Abstract
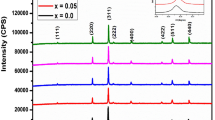
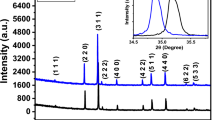
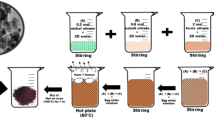
An investigation of the structural, morphological, magnetic, and optical properties of Ni0.6Mg0.2Co0.2FeCrO4 spinel ferrites prepared by the sol–gel method at different annealing temperatures conducted. The grain size and the unit cells parameters of the synthesized samples exhibit an increasing trend as the annealing temperature increases. A low coercive field was obtained from the hysteresis loops, making Ni0.6Mg0.2Co0.2FeCrO4 ferrites suitable candidates for soft magnetic devices. The bands associated with the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral [B] sites shift toward higher wavenumbers as the annealing temperature increases. In addition, the optical band gap energy decreases with annealing temperature due to the increase in grain size. From the absorbance and the Tauc method, the samples present direct optical transitions. Moreover, the determined Urbach energies are significantly low and decrease with annealing temperature. This implies that the degree of disorder and defects in the prepared samples decreases by increasing the annealing temperature. A detailed study has also been conducted on the variations versus wavelength of penetration depth, refractive index, extinction coefficient, dielectric constants, conductivity, and loss factor. From the variations of these optical parameters, some interesting optoelectronic applications were deduced for the prepared samples.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Upon a reasonable request, the data that support this study's findings are available from the corresponding author.
References
M.G. Naseri, M.K. Halimah, A. Dehzangi, A. Kamalianfar, E.B. Saion, and B.Y. Majlis, A comprehensive overview on the structure and comparison of magnetic properties of nanocrystalline synthesized by a thermal treatment method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 75, 315 (2014).
Y. Li, X. Wu, W. Wu, K. Wang, and S. Liao, Magnetic properties of Cu0.48Ni0.52Fe2O4 and thermal process of precursor. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 2153 (2013).
Y.D. Kolekar, L. Sanchez, E.J. Rubio, and C.V. Ramana, Grain and grain boundary effects on the frequency and temperature dependent dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite–hafnium composites. Solid State Commun. 184, 34 (2014).
R. Nongjai, S. Khan, K. Asokan, H. Ahmed, and I. Khan, Magnetic and electrical properties of In doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 084321 (2012).
Z. Gao, B. Xu, M. Ma, A. Feng, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, Z. Jia, and G. Wu, Electrostatic self-assembly synthesis of ZnFe2O4 quantum dots (ZnFe2O4@C) and electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos. B 179, 107417 (2019).
J. Wang, B. Wang, A. Feng, Z. Jia, and G. Wu, Design of morphology-controlled and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance of sheet-shaped ZnCo2O4 with a special arrangement. J. Alloys Compd. 834, 155092 (2020).
X. Zhou, C. Zhang, M. Zhang, A. Feng, S. Qu, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, Z. Jia, and G. Wu, Synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon foams composites with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. A 127, 105627 (2019).
E. Oumezzine, S. Hcini, M. Baazaoui, E.K. Hlil, and M. Oumezzine, Structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Zn0.6−xNixCu0.4Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles prepared by Pechini sol–gel method. Powder Technol. 278, 189 (2015).
W. Zhang, A. Sun, X. Zhao, X. Pan, Y. Han, N. Suo, L. Yu, and Z. Zuo, Structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrites prepared from sol–gel auto combustion method with different complexing agents. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 152501 (2020).
J. Pei, Z. Wang, Y. Gao, and H. Zhang, Structure and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0 5Mn0.5-xMoxFe1.5O4 ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19, 440 (2019).
N. Mechi, A. Mallah, S. Hcini, M.L. Bouazizi, M. Boudard, and A. Dhahri, Effects of sintering temperature on microstructural, magnetic, and impedance spectroscopic properties of Ni0.4Cd0.3Zn0.3Fe2O4 Ferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 1547 (2020).
F. Alresheedi, S. Hcini, M.L. Bouazizi, M. Boudard, and A. Dhahri, Synthesis and study of impendence spectroscopy properties of La0.6Ca0.2Na0.2MnO3 manganite perovskite prepared using sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 8248 (2020).
