Abstract
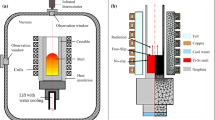
Solar grade silicon (SOG-Si) and hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with low silicon (silicon composition below 25 pct) can be successfully obtained by separation of hypereutectic Al-Si alloy with high silicon (silicon composition above 30 pct) under an alternating electromagnetic field after post-processing. To explore the separation mechanism in detail, experiments were conducted in this study using a high-frequency induction furnace with different pulling conditions of the crucible which is loaded with Al-45 wt pct Si melt. Results demonstrate that the separation of hypereutectic Al-Si alloy is feasible through either a pull-up or drop-down process. The height of each separation interface between the compact and sparse parts of the primary silicon decrease as the pull-up distance rose. When the pulling rate is very low, resultant morphologies of compact primary silicon are rounded and polygonal, allowing for more effective separation of the primary silicon. A novel physical model is presented here based on the experimental results and simulation. The model can be used to effectively describe the separation mechanism of primary silicon from hypereutectic Al-Si melts under alternating electromagnetic fields.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yoshikawa and K. Morita: J. Cryst. Growth, 2009, vol. 311, pp. 776-779.
K. Arafune, E. Ohishi, H. Sai, Y. Ohshita, and M. Yamaguchi: J. Cryst. Growth, 2007, vol. 308, pp. 5-9.
S. Zheng, W. Chen, J. Cai, J. Li, C. Chen, and X. Luo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 1268-1273.
J. Wu, Y. Dai, W Ma, B. Yang, D. Liu, Y. Wang, and K. Wei: Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 1, pp. 43–49.
X. Gu, X. Yu, and D. Yang: Sep. Purif. Technol., 2011, vol. 77, pp. 33-39.
K. Morita and T. Yoshikawa: T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2011, vol. 21, pp. 685-690.
Y. Nishi, Y. Kang, and K. Morita: Mater. Trans., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 1227-1230.
T. Yoshikawa and K. Morita: ISIJ. Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 967-971.
J. Li, Z. Guo, H. Tang, Z. Wang, and S. Sun: T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 958-963.
J. Jie, Q. Zou, H. Wang, J. Sun, Y. Lu, T. Wang, and T. Li: J. Cryst. Growth, 2014, vol. 399, pp. 43-48.
J. Jie, Q. Zou, J. Sun, Y. Lu, T. Wang, and T. Li: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 72, pp. 57-66.
S. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Tian, Y. Li and H. Ling: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 1915-1935.
A. Noeppel, A. Ciobanas, X. Wang, K. Zaidat, N. Mangelinck, O. Budenkova, A. Weiss, G. Zi mmermann, and Y. Fautrelle: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 193-208.
S. Eckert, P.A Nikrityuk, B. Willers, D. Räbiger, N. Shevchenko, H. Neumann-Heyme, V. Travnikov, S. Odenbach, A. Voigt, and K. Eckert: Eur. Phys. J.Spec. Top., 2013, vol. 220, pp. 123-137.
C. Xu and Q. Jiang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 437, pp. 451-455.
W. Wang, X. Bian, J. Qin, and S. Syliusarenko: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31, pp. 2163-2168.
X. Bian and W. Wang: Mater. Lett., 2000, vol. 44, pp. 54-58.
Y. Zhang, H. Zheng, Y. Liu, L. Shi, R. Xu, and X. Tian: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 70, pp. 162-173.
W. Yu, G. LÜ, Y. REN, H. Xue and Y. Dai: Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc., 2013, vol. 23, pp. 3476-3481.
B. Korojy and H. Fredriksson: T. Indian Inst. Metals, 2009, vol. 62, pp. 361-365.
M. W. Ullah and T. Carlberg: J. Cryst. Growth, 2011, vol. 318, pp. 212-218.
P. Kaur, D.K. Dwivedi, and P.M. Pathak: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech., 2012, vol. 63, pp. 415-420.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSFC project (No. 51466005 and U1137601), the Key project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (2013Z122), the talent training Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology (KKZ3201352011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 26, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, H., Lv, G., Ma, W. et al. Separation Mechanism of Primary Silicon from Hypereutectic Al-Si Melts Under Alternating Electromagnetic Fields. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 2922–2932 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2889-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2889-1