Abstract
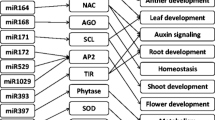
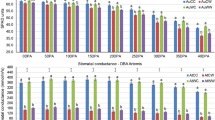
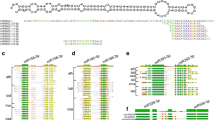
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) guide regulation at the post-transcriptional level by inducing messenger RNA (mRNA) degradation or translational inhibition of their target protein-coding genes. Durum wheat miRNAs may contribute to the genotypic water-deficit stress response in different durum varieties. Further investigation of the interactive miRNA-target regulatory modules and experimental validation of their response to water stress will contribute to our understanding of the small RNA-mediated molecular networks underlying stress adaptation in durum wheat. In this study, a comprehensive genome-wide in silico analysis using the updated Triticum transcriptome assembly identified 2055 putative targets for 113 conserved durum miRNAs and 131 targets for four novel durum miRNAs that putatively contribute to genotypic stress tolerance. Predicted mRNA targets encode various transcription factors, binding proteins and functional enzymes, which play vital roles in multiple biological pathways such as hormone signalling and metabolic processes. Quantitative PCR profiling further characterised 43 targets and 5 miRNAs with stress-responsive and/or genotype-dependent differential expression in two stress-tolerant and two stress-sensitive durum genotypes subjected to pre-anthesis water-deficit stress. Furthermore, a 5′ RLM-RACE approach validated nine mRNA targets cleaved by water-deficit stress-responsive miRNAs, which, to our knowledge, has not been previously reported in durum wheat. The present study provided experimental evidence of durum miRNAs and target genes in response to water-deficit stress in contrasting durum varieties, providing new insights into the regulatory roles of the miRNA-guided RNAi mechanism underlying stress adaptation in durum wheat.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agharbaoui Z, Leclercq M, Remita MA, Badawi MA, Lord E, Houde M, Danyluk J, Diallo AB, Sarhan F (2015) An integrative approach to identify hexaploid wheat miRNAome associated with development and tolerance to abiotic stress. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1490-8
Akpinar BA, Kantar M, Budak H (2015) Root precursors of microRNAs in wild emmer and modern wheats show major differences in response to drought stress. Funct Integr Genomics 15:587–598. doi:10.1007/s10142-015-0453-0
Alptekin B, Budak H (2016) Wheat miRNA ancestors: evident by transcriptome analysis of A, B, and D genome donors. Funct Integr Genomics. doi:10.1007/s10142-016-0487-y
Bertolini E, Verelst W, Horner DS, Gianfranceschi L, Piccolo V, Inze D, Pe ME, Mica E (2013) Addressing the role of microRNAs in reprogramming leaf growth during drought stress in Brachypodium distachyon. Mol Plant 6:423–443. doi:10.1093/mp/sss160
Borges F, Martienssen RA (2015) The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:727–741. doi:10.1038/nrm4085
Budak H, Akpinar A (2011) Dehydration stress-responsive miRNA in Brachypodium distachyon: evident by genome-wide screening of microRNAs expression. OMICS 15:791–799. doi:10.1089/omi.2011.0073
Budak H, Akpinar BA (2015) Plant miRNAs: biogenesis, organization and origins. Funct Integr Genomics 15:523–531. doi:10.1007/s10142-015-0451-2
Budak H, Bala Ani A (2016) Dissecting miRNAs in wheat D genome progenitor, Aegilops tauschii Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00606
Budak H, Kantar M, Yucebilgili Kurtoglu K (2013) Drought tolerance in modern and wild wheat. Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2013/548246
Budak H, Hussain B, Khan Z, Ozturk NZ, Ullah N (2015a) From genetics to functional genomics: improvement in drought signaling and tolerance in wheat. Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.01012
Budak H, Kantar M, Bulut R, Akpinar BA (2015b) Stress responsive miRNAs and isomiRs in cereals. Plant Sci 235:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.02.008
Budak H, Khan Z, Kantar M (2015c) History and current status of wheat miRNAs using next-generation sequencing and their roles in development and stress. Brief Funct Genomics 14:189–198. doi:10.1093/bfgp/elu021
Cao D, Wang J, Ju Z, Liu Q, Li S, Tian H, Fu D, Zhu H, Luo Y, Zhu B (2016) Regulations on growth and development in tomato cotyledon, flower and fruit via destruction of miR396 with short tandem target mimic. Plant Sci 247:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.02.012
Cheah BH, Nadarajah K, Divate MD, Wickneswari R (2015) Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1851-3
Chen J, Zheng Y, Qin L, Wang Y, Chen L, He Y, Fei Z, Lu G (2016) Identification of miRNAs and their targets through high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis in male and female Asparagus officinalis. BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/s12870-016-0770-z
