Abstract
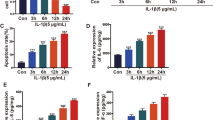
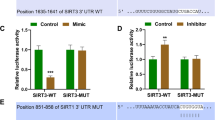
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are found to play a key role in neural cell differentiation, peripheral nerve injury, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, no study has yet been conducted highlighting their role in RA-induced peripheral neuropathy. Here, we investigated the role of miRNAs in RA-induced peripheral neuropathy. Levels of six miRNAs were detected in serum collected from 15 patients with RA and peripheral neuropathy and 16 patients with RA. In vitro, Schwann cells were treated with 0.1 ng/mL IL-6 and 20 ng/mL TNF-α. The expression level of miR-9-5p and its association with the repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) were investigated. The roles of miR-9-5p and REST in Schwann cell injury were examined after transfection of miR-9-5p mimics or REST siRNA. In patients with RA and peripheral neuropathy, serum miR-9-5p was significantly downregulated when compared with RA. In IL-6- and TNF-α-stimulated Schwann cells, apoptosis was induced, while the cell viability and level of miR-9-5p were inhibited. A significantly negative correlation was observed between miR-9-5p and REST. Transfection of miR-9-5p mimics and REST siRNA significantly reversed the inhibition of cell viability and induction of apoptosis caused by IL-6 and TNF-α. In addition, overexpression of miR-9-5p upregulated the expression of miR-132, miRNA targeting E1A binding protein EP300 (EEP300), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and forkhead box O3 (FOXO3). These results showed that Schwann cells were protected by miR-9-5p from inflammatory damage by targeting REST/miR-132 pathway, which could provide new targets for treatment of RA-induced peripheral neuropathy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal D, Singla S (2017) Prevalence of autonomic neuropathy in patients of rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with disease severity. J Clin Diagn Res 11:Oc09–oc13
Arruda JL, Sweitzer S, Rutkowski MD, DeLeo JA (2000) Intrathecal anti-IL-6 antibody and IgG attenuates peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia in the rat: possible immune modulation in neuropathic pain. Brain Res 879:216–225
Biswas M, Chatterjee A, Ghosh SK, Dasgupta S, Ghosh K, Ganguly PK (2011) Prevalence, types, clinical associations, and determinants of peripheral neuropathy in rheumatoid patients. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 14:194–197
Bitel CL, Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Frederikse PH (2010) HuB/C/D, nPTB, REST4, and miR-124 regulators of neuronal cell identity are also utilized in the lens. Mol Vis 16:2301–2316
Bruchfeld A, Goldstein RS, Chavan S, Patel NB, Rosas-Ballina M, Kohn N, Qureshi AR, Tracey KJ (2010) Whole blood cytokine attenuation by cholinergic agonists ex vivo and relationship to vagus nerve activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Intern Med 268:94–101
Chang LW, Viader A, Varghese N, Payton JE, Milbrandt J, Nagarajan R (2013) An integrated approach to characterize transcription factor and microRNA regulatory networks involved in Schwann cell response to peripheral nerve injury. BMC Genomics 14:84
Chen JQ, Papp G, Szodoray P, Zeher M (2016) The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 15:1171–1180
Chen XM, Huang QC, Yang SL, Chu YL, Yan YH, Han L, Huang Y, Huang RY (2015) Role of micro RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: novel perspectives based on review of the literature. Medicine 94:e1326
Dalakas MC (2015) Pathogenesis of immune-mediated neuropathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:658–666
de la Rica L, Garcia-Gomez A, Comet NR, Rodriguez-Ubreva J, Ciudad L, Vento-Tormo R, Company C, Alvarez-Errico D, Garcia M, Gomez-Vaquero C et al (2015) NF-kappaB-direct activation of microRNAs with repressive effects on monocyte-specific genes is critical for osteoclast differentiation. Genome Biol 16:2
DeQuattro K, Imboden JB (2017) Neurologic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 43:561–571
Du T, Zamore PD (2005) microPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development 132:4645–4652
Dugas JC, Notterpek L (2011) MicroRNAs in oligodendrocyte and Schwann cell differentiation. Dev Neurosci 33:14–20
Hwang JY, Kaneko N, Noh KM, Pontarelli F, Zukin RS (2014) The gene silencing transcription factor REST represses miR-132 expression in hippocampal neurons destined to die. J Mol Biol 426:3454–3466
Jamar F, Versari A, Galli F, Lecouvet F, Signore A (2018) Molecular imaging of inflammatory arthritis and related disorders. Semin Nucl Med 48:277–290
Jin XG, He SQ, Yan XT, Zhang G, Wan L, Wang J, Li Y, Tian X, Tian Y, Luo A (2009) Variants of neural nitric oxide synthase in the spinal cord of neuropathic rats and their effects on nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity in PC12 cells. J Pain 10:80–89
Kitagawa M, Sang HL, Mccormick F (2008) Skp2 suppresses p53-dependent apoptosis by inhibiting p300. Mol Cell 29:217–231
Koopman FA, Stoof SP, Straub RH, Van Maanen MA, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP (2011) Restoring the balance of the autonomic nervous system as an innovative approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med 17:937–948
