Abstract
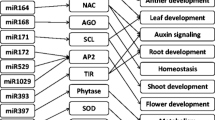
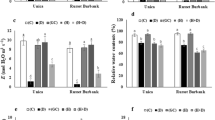
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding small RNAs that regulate gene expression by translational repression or transcript degradation. Thus far, a large number of miRNAs have been identified from model plant species and the quantity of miRNAs has been functionally characterized in diverse plants. However, the molecular characterizations of the conserved miRNAs are still largely elusive in wheat. In this study, 32 wheat miRNAs (TaMIRs) currently released in the Sanger miRBase (the microRNA database) were selected to evaluate the expression patterns under conditions of non-stress (CK) and salt stress treatment. Based on the analysis of semiquantitative RT-PCR and quantitative real qRT-PCR, TaMIR159a, TaMIR160, TaMIR167, TaMIR174, TaMIR399, TaMIR408, TaMIR11124 and TaMIR1133 were found to have responses to salinity stress, with an upregulated pattern under salt stress treatment. Based on a BLAST search against the NCBI GenBank database, the potential targets of the salt-inducible wheat miRNAs were predicted. Except for TaMIR399 not being identified to have the putative target genes, other salt-inducible TaMIRs were found to possess 2 to 7 putative target genes. Together, our results suggest that a subset of miRNAs are involved in the mediation of salt stress signaling responses in wheat via their roles on the regulation of acted target genes at post-transcriptional and translation levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aukerman M J, Sakai H (2003). Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a MicroRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell, 15(11): 2730–2741
Axtell M J, Snyder J A, Bartel D P (2007). Common functions for diverse small RNAs of land plants. Plant Cell, 19(6): 1750–1769
Chen S L, Polle A (2010). Salinity tolerance of Populus. Plant Biol (Stuttg), 12(2): 317–333
Chen X (2004). A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science, 303(5666): 2022–2025
Cui Q, Yu Z, Purisima E O, Wang E (2006). Principles of microRNA regulation of a human cellular signaling network. Mol Syst Biol, 2: 46
Ding D, Zhang L, Wang H, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zheng Y (2009). Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann Bot (Lond), 103(1): 29–38
FAO (2010). FAO Land and Plant Nutrition Management Service. 2008, http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/agll/spush (October 29, 2010)
Floyd S K, Bowman J L (2004). Gene regulation: ancient microRNA target sequences in plants. Nature, 428(6982): 485–486
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini H K, van Dongen S, Enright A J (2008). miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res, 36 (Database issue): D154–D158
Han Y, Luan F, Zhu H, Shao Y, Chen A, Lu C, Luo Y, Zhu B (2009). Computational identification of microRNAs and their targets in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Science in China C series-Life Sci, 52(11): 1091–1100
Kong Y, Elling A A, Chen B, Deng XW (2010). Differential expression of microRNAs in maize inbred and hybrid lines during salt and drought stress. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 1(2): 69–76
Laufs P, Peaucelle A, Morin H, Traas J (2004). MicroRNA regulation of the CUC genes is required for boundary size control in Arabidopsis meristems. Development, 131(17): 4311–4322
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method. Methods, 25(4): 402–408
Lu S, Sun Y H, Chiang V L (2008). Stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus. Plant J, 55(1): 131–151
Ma S, Gong Q, Bohnert H J (2006). Dissecting salt stress pathways. J Exp Bot, 57(5): 1097–1107
Millar A A, Waterhouse P M (2005). Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences. Funct Integr Genomics, 5(3): 129–135
Munns R (2005). Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol, 167(3): 645–663
Munns R, Tester M (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 59(1): 651–681
Palatnik J F, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington J C, Weigel D (2003). Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature, 425(6955): 257–263
Schwab R, Palatnik J F, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005). Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell, 8(4): 517–527
Shukla L I, Chinnusamy V, Sunkar R (2008). The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1779(11): 743–748
Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu J K (2006). Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell, 18(8): 2051–2065
Sunkar R, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Zhu J K (2008). Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol, 8(1): 25
Sunkar R, Zhu J K (2004). Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 16(8): 2001–2019
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005). Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 16(2): 123–132
Wei B, Cai T, Zhang R, Li A, Huo N, Li S, Gu Y Q, Vogel J, Jia J, Qi Y, Mao L (2009). Novel microRNAs uncovered by deep sequencing of small RNA transcriptomes in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Brachypodium distachyon (L.) Beauv. Funct Integr Genomics, 9(4): 499–511
Williams L, Grigg S P, Xie M, Christensen S, Fletcher J C (2005). Regulation of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem and lateral organ formation by microRNA miR166g and its AtHD-ZIP target genes. Development, 132(16): 3657–3668
Xin M, Wang Y, Yao Y, Xie C, Peng H, Ni Z, Sun Q (2010). Diverse set of microRNAs are responsive to powdery mildew infection and heat stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol, 10(1): 123
Yamaguchi T, Blumwald E (2005). Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci, 10(12): 615–620
Yao Y, Guo G, Ni Z, Sunkar R, Du J, Zhu J K, Sun Q (2007). Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome Biol, 8(6): R96
Yin Z J, Shen F F (2010). Identification and characterization of conserved microRNAs and their target genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genet Mol Res, 9(2): 1186–1196
Zhang H, Guo C, Li C, Xiao K (2008). Cloning, characterizatio and expression analysis of two superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Agric China, 2(2): 141–149
Zhao B, Liang R, Ge L, Li W, Xiao H, Lin H, Ruan K, Jin Y (2007). Identification of drought-induced microRNAs in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 354(2): 585–590
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, W., Li, J., Liu, F. et al. Expression pattern of wheat miRNAs under salinity stress and prediction of salt-inducible miRNAs targets. Front. Agric. China 5, 413–422 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-011-1133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-011-1133-z