Abstract
Objective
Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4) facilitates the development of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1)-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in various cancer cells. Moreover, EMT of renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs) is required for the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis. However, the role of USP4 in EMT of RTECs remains unknown. The present study aimed to explore the effect of USP4 on the EMT of RTECs as well as the involved mechanism.
Methods
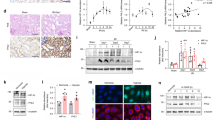
In established unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) rats and NRK-52E cells, immunohistochemistry and Western blot assays were performed.
Results
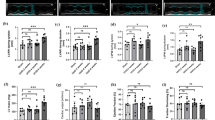
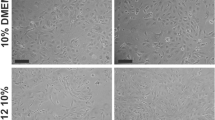
USP4 expression was increased significantly with obstruction time. In NRK-52E cells stimulated by TGF-β1, USP4 expression was increased in a time-dependent manner. In addition, USP4 silencing with specific siRNA indicated that USP4 protein was suppressed effectively. Meanwhile, USP4 siRNA treatment restored E-cadherin and weakened alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression, indicating that USP4 may promote EMT. After treatment with USP4 siRNA and TGF-β1 for 24 h, the expression of TGF-β1 receptor type I (TβRI) was decreased.
Conclusion
USP4 promotes the EMT of RTECs through upregulating TβRI, thereby facilitating renal interstitial fibrosis. These findings may provide a potential target of USP4 in the treatment of renal fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panizo S, Martínez-Arias L, Alonso-Montes C, et al. Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Consequences. Int J Mol Sci, 2021,22(1):408
Liu BC, Tang TT, Lv LL. How Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury Contributes to Renal Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019,1165:233–252
Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol, 2018,80:309–326
Sheng LL, Zhuang SG. New Insights Into the Role and Mechanism of Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Kidney Fibrosis. Front Physiol, 2020,11:569322
Yuan Q, Tan RJ, Liu Y. Myofibroblast in Kidney Fibrosis: Origin, Activation, and Regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019,1165:253–283
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rayego-Mateos S, Lamas S, et al. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2020;16(5):269–288
Faktor J, Pjechová M, Hernychová L, et al. Protein Ubiquitination Research in Oncology. Klin Onkol, 2019,32:56–64
Song L, Luo ZQ. Post-translational regulation of ubiquitin signaling. J Cell Biol, 2019,218(6):1776–1786
Li O, Ma Q, Li F, et al. Progress of small ubiquitin-related modifiers in kidney diseases. Chin Med J (Engl), 2019,132(4):466–473
Meyer-Schwesinger C. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in kidney physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2019,15(7):393–411
Young MJ, Hsu KC, Lin TE, et al. The role of ubiquitin-specific peptidases in cancer progression. J Biomed Sci, 2019,26(1):42
Lai KP, Chen J, Tse WKF. Role of Deubiquitinases in Human Cancers: Potential Targeted Therapy. Int J Mol Sci, 2020,21(7):2548
Hu B, Zhang D, Zhao K, et al. Spotlight on USP4: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021,9:595159
Wang Y, Zhou L, Lu J, et al. USP4 function and multifaceted roles in cancer: a possible and potential therapeutic target. Cancer Cell Int, 2020,20:298
Martínez-Klimova E, Aparicio-Trejo OE, Tapia E, et al. Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction as a Model to Investigate Fibrosis-Attenuating Treatments. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(4):141
Lovisa S, Zeisberg M, Kalluri R. Partial Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Other New Mechanisms of Kidney Fibrosis. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016,27(10):681–695
Pu JY, Zhang Y, Zhou JH. Effect of Huai Qi Huang on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells through miR-200a. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2016,2016:8612190
Liu BC, Tang TT, Lv LL, et al. Renal tubule injury: a driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int, 2018,93(3):568–579