S.A.S. Ebrahimi and S.M. Masoudpanah, Effects of pH and citric acid content on the structure and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by a sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 357, 77 (2014).
N. Kouki, S. Hcini, M. Boudard, R. Aldawas, and A. Dhahri, Microstructural analysis, magnetic properties, magnetocaloric effect, and critical behaviors of Ni0.6Cd0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 ferrites prepared using the sol–gel method under different sintering temperatures. RSC Adv. 9, 1990 (2019).
S. Hcini, N. Kouki, A. Omri, A. Dhahri, and M.L. Bouazizi, Effect of sintering temperature on structural, magnetic, magnetocaloric and critical behaviors of Ni-Cd-Zn ferrites prepared using sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 464, 91 (2018).
M. Hashim, S. Alimuddin, S.E. Kumar, R.K. Shirsath, H.C. Kotnala, and R. Kumar, Structural properties and magnetic interactions in Ni0.5Mg0.5Fe2−xCrxO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) ferrite nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 229, 37 (2012).
M. Naeem, N.A. Shahb, I.H. Gul, and A. Maqsood, Structural, electrical and magnetic characterization of Ni–Mg spinel ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 487, 739 (2009).
H. Moradmard, S.F. Shayesteh, P. Tohidi, Z. Abbas, and M. Khaleghi, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of magnesium doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 650, 116 (2015).
L.J. Berchmans, R. KalaiSelvan, P.N.S. Kumar, and C.O. Augustin, Structural and electrical properties of Ni1−xMgxFe2O4 synthesized by citrate gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 279, 103 (2004).
M.A. Gabal, Y.M. Al Angari, and H.M. Zaki, Structural, magnetic and electrical characterization of Mg–Ni nano-crystalline ferrites prepared through egg-white precursor.J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 363, 6 (2014).
M.A. El Hiti, AC electrical conductivity of Ni-Mg ferrites. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 29, 501 (1996).
M. Hashim, S.S. Meena, R.K. Kotnala, S.E. Shirsath, A.S. Roy, A. Parveen, P. Bhatt, S. Kumar, R.B. Jotania, and R. Kumar, and Alimuddin, Study of structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Cr doped Ni–Mg ferrite nanoparticle. J. Alloys Compd. 602, 150 (2014).
A.K.M.A. Hossain, M.R. Amin, and H. Tanaka, Increase in initial permeability due to substitution of high spin cations in nanocrystalline Ni–Mg ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 334, 124 (2013).
M.A. El Hiti, Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity of Zn-substituted Ni-Mg ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 164, 187 (1996).
P. Chavan and L.R. Naik, Investigation of energy band gap and conduction mechanism of magnesium substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi A 214, 1700077 (2017).
A. Abu El-Fadl, A.M. Hassan, and M.A. Kassem, Structural and spectroscopic studies of nanocrystalline Ni1−xMgxFe2O4 ferrites synthesized by a microwave-assisted combustion route. Phys. Scr. 95, 055813 (2020).
Q. Li, B. Guo, J. Yu, J. Ran, B. Zhang, H. Yan, and J.R. Gong, Highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production of CdS-cluster-decorated graphene nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 10878 (2011).
D.D. La, C.V. Tran, N.T.T. Hoang, M.D.D. Ngoc, T.H.P. Nguyen, H.T. Vo, P.H. Ho, T.A. Nguyen, S.V. Bhosale, X.C. Nguyen, S.W. Chang, W.J. Chung, and D.D. Nguyen, Efficient photocatalysis of organic dyes under simulated sunlight irradiation by a novel magnetic CuFe2O4@porphyrin nanofiber hybrid material fabricated via self-assembly. Fuel 281, 118655 (2020).
C. Kumari, H.K. Dubey, F. Naaz, and P. Lahiri, Structural and optical properties of nanosized Co substituted Ni ferrites by coprecipitation method. Phase Transit. 93, 207 (2020).
A.A. El-Fadl, A.M. Hassan, and M.A. Kassem, Tunable cationic distribution and structure-related magnetic and optical properties by Cr3+ substitution for Zn2+ in nanocrystalline Ni-Zn ferrites. Results Phys. 28, 104622 (2021).
A.A. Ansari, M. Abushad, M. Arshad, S. Naseem, H. Ahmed, S. Husain, and W. Khan, Microstructure, optical and dielectric properties of cobalt-doped zinc ferrite nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 21988 (2021).