Choudhury S, Panda P, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2013) Reactive oxygen species signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Signal Behav. doi:10.4161/psb.23681
Conesa A, Gotz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics. doi:10.1155/2008/619832
Curaba J, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2014) miRNAs in the crosstalk between phytohormone signalling pathways. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru002
de Deus KE, Lanna AC, Abreu FRM, Silveira RDD, Pereira WJ, Brondani C, Vianello RP (2015) Molecular and biochemical characterization of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in upland rice under drought. Aust J Crop Sci 9:744–753
Ding Q, Zeng J, He X-Q (2014) Deep sequencing on a genome-wide scale reveals diverse stage-specific microRNAs in cambium during dormancy-release induced by chilling in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/s12870-014-0267-6
Dolferus R (2014) To grow or not to grow: a stressful decision for plants. Plant Sci 229:247–261. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.10.002
Dong Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Chen L, Cai Z, Wang Y, Jin J, Li X (2013) Identification and dynamic regulation of microRNAs involved in salt stress responses in functional soybean nodules by high-throughput sequencing. Int J Mol Sci 14:2717–2738. doi:10.3390/ijms14022717
Eren H, Pekmezci MY, Okay S, Turktas M, Inal B, Ilhan E, Atak M, Erayman M, Unver T (2015) Hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum) root miRNome analysis in response to salt stress. Ann Appl Biol 167:208–216. doi:10.1111/aab.12219
Faize M, Burgos L, Faize L, Piqueras A, Nicolas E, Barba-Espin G, Clemente-Moreno M, Alcobendas R, Artlip T, Hernandez J (2011) Involvement of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase for improved tolerance against drought stress. J Exp Bot 62:2599–2613. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq432
Feng H, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Wang X, Liu J, Li M, Huang L, Kang Z (2013) Target of tae-miR408, a chemocyanin-like protein gene (TaCLP1), plays positive roles in wheat response to high-salinity, heavy cupric stress and stripe rust. Plant Mol Biol 83:433–443. doi:10.1007/s11103-013-0101-9
Ferdous J, Sanchez-Ferrero JC, Langridge P, Milne L, Chowdhury J, Brien C, Tricker PJ (2016) Differential expression of microRNAs and potential targets under drought stress in barley. Plant Cell Environ. doi:10.1111/pce.12764
Fromm S, Senkler J, Eubel H, Peterhänsel C, Braun H-P (2016) Life without complex I: proteome analyses of an Arabidopsis mutant lacking the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase complex. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/erw165
Gao F, Wang K, Liu Y, Chen Y, Chen P, Shi Z, Luo J, Jiang D, Fan F, Zhu Y (2015) Blocking miR396 increases rice yield by shaping inflorescence architecture. Nat Plants. doi:10.1038/nplants.2015.196
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Gupta OP, Meena NL, Sharma I, Sharma P (2014) Differential regulation of microRNAs in response to osmotic, salt and cold stresses in wheat. Mol Biol Rep 41:4623–4629. doi:10.1007/s11033-014-3333-0
Hackenberg M, Gustafson P, Langridge P, Shi B-J (2015) Differential expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in barley between water and drought conditions. Plant Biotech J 13:2–13. doi:10.1111/pbi.12220
Hubert DA, Tornero P, Belkhadir Y, Krishna P, Takahashi A, Shirasu K, Dangl JL (2003) Cytosolic HSP90 associates with and modulates the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance protein. EMBO J 22:5679–5689. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg547
Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, Dong G, Zeng D, Lu Z, Zhu X, Qian Q, Li J (2010) Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat Genet 42:541–544. doi:10.1038/ng.591
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:19–53. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218
Kantar M, Unver T, Budak H (2010) Regulation of barley miRNAs upon dehydration stress correlated with target gene expression. Funct Integr Genomics 10:493–507. doi:10.1007/s10142-010-0181-4
Kantar M, Lucas SJ, Budak H (2011) miRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta 233:471–484. doi:10.1007/s00425-010-1309-4
Kohli A, Sreenivasulu N, Lakshmanan P, Kumar PP (2013) The phytohormone crosstalk paradigm takes center stage in understanding how plants respond to abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 32:945–957. doi:10.1007/s00299-013-1461-y
Krasileva KV, Buffalo V, Bailey P, Pearce S, Ayling S, Tabbita F, Soria M, Wang S, Akhunov E, Uauy C, Dubcovsky J, Consortium I (2013) Separating homeologs by phasing in the tetraploid wheat transcriptome. Genome Biol. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-r66
