Summary
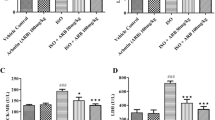
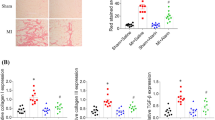
Paeoniforin (Pae) is a monoterpenoid glycoside compound and has many biological activities, such as immunosuppression, anti-inflammation and anti-cell proliferation. However, the effects and mechanisms of Pae on chronic heart failure (CHF) remain unclear. This study was conducted to assess the effects and mechanisms of Pae on myocardial fbrosis in isoprenaline (Iso)-induced CHF rats. Pae (20 mg/kg) was intragastrically administrated to CHF rats for 6 weeks. Cardiac structure and function were assessed. The protein and mRNA levels of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and p38 were detected. Compared to Iso group, Pae could alleviate myocardial fibrosis and improve cardiac function in CHF rats. The levels of collagen volume fraction (13.75%±3.77% vs. 30.97%±4.22%, P<0.001) and perivascular collagen volume area (14.32%±2.50% vs. 28.31%±3.16%, P<0.001) were signifcantly reduced in Pae group as compared with those in Iso group. The expression of TGF-β1 protein (0.30±0.07 vs. 0.66±0.07, P<0.05) and mRNA (3.51±0.44 vs. 7.58±0.58, P<0.05) decreased signifcantly in Pae group as compared with that in Iso group. The expression of p38 protein (0.36±0.12 vs. 0.81±0.38, P<0.05) and mRNA (3.84±0.05 vs. 4.40±0.17, P<0.05) also decreased markedly in Pae group as compared with that in Iso group. Pae could attenuate myocardial fbrosis and improve cardiac function in CHF rats by down-regulating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016,18(8):891–975
Kong P, Christia P, Frangogiannis NG. The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2014,71(4):549–574
Liu M, Chen J, Huang Y, et al. Triptolide alleviates isoprenaline-induced cardiac remodeling in rats via TGF-beta1/Smad3 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Pharmazie, 2016,2015(70):4–244
Ji Y, Wang T, Wei ZF, et al. Paeoniflorin, the main active constituent of Paeonia lactiflora roots, attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by suppressing the synthesis of type I collagen. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016,2013(149):3–825
Chen H, Dong Y, He X, et al. Paeoniflorin improves cardiac function and decreases adverse postinfarction left ventricular remodeling in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2018,12:823–836
Shao YX, Xu XX, Wang K, et al. Paeoniflorin attenuates incipient diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced mice by the suppression of the Toll-like receptor-2 signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2017,11:3221–3233
Ji Y, Dou YN, Zhao QW, et al. Paeoniflorin suppresses TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis through a Smad-dependent pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2016,2016(37):6–794
Liu M, Chen J, Yao J, et al. Triptolide Attenuates Cardiac Remodeling in Isoprenaline-induced Chronic Heart Failure Rats via Upregulating PTEN Pathway. J Sun Yat-sen Univ Med Sci (Chinese), 2017(1):29–35
Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG. The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis. Circ Res, 2016,2016(119):1–91
Zhang Y, Bauersachs J, Langer HF. Immune mechanisms in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016,2017(19):11–1379
Li H, Jiao Y, Xie M. Paeoniflorin Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated NF-kappaB Activation. Inflammation, 2016,2017(40):6–2042
Wang Z, Liu Z, Yu G, et al. Paeoniflorin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Glioblastoma Cells via Suppression Transforming Growth Factor beta-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Neurochem Res, 2016,2018(43):3–760
Zhao Y, Ma X, Wang J, et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HIF-1alpha through mTOR-dependent pathway. Fitoterapia, 2014,99:318–327
Zhou H, Yang HX, Yuan Y, et al. Paeoniflorin attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling via inhibition of TGFbeta/Smads and NF-kappaB pathways. J Mol Histol, 2016,2013(44):3–357
Liu X, Chen K, Zhuang Y, et al. Paeoniflorin improves pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling by modulating the MAPK signaling pathway in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019,111:695–704
Yokota T, Wang Y. p38 MAP kinases in the heart. Gene, 2016,575(2 Pt 2):369–376
Wang P, Wang W, Shi Q, et al. Paeoniflorin ameliorates acute necrotizing pancreatitis and pancreatitisinduced acute renal injury. Mol Med Rep, 2016,2016(14):2–1123
Fang C, Ma C, Jiang L, et al. p38 MAPK is crucial for Wnt1- and LiCl-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition. Curr Med Sci, 2018,38(3):473–481
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
This study was supported by grants from Scientific Research Development Program of North Sichuan Medical College (No. CBY16-A-ZD10) and Nanchong Government-University Strategic Cooperation Project in Science and Technology (No. 18SXHZ0505).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Feng, J., Du, Q. et al. Paeoniflorin Attenuates Myocardial Fibrosis in Isoprenaline-induced Chronic Heart Failure Rats via Inhibiting P38 MAPK Pathway. CURR MED SCI 40, 307–312 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-020-2178-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-020-2178-0