9(6): 2770–2775
Cheng X K, Huang Z L, Li J Q, Liu Y, Chen C L, Chi R A, Hu Y H. Self-assembled growth and pore size control of the bubble-template porous carbonated hydroxyapatite microsphere. Crystal Growth & Design, 2010, 10(3): 1180–1188
Jiang H Z, Stupp S I. Dip-pen patterning and surface assembly of peptide amphiphiles. Langmuir, 2005, 21(12): 5242–5246
Zhang W X, Yang Z H, Liu Y, Tang S P, Han X Z, Chen M. Controlled synthesis of Mn3O4 nanocrystallites and MnOOH nanorods by a solvothermal method. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 263(1–4): 394–399
Steiner Z, Rapaport H, Oren Y, Kasher R. Effect of surface-exposed chemical groups on calcium-phosphate mineralization in watertreatment systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(20): 7937–7943
Yang Z H, Zhao M, Florin N H, Harris A T. Synthesis and characterization of CaO nanopods for high temperature CO2 capture. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(24): 10765–10770
Mizushima Y, Ikoma T, Tanaka J, Hoshi K, Ishihara T, Ogawa Y, Ueno A. Injectable porous hydroxyapatite microparticles as a new carrier for protein and lipophilic drugs. Journal of Controlled Release, 2006, 110(2): 260–265
Ito M, Hidaka Y, Nakajima M, Yagasaki H, Kafrawy A H. Effect of hydroxyapatite content on physical properties and connective tissue reactions to a chitosan-hydroxyapatite composite membrane. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1999, 45(3): 204–208
Wang H X, Guan S K, Wang Y S, Liu H J, Wang H T, Wang L G, Ren C X, Zhu S J, Chen K S. In vivo degradation behavior of Cadeficient hydroxyapatite coated Mg-Zn-Ca alloy for bone implant application. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2011, 88(1): 254–259
Aoki H, Aoki H, Kutsuno T, Li W, Niwa M. An in vivo study on the reaction of hydroxyapatite-sol injected into blood. Journal of Materials Science. Materials in Medicine, 2000, 11(2): 67–72
Zhang C M, Cheng Z Y, Yang P P, Xu Z H, Peng C, Li G G, Lin J. Architectures of strontium hydroxyapatite microspheres: solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties. Langmuir, 2009, 25(23): 13591–13598
Yao A H, Ai F R, Liu X, Wang D P, Huang WH, Xu W. Preparation of hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres by the conversion of borate glass at near room temperature. Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(1): 25–28
Pon-On W, Meejoo S, Tang I M. Formation of hydroxyapatite crystallites using organic template of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 112(2): 453–460
Porter A, Patel N, Brooks R, Best S, Rushton N, Bonfield W. Effect of carbonate substitution on the ultrastructural characteristics of hydroxyapatite implants. Journal of Materials Science. Materials in Medicine, 2005, 16(10): 899–907
Wu Y J, Bose S. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite: micelle templated synthesis and characterization. Langmuir, 2005, 21(8): 3232–3234
Wang A J, Lu Y P, Zhu R F, Li S T, Xiao G Y, Zhao G F, Xu W H. Effect of sintering on porosity, phase, and surface morphology of spray dried hydroxyapatite microspheres. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A, 2008, 87(2): 557–562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, W., Yang, Z. et al. Nanostructured hollow spheres of hydroxyapatite: preparation and potential application in drug delivery. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 6, 246–252 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-012-1299-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-012-1299-9