Ku Y-S, Wong JW-H, Mui Z, Liu X, Hui JH-L, Chan T-F, Lam H-M (2015) Small RNAs in plant responses to abiotic stresses: regulatory roles and study methods. Int J Mol Sci 16:24532–24554. doi:10.3390/ijms161024532
Kumar RR, Pathak H, Sharma SK, Kala YK, Nirjal MK, Singh GP, Goswami S, Rai R (2014) Novel and conserved heat-responsive microRNAs in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 15:323–348. doi:10.1007/s10142-014-0421-0
Kurtoglu KY, Kantar M, Lucas SJ, Budak H (2013) Unique and conserved microRNAs in wheat chromosome 5D revealed by next-generation sequencing. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069801
Lavenus J, Goh T, Roberts I, Guyomarc’h S, Lucas M, De Smet I, Fukaki H, Beeckman T, Bennett M, Laplaze L (2013) Lateral root development in Arabidopsis: fifty shades of auxin. Trends Plant Sci 18:450–458. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2013.04.006
Liu N, Wu S, Van Houten J, Wang Y, Ding B, Fei Z, Clarke TH, Reed JW, Van Der Knaap E (2014) Down-regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS 6 and 8 by microRNA 167 leads to floral development defects and female sterility in tomato. J Exp Bot 65:2507–2520. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru141
Liu H, Able AJ, Able JA (2016) SMARTER de-stressed cereal breeding. Trends Plant Sci. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2016.07.006
Liu H, Searle IR, Mather DE, Able AJ, Able JA (2015a) Morphological, physiological and yield responses of durum wheat to pre-anthesis water deficit stress are genotype-dependent. Crop & Pasture Science 66:1024–1038. doi:10.1071/CP15013
Liu H, Searle IR, Watson-Haigh NS, Baumann U, Mather DE, Able AJ, Able JA (2015b) Genome-wide identification of microRNAs in leaves and the developing head of four durum genotypes during water deficit stress. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142799
Lu Y, Feng Z, Bian L, Xie H, Liang J (2011) miR398 regulation in rice of the responses to abiotic and biotic stresses depends on CSD1 and CSD2 expression. Funct Plant Biol 38:44–53. doi:10.1071/fp10178
Lu Y-Y, Deng X-P, Kwak S-S (2015) Over expression of CuZn superoxide dismutase (CuZn SOD) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) in transgenic sweet potato enhances tolerance and recovery from drought stress. Afr J Biotechnol 9:8378–8391
Ludwig-Müller J (2011) Auxin conjugates: their role for plant development and in the evolution of land plants. J Exp Bot 62:1757–1773. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq412
Ma X, Xin Z, Wang Z, Yang Q, Guo S, Guo X, Cao L, Lin T (2015) Identification and comparative analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in leaves of two wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes during dehydration stress. BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0413-9
Meng F, Liu H, Wang K, Liu L, Wang S, Zhao Y, Yin J, Li Y (2013) Development-associated microRNAs in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-13-140
Millar AH, Whelan J, Soole KL, Day DA (2011) Organization and regulation of mitochondrial respiration in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:79–104. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103857
Oh E, Kang H, Yamaguchi S, Park J, Lee D, Kamiya Y, Choi G (2009) Genome-wide analysis of genes targeted by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3-LIKE5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:403–419. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.064691
Pandey R, Joshi G, Bhardwaj AR, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S (2014) A comprehensive genome-wide study on tissue-specific and abiotic stress-specific miRNAs in Triticum aestivum. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095800
Pastore D, Trono D, Laus MN, Di Fonzo N, Flagella Z (2007) Possible plant mitochondria involvement in cell adaptation to drought stress a case study: durum wheat mitochondria. J Exp Bot 58:195–210
Peleg Z, Blumwald E (2011) Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:290–295. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2011.02.001
Procissi A, Guyon A, Pierson E, Giritch A, Knuiman B, Grandjean O, Tonelli C, Derksen J, Pelletier G, Bonhomme S (2003) KINKY POLLEN encodes a SABRE-like protein required for tip growth in Arabidopsis and conserved among eukaryotes. Plant J 36:894–904
Qu B, He X, Wang J, Zhao Y, Teng W, Shao A, Zhao X, Ma W, Wang J, Li B, Li Z, Tong Y (2015) A wheat CCAAT box-binding transcription factor increases the grain yield of wheat with less fertilizer input. Plant Physiol 167:411–423. doi:10.1104/pp.114.246959
Rubio-Somoza I, Weigel D (2013) Coordination of flower maturation by a regulatory circuit of three microRNAs. PLoS Genet. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003374