Zhang L, Chen Q, Chen Z, et al. Mechanisms Regulating Muscle Protein Synthesis in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020,31(11):2573–2587
Gai Z, Zhou G, Gui T, et al. Trps1 haploinsufficiency promotes renal fibrosis by increasing Arkadia expression. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010,21(9):1468–1476
Chen L, Yang T, Lu DW, et al. Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018,101:670–681
Cui TG, Ichikawa T, Yang M, et al. An emerging role of deubiquitinating enzyme cylindromatosis (CYLD) in the tubulointerstitial inflammation of IgA nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009,390(2):307–312
Huang K, Zhao X. USP9X prevents AGEs-induced upregulation of FN and TGF-β1 through activating Nrf2-ARE pathway in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Cell Res, 2020,393(2):112100
Soji K, Doi S, Nakashima A, et al. Deubiquitinase inhibitor PR-619 reduces Smad4 expression and suppresses renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction. PloS One, 2018,13(8):e0202409
He B, Zhao YC, Gao LC, et al. Ubiquitin-Specific protease 4 is an endogenous negative regulator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension, 2016, 67(6):1237–1248
Xu J, Chen D, Jin L, et al. Ubiquitously specific protease 4 inhibitor-Vialinin A attenuates inflammation and fibrosis in S100-induced hepatitis mice through Rheb/mTOR signalling. J Cell Mol Med, 2021,25(2):1140–1150
Zhang J, Na S, Pan S, et al. Inhibition of USP4 attenuates pathological scarring by downregulation of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep, 2019,20(2):1429–1435
Li F, Hu Q, He T, et al. The Deubiquitinase USP4 stabilizes Twist1 protein to promote lung cancer cell stemness. Cancers (Basel), 2020,12(6):1582
Qiu C, Liu Y, Mei Y, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing TGF-β signaling-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Aging (Albany NY), 2018, 10(10):2783–2799
Xiao L, Peng X, Liu F, et al. AKT regulation of mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in peritoneal dialysis is modulated by Smurf2 and deubiquitinating enzyme USP4. BMC Cell Biol, 2015,16:7
Qin N, Han F, Li L, et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme 4 facilitates chemoresistance in glioblastoma by inhibiting P53 activity. Oncol Lett, 2019,17(1):958–964
Zhou Y, Liang P, Ji W, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes glioblastoma multiforme via activating ERK pathway. Onco Targets Ther, 2019,12:1825–1839
Li T, Yan B, Ma Y, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via cyclophilin A stabilization and deubiquitination. Cell Death Dis, 2018,9(2):148
Ma TT, Meng XM. TGF-β/Smad and Renal Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019,1165:347–364
Gu YY, Liu XS, Huang XR, et al. Diverse role of TGF-β in kidney disease. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020,8:123
Ahmadi A, Najafi M, Farhood B, et al. Transforming growth factor-β signaling: Tumorigenesis and targeting for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol, 2019,234(8):12173–12187
Vander Ark A, Cao J, Li X. TGF-β receptors: In and beyond TGF-β signaling. Cell Signal, 2018,52:112–120
Kim SY, Baek KH. TGF-β signaling pathway mediated by deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019,76(4):653–665
Vlasschaert C, Xia X, Coulombe J, et al. Evolution of the highly networked deubiquitinating enzymes USP4, USP15, and USP11. BMC Evol Biol, 2015,15:230
Zhang L, Zhou F, Drabsch Y, et al. USP4 is regulated by AKT phosphorylation and directly deubiquitylates TGF-β type I receptor. Nat Cell Biol, 2012,14(7):717–726
Liao W, Liang P, Liu B, et al. MicroRNA-140-5p mediates renal fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway by directly targeting TGFBR1. Front Physiol, 2020,11:1093
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, Jy., Zhang, Y., Wang, Lx. et al. Inhibition of Ubiquitin-specific Protease 4 Attenuates Epithelial—Mesenchymal Transition of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells via Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor Type I. CURR MED SCI 42, 1000–1006 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2632-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2632-2