A. Iftikhar, M.U. Islam, M.S. Awan, M. Ahmad, S. Naseem, and M.A. Iqbal, Synthesis of super paramagnetic particles of Mn1−xMgxFe2O4 ferrites for hyperthermia applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 601, 116 (2014).
H.M. Rietveld, A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2, 65 (1969).
B. Antic, A. Kremenovic, A.S. Nikolic, and M. Stoiljkovic, Cation distribution and size-strain microstructure analysis in ultrafine Zn−Mn ferrites obtained from acetylacetonato complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 12646 (2004).
S. Torkian, A. Ghasemi, and R.S. Razavi, Cation distribution and magnetic analysis of wideband microwave absorptive CoxNi1−xFe2O4 ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 6987 (2017).
Q. Lin, Y. He, J. Lin, F. Yang, L. Wang, and J. Dong, Structural and magnetic studies of Mg substituted cobalt composite oxide catalyst Co1−xMgxFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, 89 (2019).
S.M. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Jadhav, and K.M. Jadhav, Cation distribution study of nanocrystalline NiFe2−xCrxO4 ferrite by XRD, magnetization and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi A 209, 347 (2012).
A.M. Gismelseed and A.A. Yousif, Mössbauer study of chromium-substituted nickel ferrites. Physica B 370, 215 (2005).
F. Hcini, S. Hcini, B. Alzahrani, S. Zemni, and M.L. Bouazizi, Effect of Cr substitution on structural, magnetic and impedance spectroscopic properties of Cd0.5Zn0.5Fe2−xCrxO4 ferrites. Appl. Phys. A. 126, 362 (2020).
K.A. Mohammed, A.D. Al-Rawas, A.M. Gismelseed, A. Sellai, H.M. Widatallah, A. Yousif, M.E. Elzain, and M. Shongwe, Infrared and structural studies of Mg1–xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. Physica B 407, 795 (2012).
R.P. Patil, P.P. Hankare, K.M. Garadkar, and R. Sasikala, Effect of sintering temperature on structural, magnetic properties of lithium chromium ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 523, 66 (2012).
M. Rahimi, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, and H. Salamati, The effect of sintering temperature on evolution of structural and magnetic properties of nanostructured Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 ferrite. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1865 (2013).
A. Gholizadeh and E. Jafari, Effects of sintering atmosphere and temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nano-particles: magnetic enhancement by a reducing atmosphere. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 328 (2017).
K.S. Lohar, S.M. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, and S.S. Jadhav, Structural and frequency dependence dielectric properties of magnesium doped nickel ferrite. International Conference on Nanoscience, Technology and Societal Implications (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/NSTSI.2011.6111774.
H. Shokrollahi and K. Janghorban, Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J. Mater. Process. Tech. 189, 1 (2007).
P.K. Chakrabarti, B.K. Nath, S. Brahma, S. Das, D. Das, M. Ammar, and F. Mazaleyrat, Magnetic and hyperfine properties of chemically synthesized nanocomposites of (Al2O3)x(Ni 0.2 Zn0.6Cu0.2Fe2O4)(1–x) (x=0.15,0 30,0.45). Solid State Commun. 144, 305 (2007).
S. Modak, M. Ammar, F. Mazaleyrat, S. Das, and P.K. Chakrabarti, XRD, HRTEM and magnetic properties of mixed spinel nanocrystalline Ni–Zn–Cu-ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 473, 15 (2009).
Ch. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, K.S. Babu, A.R. Reddy, and K.H. Rao, Effects of heat treatment conditions on the structural and magnetic properties of MgCuZn nano ferrite. Ceram. Int. 38, 5813 (2012).
V. Manikandan, A. Vanitha, E.R. Kumar, and S. Kavita, Influence of sintering temperature on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Li substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 11 (2017).
L. Néel, Magnetism and the local molecular field. Science 174, 985 (1971).
M. Satalkar and S.N. Kane, On the study of structural properties and Cation distribution of Zn0.75-xNixMg0.15Cu0.1Fe2O4 nano ferrite: effect of Ni addition. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 755, 012050 (2016).
G. Satyanarayana, G.N. Rao, K.V. Babu, G.V.S. Kumar, and G.D. and Reddy, Effect of Cr3+ substitution on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ni0.7Zn0.2Cu0.1Fe2−xCrxO4 ferrites. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 684 (2019).
