Abstract
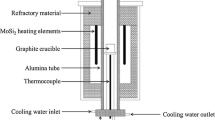
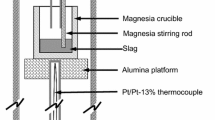
The oxygen transfer mechanism in gas–slag–metal systems is important for controlling the oxygen content of liquid alloy, which is a concern in the production of advanced clean alloy. Here, we report a new method of in situ measurement of the oxygen content of slag and alloy at different atmospheric oxygen contents. This technique is based on the electrochemical method and aims to clarify the behavior of oxygen transport in metallurgical processes. The concentration gradients of Fe3+ at 1773 K were investigated in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-Fe2O3 slag, and the oxygen contents of molten slag and liquid alloy were determined using the Nernst equation at 1823 K and various oxygen contents. A kinetic model of the mass transfer among the gas–slag interface, slag, and slag–metal interface was established on the basis of permeation theory. The results indicated a small difference between the final oxygen contents of slag and liquid alloy at different atmospheric oxygen contents. Therefore, the atmospheric oxygen content does not significantly affect the equilibrium oxygen content of the alloy when the metallurgical process is not fully protected by Ar gas. Fe3+ is mainly enriched at the gas–slag interface while Fe2+ is enriched at the slag–metal interface, which is mainly due to a stepwise reduction in Fe3+. The interfacial oxygen transfer rate, final oxygen content, and oxygen diffusion coefficient increase with increasing the atmospheric oxygen content. When the atmospheric oxygen content rises from 1 to 21 vol pct, the diffusion coefficient at the gas–slag interface increases from 1.09 × 10−8 to 1.76 × 10−8 cm2/s, and the diffusion coefficient at the slag–metal interface increases from 9.36 × 10−9 to 1.04 × 10−8 cm2/s.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Weber, A. Jardy, B. Dussoubs, D. Ablitzer, S. Ryberon, V. Schmitt, S. Hans, and H. Poisson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 271–80.
Y.W. Dong, Z.H. Jiang, Y.L. Cao, A. Yu, and D. Hou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 1315–24.
Q. Wang, R. Wang, Z. He, G. Li, B. Li, and H. Li: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2018, vol. 125, pp. 1333–44.
Z.H. Jiang, Y.W. Dong, X. Geng, and F.B. Liu: Electroslag metallurgy, Science Press, Beijing, 2015.
C. Shi: ISIJ Int., 2020, vol. 60, pp. 1083–96.
S.-C. Duan, X. Shi, F. Wang, M.-C. Zhang, Y. Sun, H.-J. Guo, and J. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2019, vol. 50, pp. 3055–71.
L.Z. Chang, X.F. Shi, and J.Q. Cong: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2014, vol. 41, pp. 182–86.
C.X. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Fu, and E.P. Chen: Acta Metall. Sin., 1981, vol. 17, pp. 50–57.
Z.B. Li: Electroslag Metallurgy Theory and Practice, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2010.
A. Mitchell, F. Reyes-carmona, and E. Samuelsson: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1984, vol. 24, pp. 547–56.
M. Sasabe and K.S. Goto: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 2225–33.
A.J. Deng, D.D. Fan, H.C. Wang, and C.H. Li: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2020, vol. 27, pp. 409–19.
W.F. Caley, B.R. Marple, and C.R. Masson: Can. Metall. Q., 1981, vol. 20, pp. 215–23.
X. Huang, B. Li, and Z. Liu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol. 49, pp. 709–22.
X. Huang, B. Li, and Z. Liu: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2018, vol. 120, pp. 458–70.
Q. Wang, G. Li, Y. Gao, Z. He, and B. Li: J. Appl. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 47, pp. 445–56.
S.J. Li, G.G. Cheng, Z.Q. Miao, L. Chen, C.W. Li, and X.Y. Jiang: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 57, pp. 2148–56.
Q. Wang, F. Wang, G. Li, Y. Gao, and B. Li: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer., 2017, vol. 113, pp. 1021–30.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, and J. Bohacek: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51, pp. 871–79.
H. Keller, K. Schwerdtfeger, H. Petri, R. Hlzle, and K. Hennesen: Metall. Trans. B., 1982, vol. 13, pp. 237–40.
Y. Shiraishi, H. Nagahama, and H. Ohta: Can. Metall. Q., 1983, vol. 22, pp. 37–43.
J. Wei and Z. Liu: Acta Metall. Sin., 1994, vol. 30, pp. 350–60.
J.H. Wei and A. Mitchell: Acta Metall. Sin., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 387–405.
J.H. Wei and A. Mitchell: Acta Metall. Sin., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 406–13.
S.S. Li, W.M. Li, D.J. Li, Y.L. Sun, J.W. Dong, X.T. Yin and X.M. Zang: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2021, online https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00608-z
W. Kim and I. Sohn: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 63–70.
D.J. Shin and D.J. Min: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 434–40.
K.M. Gg, A. Hasham, and U.B. Pal: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 408–13.
G.K. Murthy, A. Hasham, and U. Pal: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1993, vol. 20, pp. 191–200.
G.K. Murthy, Y. Sawada, and J. Elliott: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1993, vol. 20, pp. 179–90.
M. Barati and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2006, vol. 37, pp. 41–49.
S. Hara, H. Hashimoto, and K. Ogino: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1983, vol. 23, pp. 1053–58.
J.-H. Liu, G.-H. Zhang, Y.-D. Wu, and K.-C. Chou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2016, vol. 47, pp. 798–803.
T. Liu, X. Wang, X. Zhang, X. Gao, L. Li, J. Yu, and X. Yin: Sens. Actuat. B., 2018, vol. 277, pp. 216–23.
K.E. Oberg, L.M. Friedman, W.M. Boorstein, and R.A. Rapp: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 61–67.
S. Duan, X. Shi, M. Mao, W. Yang, S. Han, H. Guo, and J. Guo: Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, p. 5232.
D. Hou, Z.H. Jiang, Y.W. Dong, W. Gong, Y.L. Cao, and H.B. Cao: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1410–19.
C.B. Shi, X.C. Chen, H.J. Guo, Z.J. Zhu, and H. Ren: Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 83, pp. 472–86.
T. Zhang and Z. Dou: Research Methods for Macrokinetics, 1st ed. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2014.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully express their appreciation to National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51974153 and U1960203), the Joint Fund of State Key Laboratory of Marine Engineering and University of Science and Technology Liaoning (SKLMEA-USTLN-201901, SKLMEA-USTL-201707), and the 2020 Graduate Science and Technology Innovation Program of University of Science and Technology Liaoning.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Li, W., Sun, Y. et al. Oxygen Transfer Mechanism of ESR-Slag at Different Atmospheric Oxygen Contents. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 1112–1121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02431-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02431-7