Santhanagopalan I, Basha E, Ballard KN, Bopp NE, Vierling E (2015) Model chaperones: small heat shock proteins from plants. In: Tanguay RM, Hightower LE (eds) The big book on small heat shock proteins, 1st edn. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp. 119–153
Sharma E, Sharma R, Borah P, Jain M, Khurana JP (2015) Emerging roles of auxin in abiotic stress responses. In: Pandey GK (ed) Elucidation of abiotic stress signaling in plants, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp. 299–328
Singh A, Singh S, Panigrahi KC, Reski R, Sarkar AK (2014) Balanced activity of microRNA166/165 and its target transcripts from the class III homeodomain-leucine zipper family regulates root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 33:945–953. doi:10.1007/s00299-014-1573-z
Su Y-H, Liu Y-B, Zhang X-S (2011) Auxin-cytokinin interaction regulates meristem development. Mol Plant 4:616–625. doi:10.1093/mp/ssr007
Sun G, Stewart CN Jr, Xiao P, Zhang B (2012) MicroRNA expression analysis in the cellulosic biofuel crop switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) under abiotic stress. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032017
Sun F, Guo G, Du J, Guo W, Peng H, Ni Z, Sun Q, Yao Y (2014) Whole-genome discovery of miRNAs and their targets in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-142
Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu J-K (2006) Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by downregulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 18:2051–2065. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.041673
Sunkar R, Viswanathan C, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2007) Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12:301–309. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.05.001
Sunkar R, Li YF, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 17:196–203. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2012.01.010
Tabata R, Ikezaki M, Fujibe T, Aida M, C-e T, Ueno Y, Yamamoto KT, Machida Y, Nakamura K, Ishiguro S (2010) Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR6 and 8 regulate jasmonic acid biosynthesis and floral organ development via repression of class 1 KNOX genes. Plant Cell Physiol 51:164–175. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcp176
Turchi L, Baima S, Morelli G, Ruberti I (2015) Interplay of HD-Zip II and III transcription factors in auxin-regulated plant development. J Exp Bot 66:5043–5053. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv174
Vazquez F, Legrand S, Windels D (2010) The biosynthetic pathways and biological scopes of plant small RNAs. Trends Plant Sci 15:337–345. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2010.04.001
Wang HLV, Chekanova JA (2016) Small RNAs: essential regulators of gene expression and defenses against environmental stresses in plants. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. doi:10.1002/wrna.1340
Wang W, Vinocur B, Shoseyov O, Altman A (2004) Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci 9:244–252. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.006
Wang J-W, Wang L-J, Mao Y-B, Cai W-J, Xue H-W, Chen X-Y (2005) Control of root cap formation by microRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2204–2216. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.033076
Wang M, Wang Q, Zhang B (2013) Response of miRNAs and their targets to salt and drought stresses in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Gene 530:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.009
Wang Y, Li K, Chen L, Zou Y, Liu H, Tian Y, Li D, Wang R, Zhao F, Ferguson BJ, Gresshoff PM, Li X (2015) microRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors, GmARF8a and GmARF8b, is required for soybean nodulation and lateral root development. Plant Physiol. doi:10.1104/pp.15.00265
Wu M-F, Tian Q, Reed JW (2006) Arabidopsis microRNA167 controls patterns of ARF6 and ARF8 expression, and regulates both female and male reproduction. Development 133:4211–4218. doi:10.1242/dev.02602
Xia K, Wang R, Ou X, Fang Z, Tian C, Duan J, Wang Y, Zhang M (2012) OsTIR1 and OsAFB2 downregulation via OsmiR393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030039
Xie F, Stewart CN, Taki FA, He Q, Liu H, Zhang B (2014) High-throughput deep sequencing shows that microRNAs play important roles in switchgrass responses to drought and salinity stress. Plant Biotech J 12:354–366. doi:10.1111/pbi.12142
Xie F, Jones DC, Wang Q, Sun R, Zhang B (2015a) Small RNA sequencing identifies miRNA roles in ovule and fibre development. Plant Biotech J 13:355–369. doi:10.1111/pbi.12296
Xie F, Wang Q, Sun R, Zhang B (2015b) Deep sequencing reveals important roles of microRNAs in response to drought and salinity stress in cotton. J Exp Bot 66:789–804. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru437