Y. Han, A. Sun, X. Pan, W. Zhang, and X. Zhao, Effect of different sintering temperatures on structural and magnetic properties of Zn–Co ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32, 3823 (2019).
Y.B. Kannan, R. Saravanan, N. Srinivasan, and I. Ismail, Sintering effect on structural, magnetic and optical properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ferrite nano particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 217 (2017).
A.C.F.M. Costa, E. Tortella, M.R. Morelli, and R.H.G.A. Kiminami, Synthesis, microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256, 174 (2003).
M.S. Shah, K. Ali, I. Ali, A. Mahmood, S.M. Ramay, and M.T. Faridc, Structural and magnetic properties of praseodymium substituted barium-based spinel ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 77 (2018).
M.D. Rahaman, M.D. Mia, M.N.I. Khan, and A.K.M.A. Hossain, Study the effect of sintering temperature on structural, microstructural and electromagnetic properties of 10% Ca-doped Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 404, 238 (2016).
N. Kouki, S. Hcini, R. Aldowas, and M. Boudard, Structural, infrared, magnetic, and electrical properties of Ni0.6Cd0.2Cu0.2Fe2O4 ferrites synthesized using sol–gel method under different sintering temperatures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32, 2209 (2019).
M.P. Reddy, R.A. Shakoora, A.M.A. Mohamed, M. Gupta, and Q. Huang, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 42, 4221 (2016).
K. Souifi, O. Rejaiba, O. Amorri, M. Nasri, B. Alzahrani, M.L. Bouazizi, K. Khirouni, and J. Khelifi, Detailed investigation of structural, morphology, magnetic, electical and optical properties of the half-doped perovsikte Nd0.5Ba0.5FeO3. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 32, 4515 (2022).
G. Raddaoui, O. Rejaiba, M. Nasri, K. Khirouni, B. Alzahrani, M.L. Bouazizi, and J. Khelifi, Investigation studies of structural, electrical, dielectric, and optical of DyTi0.5Mn0.5O3 multiferroic for optoelectronics applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33, 21890 (2022).
J. Wang, C. Zhang, H. Liu, R. McLaughlin, Y. Zhai, S.R. Vardeny, X. Liu, S. McGill, D. Semenov, H. Guo, R. Tsuchikawa, V.V. Deshpande, D. Sun, and Z.V. Vardeny, Spin-optoelectronic devices based on hybrid organic-inorganic trihalide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 10, 129 (2019).
O. Rejaiba, K. Khirouni, M.H. Dhaou, B. Alzahrani, M.L. Bouazizi, and J. Khelifi, Investigation study of optical and dielectric parameters using absorption and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy method on La0.57Nd0.1Sr0.13Ag0.2MnO3 perovskite for optoelectronic application. Opt. Quantum Electron. 54, 315 (2022).
S.K. Gagandeep, B.S. Lark, and H.S. Sahota, Attenuation measurements in solutions of some carbohydrates. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 134, 208 (2000).
S.M.H. Qaid, B.A. Al-Asbahi, H.M. Ghaithan, M.S. AlSalhi, and A.S. Al dwayyan, Optical and structural properties of CsPbBr 3 perovskite quantum dots/PFO polymer composite thin films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 563, 426 (2020).
P. Thakur, R. Sharma, V. Sharma, and P. Sharma, Structural and optical properties of Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nano ferrites: effect of sintering temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 193, 285 (2017).
S. AbuBakar, N. Soltani, W.M.M. Yunus, E. Saion, and A. Bahrami, Structural and paramagnetic behavior of spinel NiCr2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by thermal treatment method: effect of calcination temperature. Solid State Commun. 192, 15 (2014).
A. Fujishima, X. Zhang, and D.A. Tryk, TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 63, 515 (2008).
J. Xie, H. Wang, M. Duan, and L. Zhang, Synthesis and photocatalysis properties of ZnO structures with different morphologies via hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 6358 (2011).
N.R. Dhineshbabu, V. Rajendran, N. Nithyavathy, and R. Vetumperumal, Study of structural and optical properties of cupric oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 933 (2016).
F. Hcini, S. Hcin, M.M. Almoneef, M.H. Dhaou, M.S. Alshammari, A. Mallah, S. Zemni, N. Lefi, and M.L. Bouazizi, Thermal, microstructural, optical, magnetic and magnetocaloric studies for Ni0.5Mn0.5Cr2O4 chromite spinel prepared using sol–gel method. J. Mol. Struct. 1243, 130769 (2021).