Koopman FA, van Maanen MA, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP (2017) Balancing the autonomic nervous system to reduce inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Intern Med 282:64–75
Lagos D, Pollara G, Henderson S, Gratrix F, Fabani M, Milne RS, Gotch F, Boshoff C (2010) miR-132 regulates antiviral innate immunity through suppression of the p300 transcriptional co-activator. Nat Cell Biol 12:513–519
Lee J, Saloman JL, Weiland G, Auh QS, Chung MK, Ro JY (2012) Functional interactions between NMDA receptors and TRPV1 in trigeminal sensory neurons mediate mechanical hyperalgesia in the rat masseter muscle. Pain 153:1514–1524
Lubrano E, Mesina F, Caporali R (2018) Clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:900–910
Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, Xu T, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang L, Lv XW, Jin Y, Li J (2013) New advances of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, with a focus on the crosstalk between DNA methylation and the microRNA machinery. Cell Signal 25:1118–1125
Nadkar MY, Agarwal R, Samant RS, Chhugani SJ, Idgunji SS, Iyer S, Borges NE (2001) Neuropathy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Assoc Physicians India 49:217–220
Peng L, Ma W, Yi F, Yang YJ, Lin W, Chen H, Zhang X, Zhang LH, Zhang F, Du Q (2014) MicroRNA profiling in Chinese patients with primary Sjogren syndrome reveals elevated miRNA-181a in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Rheumatol 41:2208–2213
Qin W, Zhao W, Ho L, Wang J, Walsh K, Gandy S, Pasinetti GM (2010) Regulation of forkhead transcription factor FoxO3a contributes to calorie restriction-induced prevention of Alzheimer’s disease-type amyloid neuropathology and spatial memory deterioration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:335–347
Rachana KS, Manu MS, Advirao GM (2018) Insulin-induced upregulation of lipoprotein lipase in Schwann cells during diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Syndr 12:525–530
Ramer MS, Ma W, Murphy PG, Richardson PM, Bisby MA (1998) Galanin expression in neuropathic pain: friend or foe? Ann N Y Acad Sci 863:390–401
Ramos-Remus C, Duran-Barragan S, Castillo-Ortiz JD (2012) Beyond the joints: neurological involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 31:1–12
Sharma AR, Sharma G, Lee SS, Chakraborty C (2016) miRNA-regulated key components of cytokine signaling pathways and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Med Res Rev 36:425–439
Sim MK, Kim DY, Yoon J, Park DH, Kim YG (2014) Assessment of peripheral neuropathy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who complain of neurologic symptoms. Ann Rehabil Med 38:249–255
Tanaka Y, Ohira T (2018) Mechanisms and therapeutic targets for bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis, in particular the RANK-RANKL system. Curr Opin Pharmacol 40:110–119
Vicente R, Noel D, Pers YM, Apparailly F, Jorgensen C (2016) Deregulation and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in arthritic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:211–220
Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhu B, Duan T, Q X, Wang R, L L, Jiao Z (2015) Plasma microRNA expression profiles in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget 6:42557–42568
Wong HK, Veremeyko T, Patel N, Lemere CA, Walsh DM, Esau C, Vanderburg C, Krichevsky AM (2013) De-repression of FOXO3a death axis by microRNA-132 and -212 causes neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22:3077–3092
Wu D, Raafat A, Pak E, Clemens S, Murashov AK (2012) Dicer-microRNA pathway is critical for peripheral nerve regeneration and functional recovery in vivo and regenerative axonogenesis in vitro. Exp Neurol 233:555–565
Zeng Y, Liu JX, Yan ZP, Yao XH, Liu XH (2015) Potential microRNA biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Int J Mol Med 36:1639–1647
Zhu L, Hao J, Cheng M, Zhang C, Huo C, Liu Y, Du W, Zhang X (2018) Hyperglycemia-induced Bcl-2/Bax-mediated apoptosis of Schwann cells via mTORC1/S6K1 inhibition in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp Cell Res 367:186–195
Zhu Y, Hoell P, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J (2006) PTEN: a crucial mediator of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Apoptosis 11:197–207
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Linyi Medical Science Development Plan (201515002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ. L. and XF. L. designed the study. ZZ. L., YS. L., and QH. L. performed experiments and collected data. ZZ. L., ZC. Z., and L. J. analyzed and interpreted the data. ZZ. L. and XF. L. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All protocols were approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Li, Y., Li, Q. et al. Role of miR-9-5p in preventing peripheral neuropathy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by targeting REST/miR-132 pathway. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 55, 52–61 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0310-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0310-2