Xu Z, Dooner HK (2006) The maize aberrant pollen transmission 1 gene is a SABRE/KIP homolog required for pollen tube growth. Genetics 172:1251–1261. doi:10.1534/genetics.105.050237
Xu J, Xue C, Xue D, Zhao J, Gai J, Guo N, Xing H (2013) Overexpression of GmHsp90s, a heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) gene family cloning from soybean, decrease damage of abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069810
Xu MY, Zhang L, Li WW, Hu XL, Wang M-B, Fan YL, Zhang CY, Wang L (2014) Stress-induced early flowering is mediated by miR169 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 65:89–101. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert353
Yadav SR, Khanday I, Majhi BB, Veluthambi K, Vijayraghavan U (2011) Auxin-responsive OsMGH3, a common downstream target of OsMADS1 and OsMADS6, controls rice floret fertility. Plant Cell Physiol 52:2123–2135. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcr142
Yang C, Li D, Mao D, Liu X, Ji C, Li X, Zhao X, Cheng Z, Chen C, Zhu L (2013) Overexpression of microRNA319 impacts leaf morphogenesis and leads to enhanced cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ 36:2207–2218. doi:10.1111/pce.12130
Zhai L, Liu Z, Zou X, Jiang Y, Qiu F, Zheng Y, Zhang Z (2013) Genome-wide identification and analysis of microRNA responding to long-term waterlogging in crown roots of maize seedlings. Physiol Plant 147:181–193. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01653.x
Zhang B (2015) MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 66:1749–1761. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv013
Zhang B, Wang Q (2015) MicroRNA-based biotechnology for plant improvement. J Cell Physiol 230:1–15. doi:10.1002/jcp.24685
Zhang Y-C, Yu Y, Wang C-Y, Li Z-Y, Liu Q, Xu J, Liao J-Y, Wang X-J, Qu L-H, Chen F, Xin P, Yan C, Chu J, Li H-Q, Chen Y-Q (2013) Overexpression of microRNA OsmiR397 improves rice yield by increasing grain size and promoting panicle branching. Nat Biotechnol 31:848–852. doi:10.1038/nbt.2646
Zhang T, Poudel AN, Jewell JB, Kitaoka N, Staswick P, Matsuura H, Koo AJ (2015) Hormone crosstalk in wound stress response: wound-inducible amidohydrolases can simultaneously regulate jasmonate and auxin homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv521
Zhu C, Ding Y, Liu H (2011) MiR398 and plant stress responses. Physiol Plant 143:1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01477.x
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by the Grains Research and Development Corporation (GRDC). We thank Durum Breeding Australia’s southern breeding program, who supplied germplasm for this study. Haipei Liu is supported by a China Scholarship Council (CSC) scholarship and the University of Adelaide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of Functional and Integrative Genomics entitled ‘miRNA in model and complex organisms’ (Issue Editors: Hikmet Budak and Baohong Zhang)
Electronic supplementary material
Electronic supplementary materials Table S1
qPCR primers of 43 target genes used in this study. (XLSX 15 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S2
Forward qPCR primers of five stress-responsive durum miRNAs used in this study. (XLSX 9 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S3
5′ RLM-RACE adaptor and primers used in this study. (XLSX 10 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S4
Predicted target genes of 69 conserved water-deficit stress-responsive miRNAs and their GO annotations. (XLSX 182 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S5
Predicted targets of 44 conserved durum miRNAs (identified using MiRBase) and their GO analysis results. (XLSX 165 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S6
Predicted targets of four novel stress-responsive durum miRNAs identified using the new Triticum assembly and their GO analysis results. (XLSX 31 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S7
Combined Gene Ontology classification at different GO levels of the predicted targets of 69 conserved stress-responsive miRNAs for biological processes (a), molecular functions (b) and cell components (c). (XLSX 277 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S8
Combined Gene Ontology classification at different GO levels of predicted targets of four novel stress-responsive miRNAs for biological processes (a), molecular functions (b) and cell components (c). (XLSX 87 kb)
Electronic supplementary materials Table S9
Combined Gene Ontology classification at different GO levels of predicted targets of 44 conserved durum miRNAs for biological processes (a), molecular functions (b) and cell components (c). (XLSX 168 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Able, A.J. & Able, J.A. Water-deficit stress-responsive microRNAs and their targets in four durum wheat genotypes. Funct Integr Genomics 17, 237–251 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0515-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0515-y