A.M. El Nahrawy, B.A. Hemdan, A.M. Mansour, A. Elzwawy, and A.B. AbouHammad, Structural and opto-magnetic properties of nickel magnesium copper zircon silicate nano-composite for suppress the spread of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. SILICON 14, 6645 (2022).
A.K.S. Ben Jazia KharratKahouliChaabouni, Detailed investigation of the optical properties of the (C8H11BrN)3BiCl6 compound by UV–visible measurements. Bull. Mater. Sci. 43, 275 (2020).
B.A. Hemdan, A.M. El Nahrawy, A.F.M. Mansour, and A.B. Abou Hammad, Green sol–gel synthesis of novel nanoporous copper aluminosilicate for the eradication of pathogenic microbes in drinking water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 9508 (2019).
F. Hcini, S. Hcini, M.A. Wederni, B. Alzahrani, H. Al Robei, K. Khirouni, S. Zemni, and M.L. Bouazizi, Structural, optical, and dielectric properties for Mg0.6Cu0.2Ni0.2Cr2O4 chromite spinel. Physica B. 624, 413439 (2022).
A.M. Mansour, B.A. Hemdan, A. Elzwawy, A.B. Abou Hammad, and A.M. El Nahrawy, Ecofriendly synthesis and characterization of Ni2+ codoped silica magnesium zirconium copper nanoceramics for wastewater treatment applications. Sci. Rep. 12, 9855 (2022).
S.H. Wemple and M. Didomenico, Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys. Rev. B. 3, 1338 (1971).
N. Tounsi, A. Barhoumi, F.C. Akkari, M. Kanzarin, H. Guermazi, and S. Guermazi, Structural and optical characterization of copper oxide composite thin films elaborated by GLAD technique. Vacuum 121, 9 (2015).
H. Yokokawa, N. Sakai, T. Kawada, and M. Dokiya, Thermodynamic stabilities of perovskite oxides for electrodes and other electrochemical materials. Solid State Ion. 52, 43 (1992).
R. Mguedla and A.Ben Jazia Kharrat, N. Moutia, K. Khirouni, N. Chniba-Boudjadaa, W. Boujelben, Gd doping effect on structural, electrical and dielectric properties in HoCrO3 orthochromites for electric applications. J. Alloys Compd. 836, 155186 (2020).
E.A. Davis and N.F. Mott, Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. A. 22, 903 (1970).
Z. Raddaoui, B. Smiri, A. Maaoui, J. Dhahri, and R. M’ghaieth, N. Abdelmoulad, K. Khirouni, Correlation of crystal structure and optical properties of Ba0.97Nd0.0267Ti(1–x)WxO3 perovskite. RSC Adv. 8, 27870 (2018).
Y. Feng, S. Lin, S. Huang, S. Shrestha, and G. Conibeer, Can Tauc plot extrapolation be used for direct-band gap semiconductor nanocrystals? J. Appl. Phys. 117, 125701 (2015).
S.A. Moyez and S. Roy, Thermal engineering of lead-free nanostructured CH3NH3SnCl3 perovskite material for thin-film solar cell. J. Nanoparticle Res. 20, 5 (2017).
A. Bougrine, A. El Hichou, M. Addou, J. Ebothé, A. Kachouane, and M. Troyon, Structural, optical and cathodoluminescence characteristics of undoped and tin-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 438 (2003).
A.M. Mansour, M. Nasr, H.A. Saleh, and G.M. Mahmoud, Physical characterization of 5′,5″-dibromo-o-cresolsulfophthalein (BCP) spin-coated thin films and BCP/p-Si based diode. Appl. Phys. A. 125, 625 (2019).
S. Husain, A.O.A. Keelani, and W. Khan, Influence of Mn substitution on morphological, thermal and optical properties of nanocrystalline GdFeO3 orthoferrite. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects. 15, 17 (2018).
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number (IF2/PSAU/2022/01/22494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, analysis, design, and writing. The final manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests that are relevant to the content of this article to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bouazizi, M.L., Hcini, S., Khirouni, K. et al. Annealing Temperature Effects on Structural, Magnetic, and Optoelectronic Properties of Mixed Ni0.6Mg0.2Co0.2FeCrO4 Ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2878–2893 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10254-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10254-8