Abstract
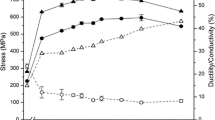
Components were fabricated via selective laser melting (SLM) of prealloyed Cu-4.3 pct Sn powder and heat treated at 873 K and 1173 K (600 °C and 900 °C) for 1 hour. Tensile testing, conductivity measurement, and detailed microstructural characterization were carried out on samples in the as-printed and heat-treated conditions. Optimization of build parameters resulted in samples with around 97 pct density with a yield strength of 274 MPa, an electrical conductivity of 24.1 pct IACS, and an elongation of 5.6 pct. Heat treatment resulted in lower yield strength with significant increases in ductility due to recrystallization and a decrease in dislocation density. Tensile sample geometry and surface finish also showed a significant effect on measured yield strength but a negligible change in measured ductility. Microstructural characterization indicated that grains primarily grow epitaxially with a submicron cellular solidification substructure. Nanometer scale tin dioxide particles identified via X-ray diffraction were found throughout the structure in the tin-rich intercellular regions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Gibson, D. Rosen, and B. Stucker: Additive Manufacturing Technologies,1st ed., Springer, New York, NY, 2010, p. 459.
J.P. Kruth et al.: Rap. Prototyp. J., 2005, vol. 11 (1), pp. 26–36.
D. Ramirez et al.: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59 (10), pp. 4088–99.
M. Lodes, R. Guschlbauer, and C. Körner: Mater. Lett., 2015, vol. 143, pp. 298–301.
N. Tolochko et al.: Rap. Prototyp. J., 2000, vol. 6 (3), pp. 155–61.
S. Pogson et al.: Rap. Prototyp. J., 2003, vol. 9 (5), pp. 334–43.
D. Gu et al.: Int. Mater. Rev., 2012, vol. 57 (3), pp. 133–64
B. Song et al.: Front. Mech. Eng., 2015, vol. 10 (2), pp. 111–25.
L. Loh et al.: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2015, vol. 80, pp. 288–300.
L. Thijs et al.: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58 (9), pp. 3303–12.
E. Yasa and J.P. Kruth: Proc. Eng., 2011, vol. 19, pp. 389–95.
W. Shifeng et al.: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, vol. 214 (11), pp. 2660–67.
B. Vrancken et al.: J. Alloys Compds., 2012, vol. 541, pp. 177–85.
A.A. Antonysamy et al.: Mater. Charact., 2013, vol. 84, pp. 153–68.
J. Donoghue et al.: Mater. Charact., 2016, vol. 114, pp. 103–14.
L. Thijs et al.: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61 (5), pp. 1809–19.
T. Niendorf et al.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 794–96.
J. Davis: ASM Specialty Handbook: Copper and Copper Alloys, 1st ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2001, pp. 3–5 and 32–50.
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy, 1st ed., John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2003, p. 478.
T. Kals and R. Eckstein: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, vol. 103 (1), pp. 95–101.
C.H. Suh, Y.C. Jung, and Y.S. Kim: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 24 (10), pp. 2091–98.
B. Vrancken et al.: Solid Freeform Fabrication Symp. Proc., 2013, pp. 393–407.
P. Mercelis and J.P. Kruth: Rap. Prototyp. J., 2006, vol. 12 (5), pp. 254–65.
H. McQueen and W.J M. G Tegart: Sci. Am., 1975, vol. 232 (4), pp. 116–25.
H. Ellingham: J. Soc. Chem. Ind., 1944, vol. 63 (5), pp. 125–60.
D. Porterling and K. Easterling: Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 3rd ed., Boca Raton, FL, 2009, pp. 100–04.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank TE Connectivity, Ltd. for the partial funding of this research along with collaboration throughout the study. The authors also thank the Loewy Family Foundation for financially supporting this project and two of the authors (APV, as a Loewy Graduate Fellow, and WZM, through the Loewy Professorship at Lehigh University).
This material is based on research sponsored by the Air Force Research Laboratory under Agreement No. FA8650-12-2-7230 and by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, acting through the Department of Community and Economic Development, under Contract No. C000053981. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for governmental purposes notwithstanding any copyright notation thereon. Any opinions, views, findings, recommendations, and conclusions contained herein are those of the author(s) and should not be interpreted as necessarily representing the official policies or endorsements, either expressed or implied, of the Air Force Research Laboratory, the U.S. Government, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, Carnegie Mellon University, or Lehigh University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 23, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ventura, A.P., Wade, C.A., Pawlikowski, G. et al. Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characterization of Cu-4.3 Pct Sn Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 178–187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3779-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3779-x